*
It is not possible to program the instructions FCALL, ECALL and EFCALL with the GX IEC Developer.
6–6 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Applied Instructions Reference More Advanced Programming
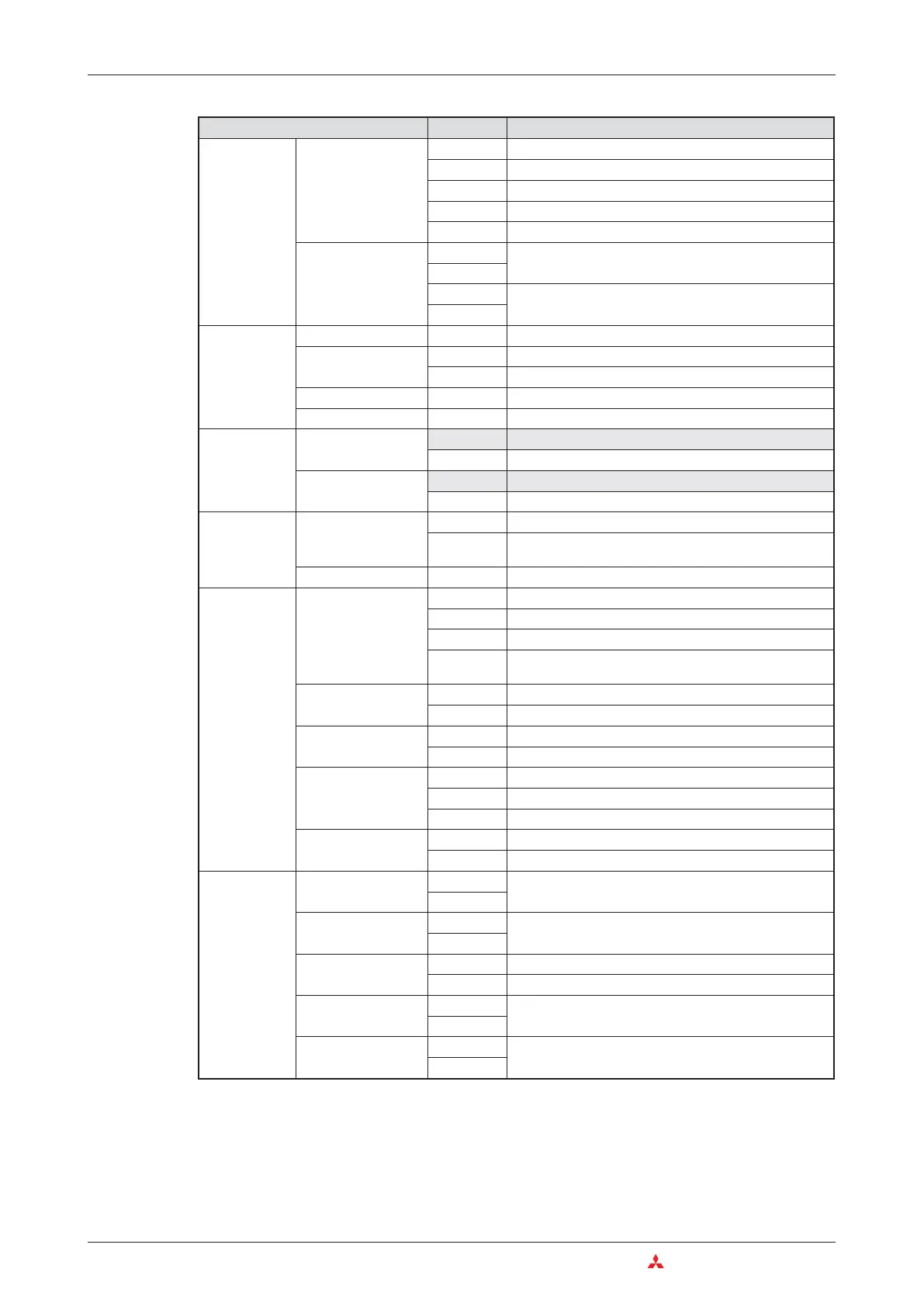
Category Instruction Function
Structured
program
instructions
Subroutine programs
CALL
Subroutine program call
RET
End of subroutine
FCALL*
Reset outputs in subroutines
ECALL*
Calling a subroutine program in a program file
EFCALL*
Reset outputs in subroutine programs in program files
Index qualification
IX
Index qualification of an entire program parts
IXEND
IXDEV
Store indexed device numbers in an index qualification
list
IXSET
Data table
operation
instructions
Write data
FIFW
Write data to a data table
Read data
FIFR
Read data entered first from data table
FPOP
Read data entered last from data table
Delete data
FDEL
Delete specified data blocks from data table
Insert data
FINS
Insert specified data blocks in data table
Buffer memory
access instruc
-
tions
Read
FROM
Read 16-bit data from special function module
DFRO
Read 32-bit data from special function module
Write
TO
Write 16-bit data to special function module
DTO
Write 32-bit data to special function module
Display
instructions
ASCII character
output
PR
Output of an ASCII character string to a peripheral device
PRC
Output of a comment (in ASCII code) to a peripheral
device
Clear display
LEDR
Reset annunciators and LED display
Failure
diagnosis and
debugging
Failure check
CHKST
Start instruction for the CHK instruction
CHK
Failure check
CHKCIR
Generate check circuits for the CHK instruction
CHKEND
End instruction for a program part with generated check
circuits
Store device status
SLT
Set status latch (Store device status)
SLTR
Reset status latch (clear device status)
Sampling trace
STRA
Set sampling trace
STRAR
Reset sampling trace
Program trace
PTRA
Set program trace
PTRAR
Reset program trace
PTRAEXE
Execute program trace
Trace
TRACE
Set trace
TRACER
Clear data stored by the trace instruction
Character
string process
-
ing instructions
Binary ->
Decimal (ASCII)
BINDA
Convert 16-/32-bit binary data into decimal values in
ASCII code
DBINDA
Binary ->
Hexadecimal (ASCII)
BINHA
Convert 16-/32-bit binary data into hexadecimal values in
ASCII code
DBINHA
BCD -> ASCII
BCDDA
Convert 4-digit BCD data into ASCII-Code
DBCDDA
Convert 8-digit BCD data into ASCII-Code
Decimal (ASCII) ->
Binary
DABIN
Convert decimal ASCII into 16-/32-bit binary data
DDABIN
Hexadecimal (ASCII)
-> Binary
HABIN
Convert decimal ASCII into 16-/32-bit binary data
DHABIN

 Loading...
Loading...











