This document and the information contained herein, is the exclusive property of MODE. And represents a nonpublic,
confidential and proprietary trade secret that may not be reproduced, disclosed to third parties, or otherwise employed in
any manner. whatsoever without the express written consent of MODE. Copyright © (2016) MODE. Allrights reserved.
2 SAFETY FIRST!
Safety requirements must be understood and followed.
2.1 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Note: This chapter proposes personal protective equipment to ensure
operator's full safety. Local regulations and requirements of the working
environment shall be followed.
For safety, operator or others in close proximity to the product may be required to wear
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Various types of PPE are available and must be
selected according to the requirements of the working environment. Some examples of
different types of PPE are:
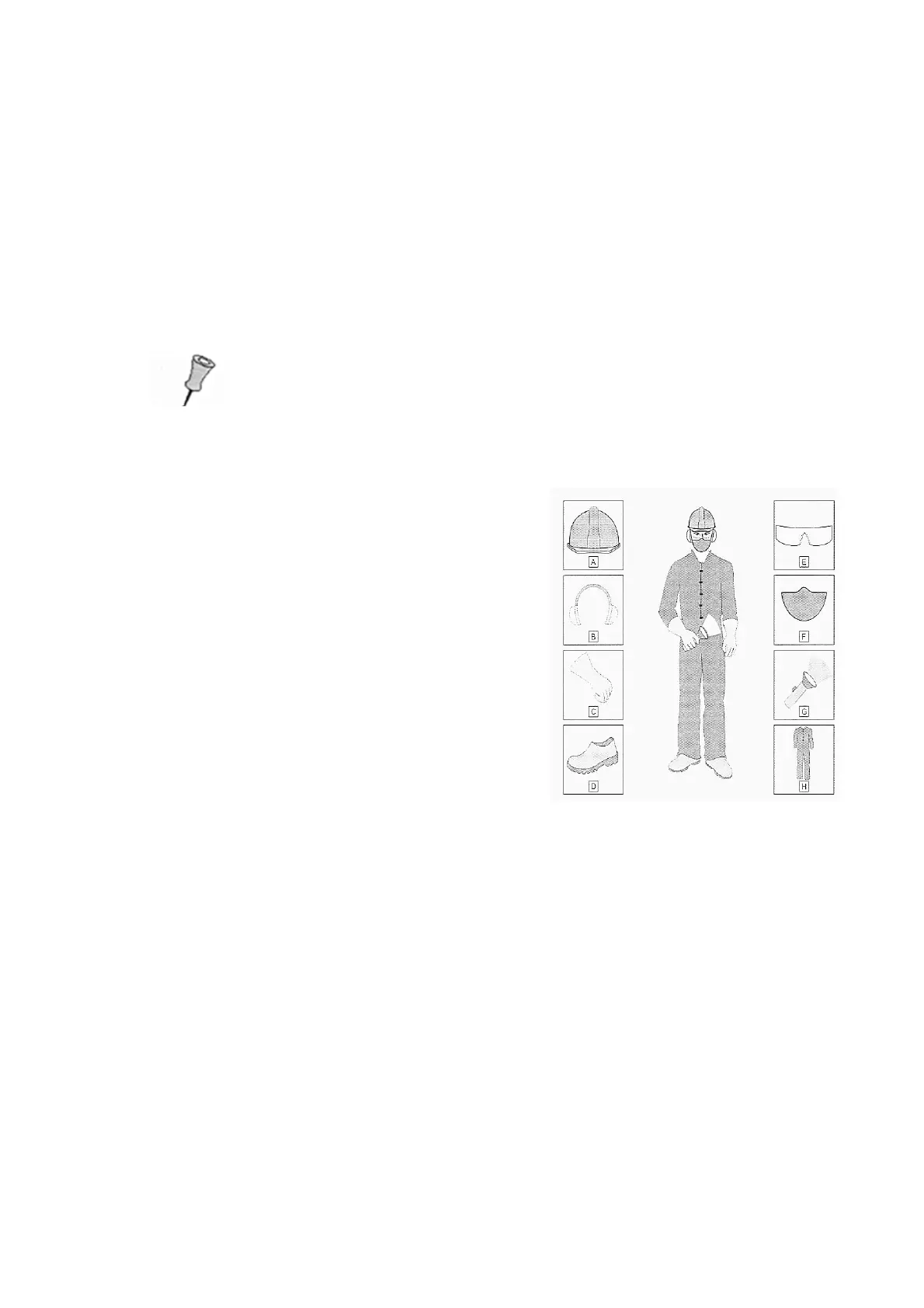
Typical PPE
A. Hard hat
B. Hearing protection
C. Gloves
D. Safety shoes
E. Safety goggles
F. Face mask
G. Flashlight for use in case of power failure
H. Overalls
Appropriate clothing must be selected for each task. For example:
Fire-resistant clothing must be worn when welding, flame cutting or using an angle grinder.
Tear-resistant clothing must resist damage from sharp edges in the steel structure.
Anti-static clothing must be worn when working on electrical circuits so that components
do not get damaged by a discharge of static electricity.
When working with lubricants, clothing must prevent direct skin contact with the lubricant.
Clothing should be chosen with consideration to the temperature at the working site.
 Loading...
Loading...