Network Setup
4-13
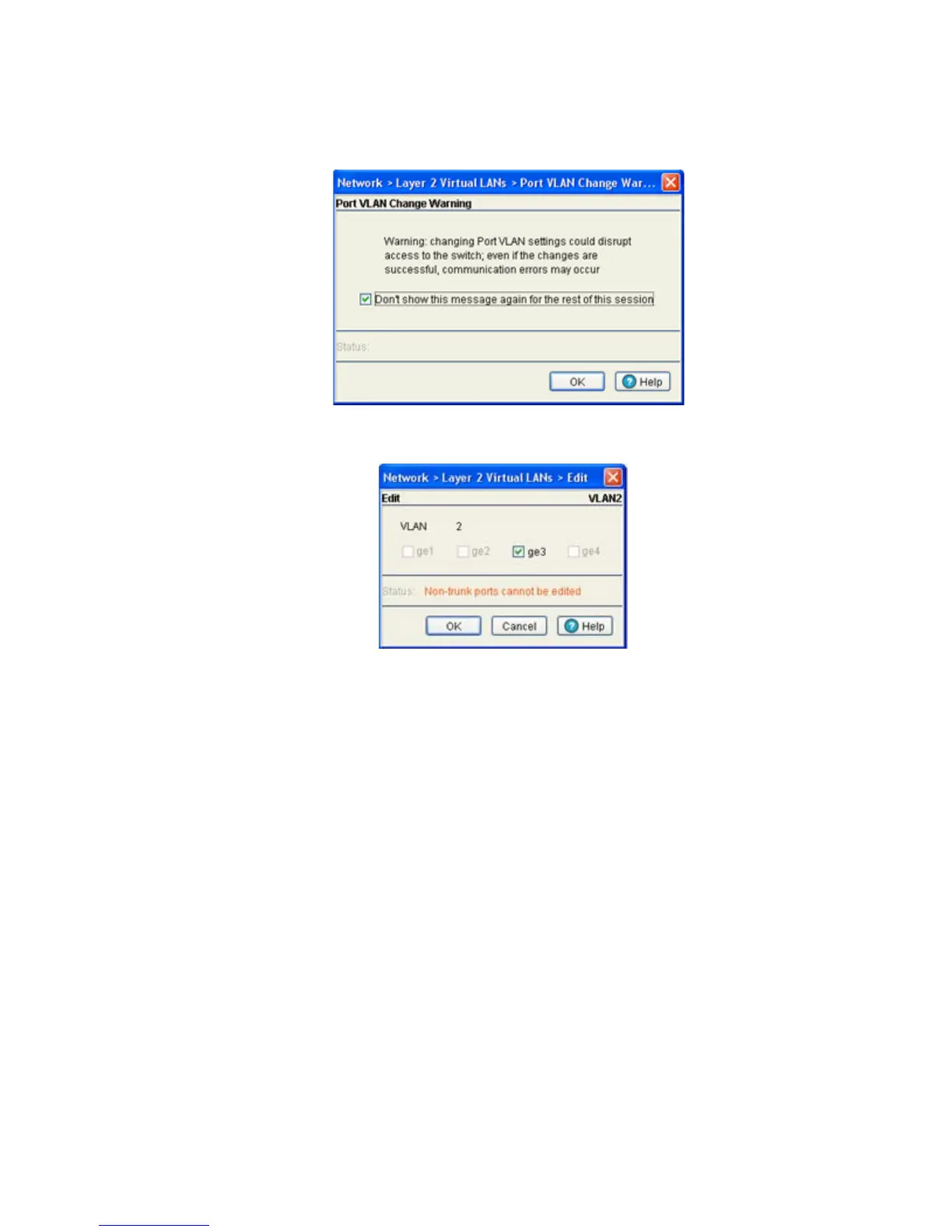
3. Highlight an existing VLAN and click the Edit button. The system displays a Port VLAN Change
Warning message. Be advised, changing VLAN designations could disrupt access to the switch.
4. Click OK to continue. A new window displays wherein the VLAN assignments can be modified for the
selected VLAN.
5. Change VLAN port designations as required.
6. Click OK to use the changes to the running configuration and close the dialog.
7. Click Cancel to close the dialog without committing updates to the running configuration.
4.4 Configuring Switch Virtual Interfaces
A switch virtual interface (SVI) is required for layer 3 (IP) access to the switch or provide layer 3 service on a
VLAN. The SVI defines which IP address is associated with each VLAN ID the switch is connected to. A SVI is
created for the default VLAN (VLAN 1) to enable remote switch administration. A SVI is also used to map a
VLANs to IP address ranges. This mapping determines the destination networks for switch routing.
Each IP address range (IP Address and Subnet Mask) can be mapped to one (and only one) VLAN ID. A VLAN
ID does not require an IP address be defined on the switch. Each VLAN ID must be mapped to a physical port
using the Layer 2 Virtual LANs configuration to communicate with the rest of the network.
VLAN Displays a read-only field and with the name of the VLAN
selected.
ge# Displays the ge ports on the switch. To associate a port with
the VLAN, check the box next to it. To unassociate the port or
security associator from the VLAN, uncheck the box. Non-
trunked ports cannot be edited, and are greyed out.

 Loading...
Loading...