CHAPTER 4 APPLIED OPERATION
E5CK
4–2
4.1 Selecting the Control Method
Heating and cooling control is achieved when the control output (cool)"
function is assigned as the output. Discriminately use standard heating
control or cooling control according to the following table:
Parameter
Control
Method
Control Output 1
Assignment
Control Output 2
Assignment
Direct/Reverse
operations
Heating control
(Standard)
Control output (heat)
-
Reverse operation
Cooling control
(Standard)
Control output (heat)
-
Direct operation
Heating and cooling
control
Control output (heat) Control output (cool) Reverse operation
(Parameters are factoryĆset to heating control.)
Ă• For details on how to assign outputs, see 3.3 Setting Output SpecificaĆ
tions (page 3Ć7).
Ă• When heating and cooling control is selected, the dead band" and coolĆ
ing coefficient" parameters can be used.
The dead band is set with the set point as its center. The dead band width
is the set value of the dead band" parameter (level 1 mode). Setting a posiĆ
tive value produces a dead band, while setting a negative value produces
an overlap band.
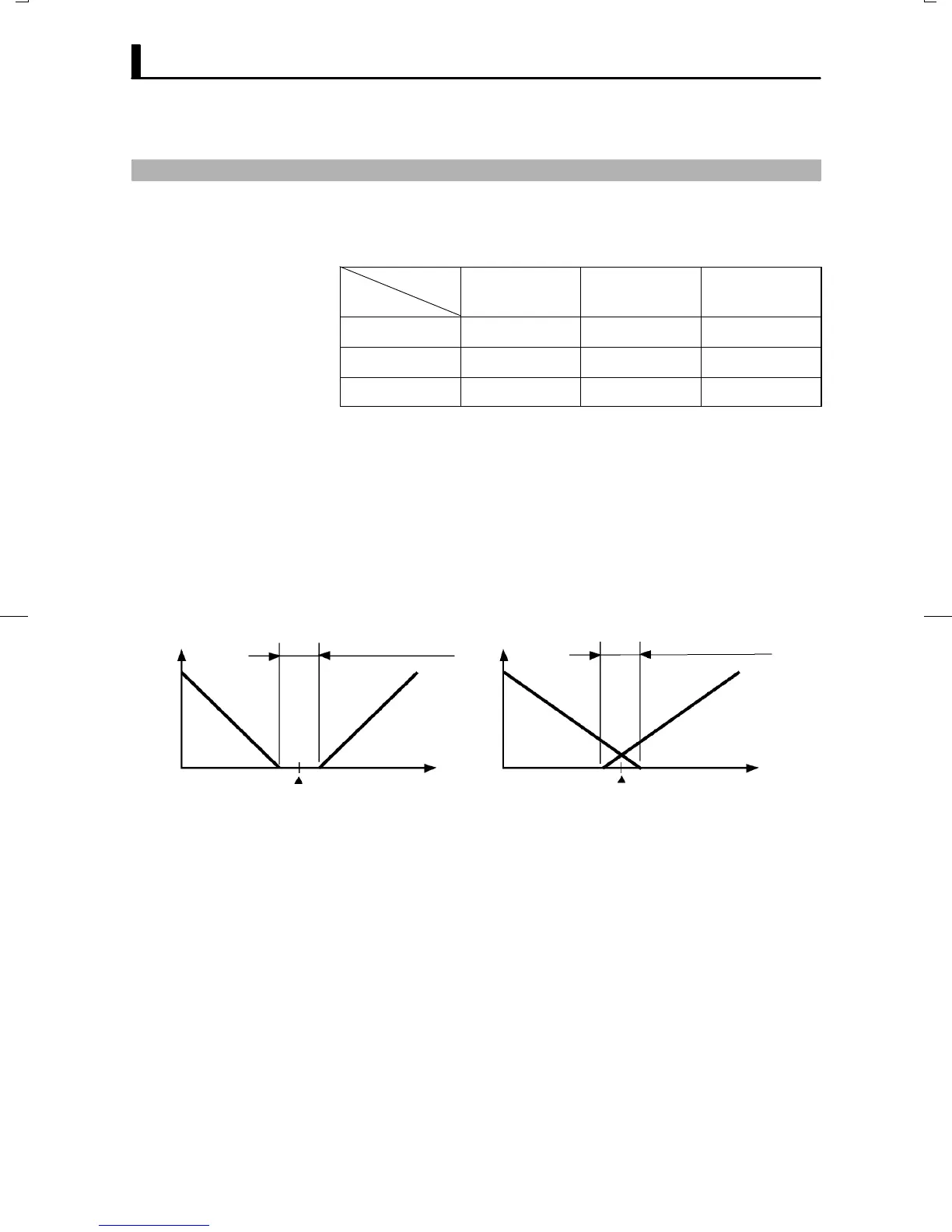
The dead band is factoryĆset to 0.00:0.00%FS."
0
PV
0
PV
Output Output
Dead band: dead
band width = positive
Overlap band: dead
band width = negative
Heating
side
Heating
side
Cooling
side
Cooling
side
Set point Set point
If the heating and cooling characteristics of the control target greatly difĆ
fer, preventing satisfactory control characteristics from being obtained by
the same PID parameters, adjust the proportional band (P at cooling side)
using the cooling coefficient to balance control between the heating and
cooling sides. In heating and cooling control, P at the heating or cooling
side is calculated by the following formula:
Heating side P = P; Cooling side P = cooling coefficient P
JHeating and
cooling control
F Dead band
F Cooling
coefficient
 Loading...
Loading...