moog
MSD Servo Drive DC-AC Operation Manual
60
Id.-No.: CA97554-001 Date: 06/2012
to glossaryto table of contents
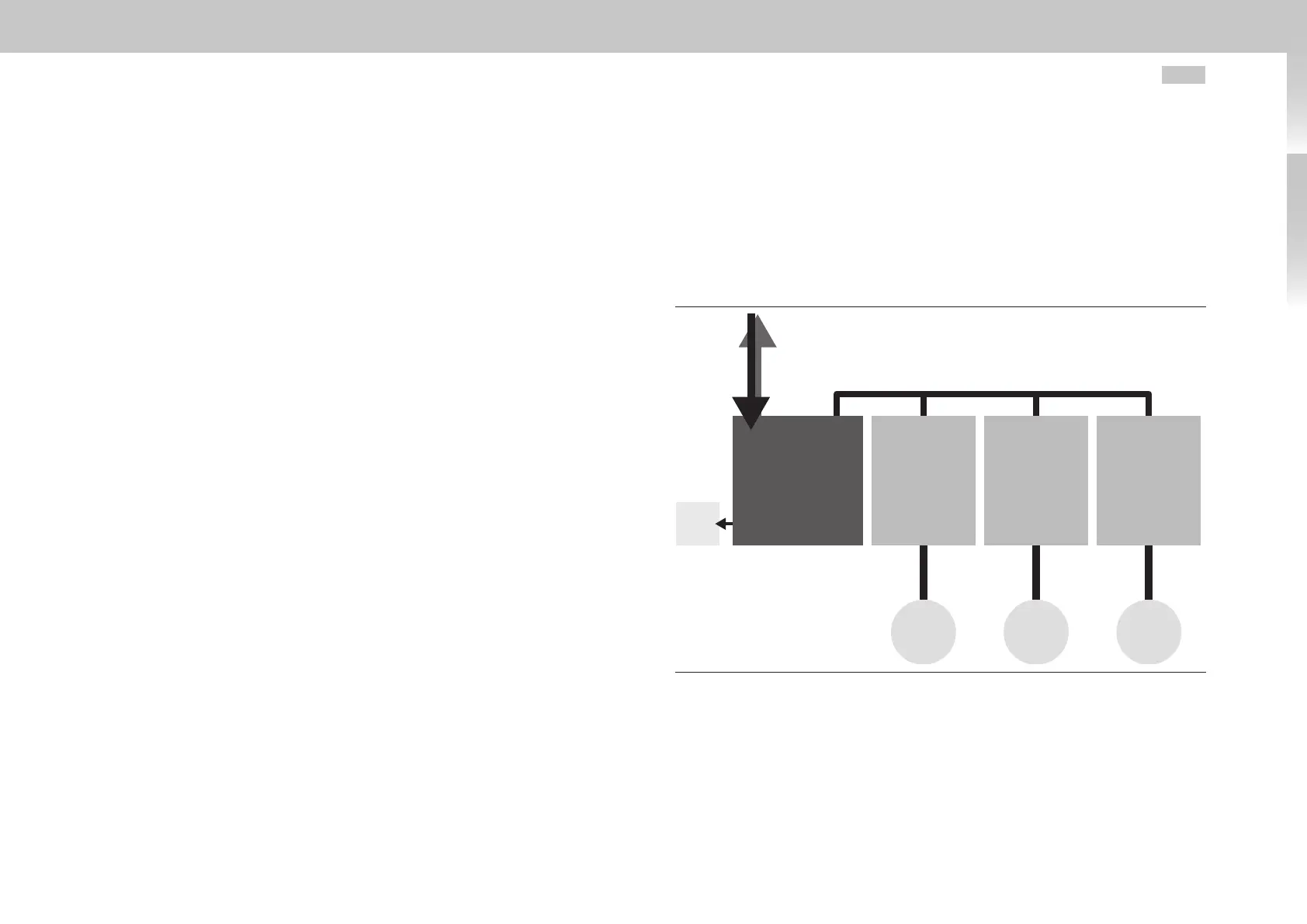
A.3 Operation with MSDPowerSupplyUnit
In this system variant the DC-fed DC-AC servo drives are connected to a central power
supply unit.
Advantages
• Regenerative power from an axis is available to the other axes via the central
DC link
• Surplus power in the DC DC link is fed back into the supply grid centrally via the
power supply unit
• Sinusoidal mains current with very low harmonics in motorized and regenerative
mode
• Controlability of power factor to cos ϕ = 1 (reactive current compensation)
• Identical power values in motorized and regenerative mode
• The system can have more axes than in the case of supply with an AC-AC servo
drive
• Depending on the configuration of the power supply unit, all axes can be operated
simul- taneously at rated power
• Installation of the supply cables between the power supply unit and DC-AC servo
drive is convenient and space-saving, using a through-going rail system (Size 1 to
Size 5)
• The operating cost is below that of a system comprising an AC-AC servo drive or
AC-AC servo drives as the supply source
• Higher DC link voltage than with a corresponding AC feed, meaning smaller-sized
motors can be used
• Loop-controlled DC link voltage, so mains voltage fluctuations no longer have to
be allowed for in the system by way of a reserve
• Higher DC link voltage enables compensation for weak supply systems and maxi-
mum motor torques in the field-weakening range
• Full compensation for mains voltage drops based on the ability to increase voltage
• High dynamism based on rapid changes in power flux on the load side
• In case of power failure, braking is possible by way of built-in braking choppers
Disadvantages
• Due to the power supply unit and its external circuitry, more space may be
required than in operation with an AC-AC servo drive as the supply source or a
system comprising AC-AC servo drives.
• The investment cost is higher than that for a system comprising an AC-AC servo
drive or AC-AC servo drives as the supply source.
Power
supply unit
DC-AC
servo drive
Motor
Braking
resistor
AC mains connection
with feedback
Central DC link
Motor Motor
DC-AC
servo drive
DC-AC
servo drive
Fig. A.1 Block diagram of a multi-axis system with power supply unit and mains feedback

 Loading...
Loading...