7210 SAS-M, T, R6, R12, Mxp, Sx, S Basic System
Configuration Guide
System Management
3HE 17358 AAAB TQZZA © 2021 Nokia.
Use subject to Terms available at: www.nokia.com
297
6.5.9 PTP Boundary Clock for Frequency and Time
Although IEEE 1588v2 can function across a packet network that is not PTP-aware,
performance may be unsatisfactory and unpredictable. PDV across the packet
network varies with the number of hops, link speeds, utilization rates, and the
inherent behavior of routers. By using routers with boundary clock functionality in the
path between the grandmaster clock and the slave clock, one long path over many
hops is split into multiple shorter segments, allowing better PDV control and
improved slave performance. This allows PTP to function as a valid timing option in
more network deployments and allows for better scalability and increased
robustness in certain topologies, such as rings.
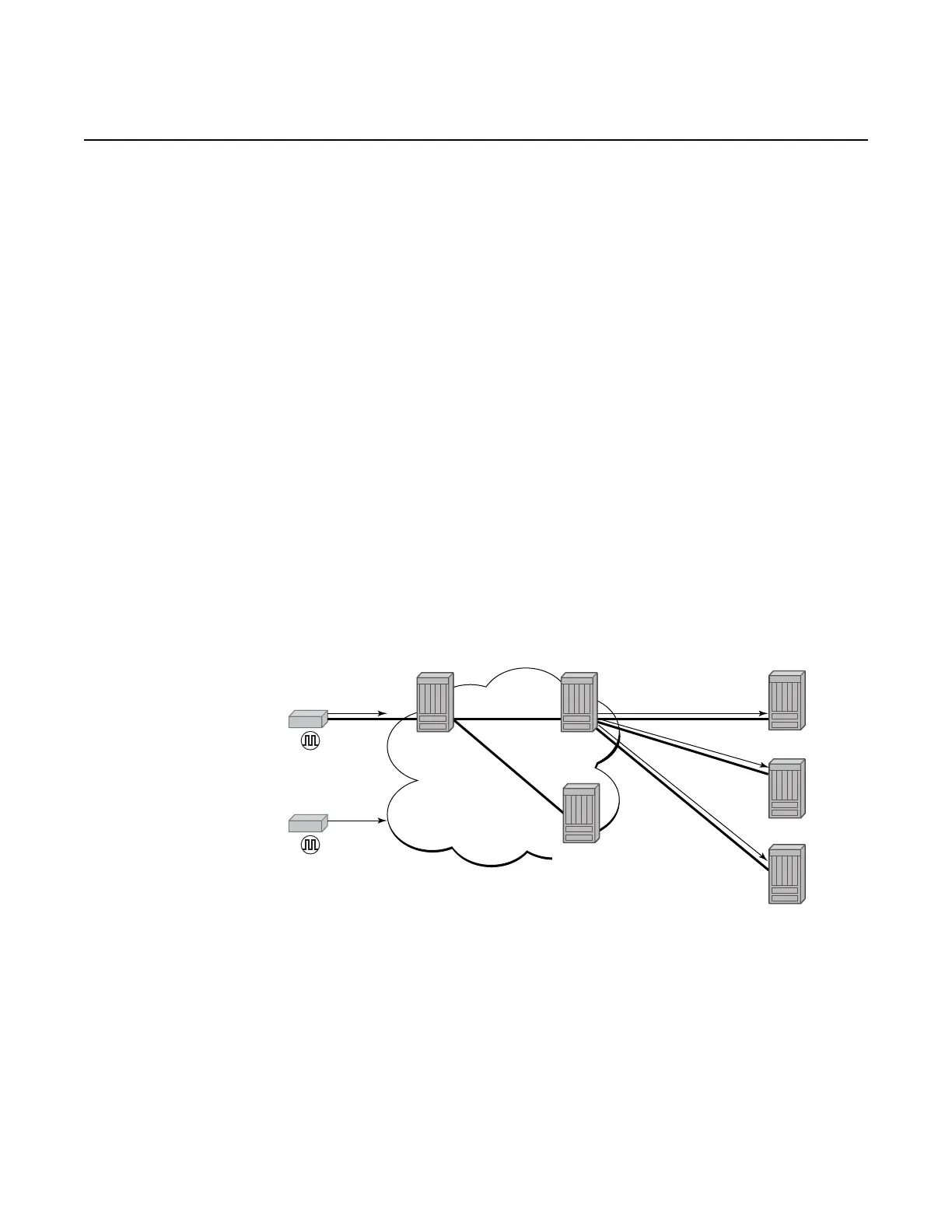
Boundary clocks can simultaneously function as a PTP slave of an upstream
grandmaster (ordinary clock) or boundary clock, and as a PTP master of downstream
slaves (ordinary clock) and boundary clocks. The time scale recovered in the slave
side of the boundary clock is used by the master side of the boundary clock. This
allows time distribution across the boundary clock.
Figure 31 shows routers with boundary clock functionality in the path between
grandmaster clock and the slave clock.
Figure 31 Boundary Clock
Packet
Network
1588v2
Grand
Master
PTP Slave
PTP Slave
PTP Slave
PTP
Boundary
Clock
PTP
Boundary
Clock
PTP
Boundary
Clock
OSSG741
1588v2
Grand
Master

 Loading...
Loading...




