5.3 Timers
When you are controlling processes you will often want to program a specific delay before
starting and stopping certain operations. In hard-wired controllers this is achieved with timer
relays. In PLCs this is achieved with programmable internal timers.
Timers are really just counters that count the PLCs internal clock signals (e.g. 0.1s pulses).
When the counter value reaches the setpoint value the timer’s output is switched on.
A timer is represented by four elements:
–
Set value (
TValue
)
–
Actual value (
TN
)
–
Timer coil (
TCoil
,
TC
)
–
Timer contact (
TS
)
All timers function as make delay switches and are activated with a “1” signal.To start and reset
timers you program them in the same way as outputs.You can poll the outputs of timers (TS) as
often as you like in your program.
The timer of the MELSEC System Q are distinguished between low speed and high speed
timer.With the GX IEC Developer the time base for the timer (i. e.the frequency of the clock sig
-
nal counted by the timer) can be set in the range from 1 ms to 1000 ms in the PLC parameters.
The initial value is 100 ms. The time base for high speed timer can be set in the range from
0.1 ms to 100 ms. The initial value in this case is 100 ms.
Whether a timer functions as low or as high speed timer is determined by the instruction which
starts the timer.
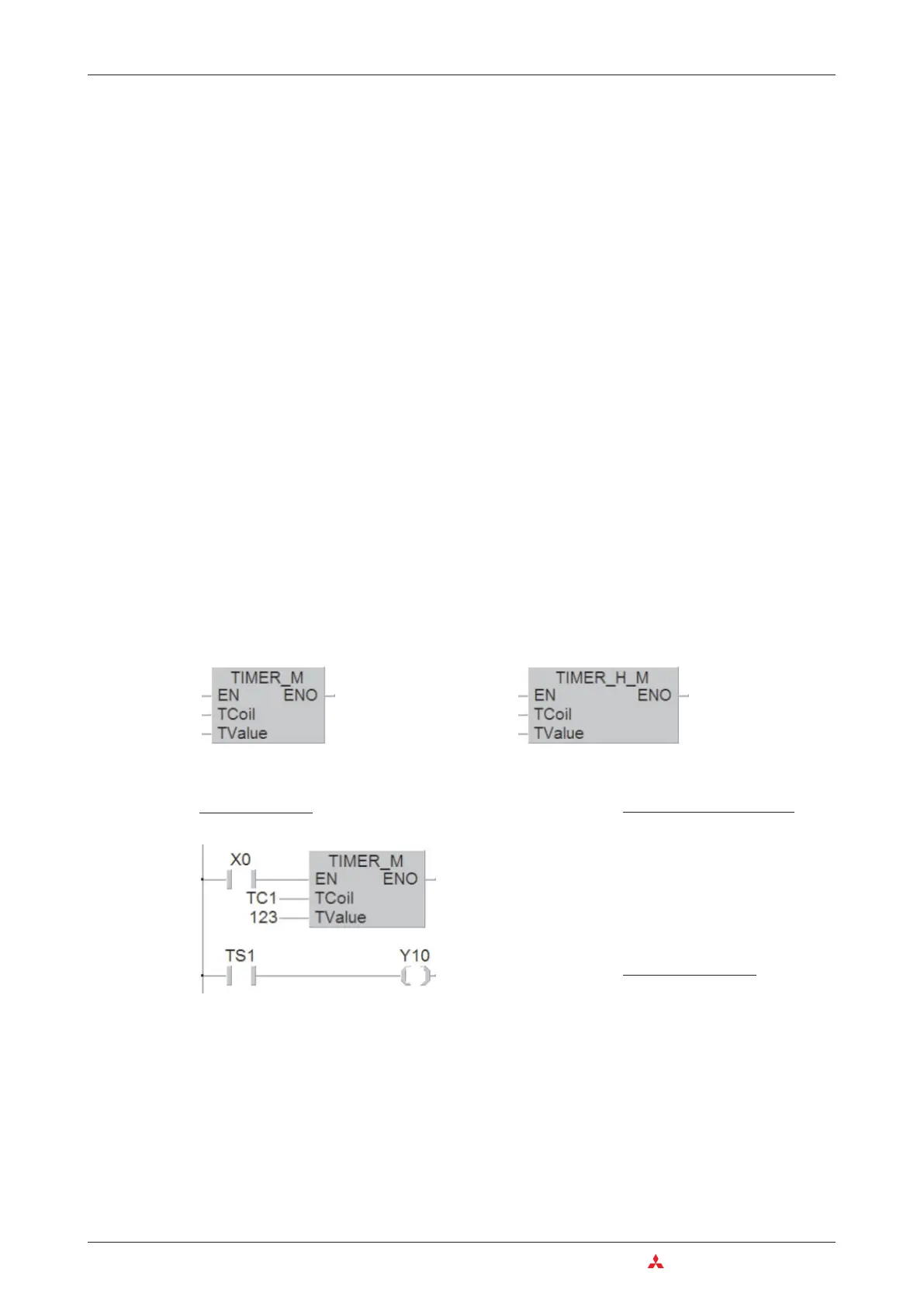
Example of a program using low speed timer
In the above example timer T1 is started when input X0 is switched on. The setpoint value is
123 x 100 ms = 12,3 s, so T200 switches on output Y10 after a delay of 1.23 s. The signal
sequence generated by the following program example is as follows:
5–6 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Timers Devices in Detail
Ladder Diagram
MELSEC Instruction List
LD X0
OUT T1
K123
LD T1
OUT Y10
IEC Instruction List
LD X0
TIMER_M TC1, 123
LD TS1
ST Y10
As variable for the TCoil input of the
TIMER_M instruction the device address of
the timer is specified (in this example TC1).
Operation as low speed timer Operation as high speed timer

 Loading...
Loading...











