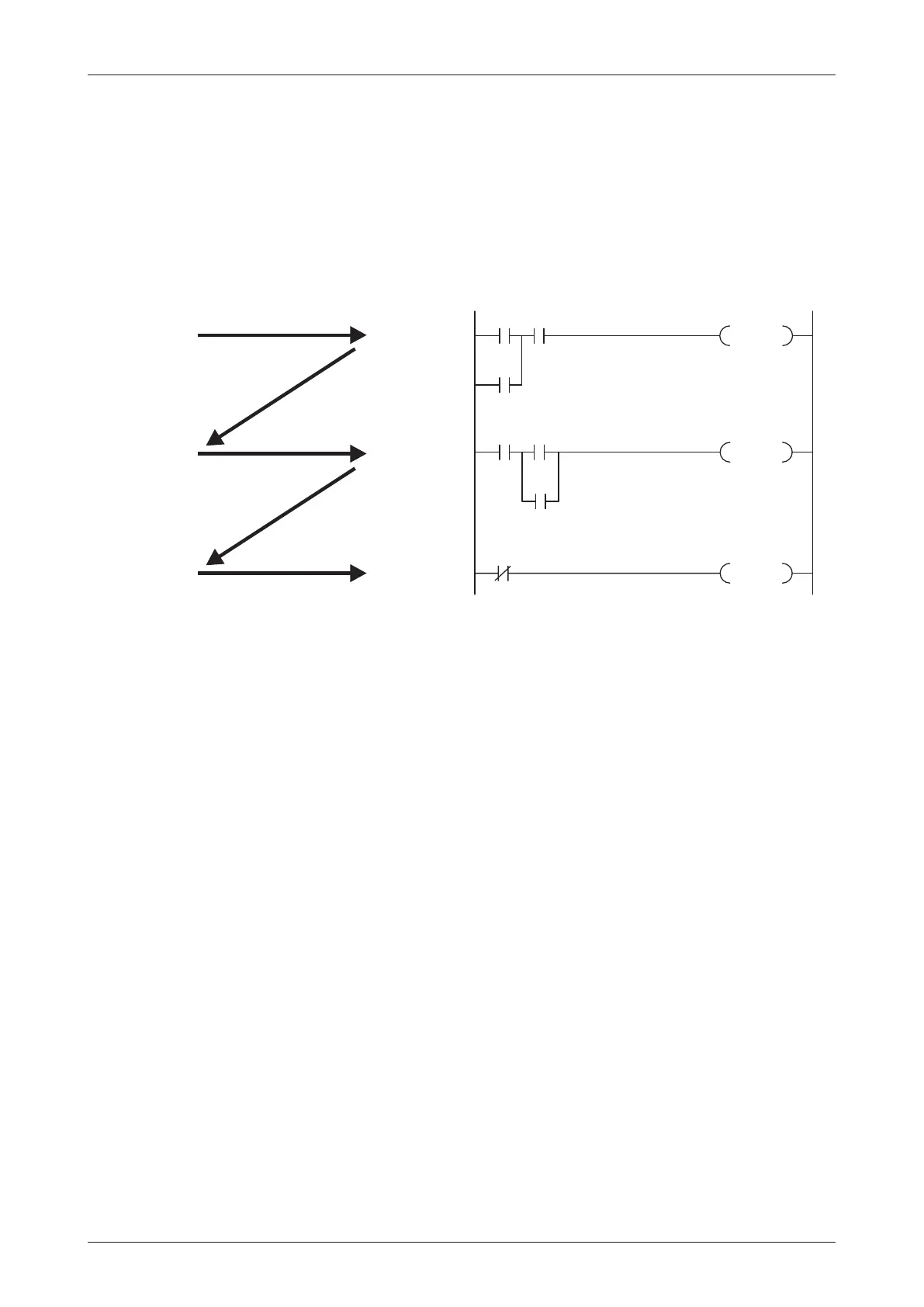
Program execution
After this the program is executed, during which the PLC accesses the stored states of the
inputs in the process image. This means that any subsequent changes in the input states will
not be registered until the next program cycle!
The program is executed from top to bottom, in the order in which the instructions were pro
-
grammed.Results of individual programming steps are stored and can be used during the cur
-
rent program cycle.
Output process image
Results of logical operations that are relevant for the outputs are stored in an output buffer – the
output process image.The output process image is stored in the output buffer until the buffer is
rewritten. After the values have been written to the outputs the program cycle is repeated.
Differences between signal processing in the PLC and in hard-wired controllers
In hard-wired controllers the program is defined by the functional elements and their connec
-
tions (the wiring). All control operations are performed simultaneously (parallel execution).
Every change in an input signal state causes an instantaneous change in the corresponding
output signal state.
In a PLC it is not possible to respond to changes in input signal states until the next program
cycle after the change.Nowadays this disadvantage is largely compensated by very short pro
-
gram cycle periods. The duration of the program cycle period depends on the number and type
of instructions executed.
MELSEC System Q Beginners Manual 2 – 3
Programmable Logic Controllers How PLCs Process Programs
M6
M2
M1 M8013
4
X000 X001
0
9
M0
Y000
M0
Y001
Store result
Program execution
Process stored result
Control output

 Loading...
Loading...











