moog
MSD Servo Drive DC-AC Operation Manual
[]
Appendix
Project planning
61
Id.-No.: CA97554-001 Date: 06/2012
to glossaryto table of contents
A.4 Operation with MSDServoDrive AC-AC as
supply
Advantages
• The investment cost is lower than in operation with a power supply unit
• As no additional power supply unit is required, the space needed is usually less
than in operation with a power supply unit
• Regenerative power is available to the other axes via the central DC link
• Surplus power is dissipated centrally via the braking resistor of the AC-AC servo
drive
Disadvantages
• In this system variant the full rated power can usually not be requested simultane-
ously on all axes, as otherwise the DC link of the AC-fed AC-AC servo drive may be
overloaded
• The supplying AC-AC servo drive may need to be overdimensioned
• Regenerative power cannot be fed back into the supply grid, but can only be con-
verted into heat by way of a braking resistor
• Similarly to the AC-AC servo drive, the braking resistor may need to be overdi-
mensioned, as a result of which the heat it generates might necessitate additional
effort and expense for installation and air-conditioning
• The operating cost is higher than that of a system comprising an AC-AC servo drive
or AC-AC servo drives as the supply source
• Lower DC link voltage than in operation with a power supply unit
• Owing to the complete DC link capacitance, fewer DC-AC servo drives can be con-
nected than in the case of the power supply unit
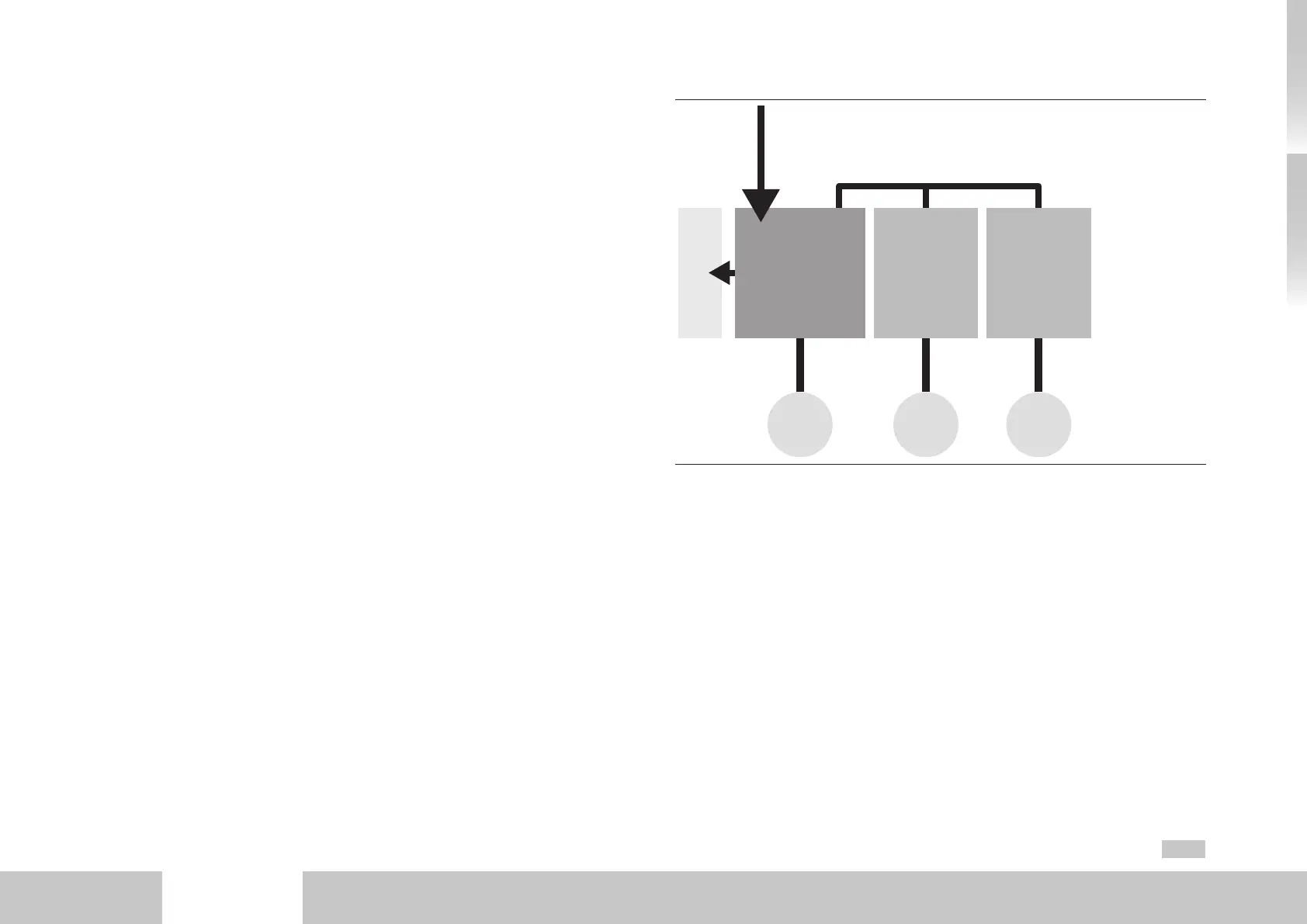
Motor
DC-AC
servo drive
Braking
resistor
AC mains connection
Central DC link
MotorMotor
DC-AC
servo drive
AC-AC
servo drive
Fig. A.2 Block diagram of a multi-axis system with AC-AC servo drive as supply

 Loading...
Loading...