5.6 Constants
5.6.1 Decimal and Hexadecimal constants
Decimal and hexadecimal constants are devices which designate decimal resp. hexadecimal
data in sequence programs (e. g. setpoints for Timer and Counter). The constant is converted
by the PLC CPU into a binary number.
Decimal constants are not particularly denoted in the Ladder Diagram or the IEC instruction
list. Hexadecimal constants are prefixed with "16#". For example the notation 16#12 is inter
-
preted by the PLC CPU as hexadecimal value 12.
In the MELSEC instruction list decimal constants are prefixed with the letter "K" and hexadeci
-
mal constants are prefixed with the letter "H". Examples: K100 = decimal value 100; K64 = hex
-
adecimal value 64.
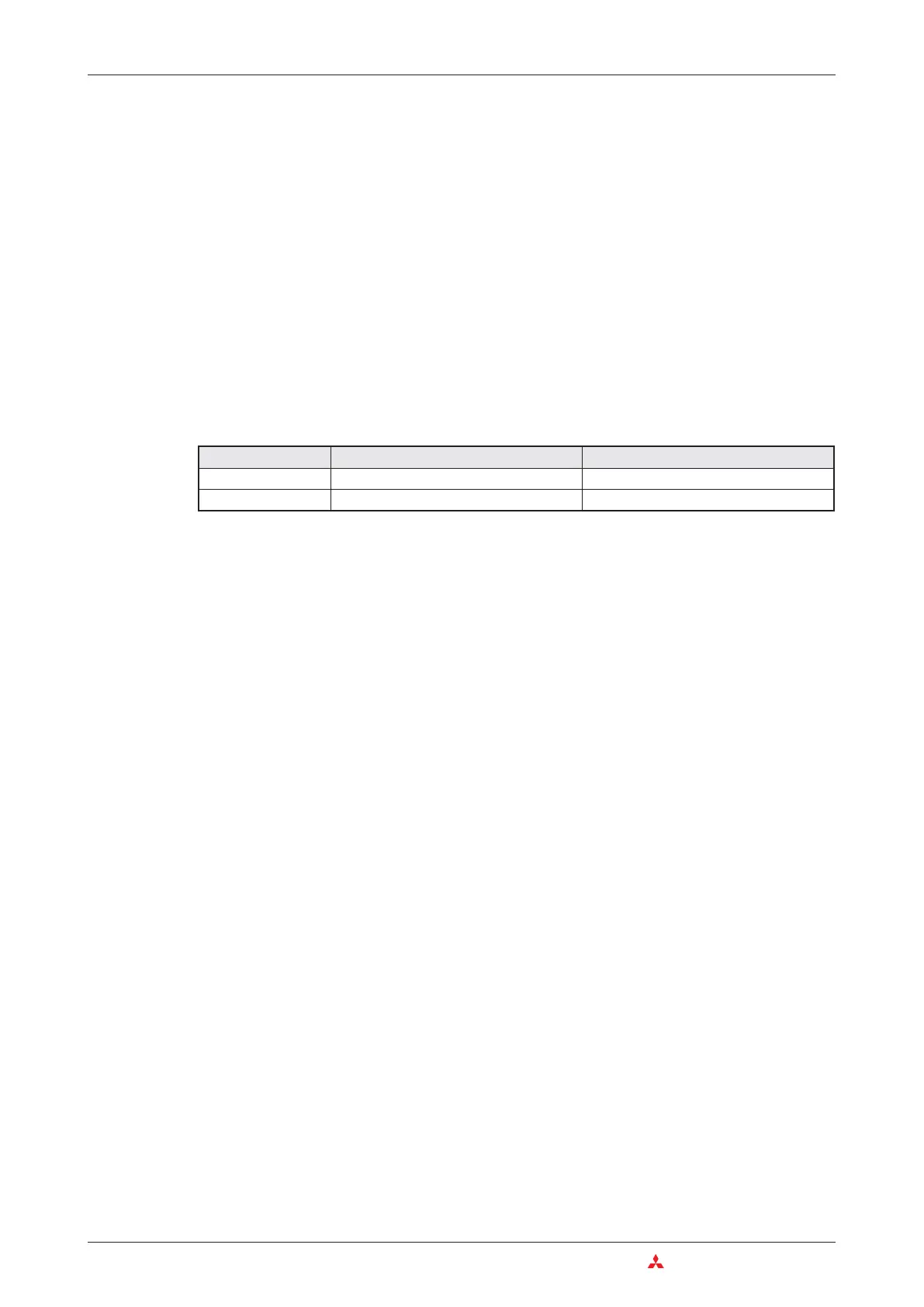
The following table shows the value ranges of the decimal and hexadecimal constants
5.6.2 Floating decimal point constants
Decimal constants are integer values.Floating decimal point values (or real numbers) however
have decimal places and therefore offer advantages for arithmetical operations.
Floating decimal point constants are prefixed by an "E" in the sequence program (for example
E1.234 or E1.234 + 3). As you see, these constants can be designated in the program by an
expression with or without exponent.
– Designation of a constant without exponent
The specified value is designated in the "normal" way. For example 10.2345 becomes
"E10.2345".
–
Designation of a constant with exponent
The value is divided into a base and an exponent.The base of the exponent is 10 (10
n
).For
example, 1234 can be expressed as 1.234 x 1000 or – in exponential expression – as
1.234 x 10
3
.In the sequence program this value becomes E1.234 + 3.(+3 represents 10
3
).
The value ranges for floating decimal point constants are:
-1.0 x 2
128
to -1.0 x 2
-126
,
0
and 1.0 x 2
-126
to 1.0 x 2
+128
5.6.3 Character string constants
When characters are designated in the sequence program by quotation marks they are inter
-
preted as ASCII code (e. g. "MOTOR12").One character occupies 1 byte.You can use up to 32
characters for a character string.
5–14 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Constants Devices in Detail
Constants 16 bit 32 bit
Decimal
-32 768 to +32 767 -2 147 483 648 to +2 147 483 647
Hexadecimal
0 to FFFF 0 to FFFFFFFF

 Loading...
Loading...











