PSR-TRISAFE-S
2-6
PHOENIX CONTACT 103503_en_03
The table below lists the functional blocks that offer these parameters.
To configure a startup inhibit for a specific safe output, for example, this output must be
directly connected in the safety logic to the output of a safe functional block, for which the
startup inhibit is set via the parameters.
Example In the example below, EmergencyStop as well as a startup inhibit (S_RES parameter =
FALSE) and a restart inhibit (A_RES = FALSE) are specified for the safe functional block.
The OUT enable output for the functional block is connected directly to safe output O0,
where O0 offers a restart inhibit and a startup inhibit. (EmergencyStop executes stop
category 0 at the output, which is also transmitted to O0 by the direct connection.)
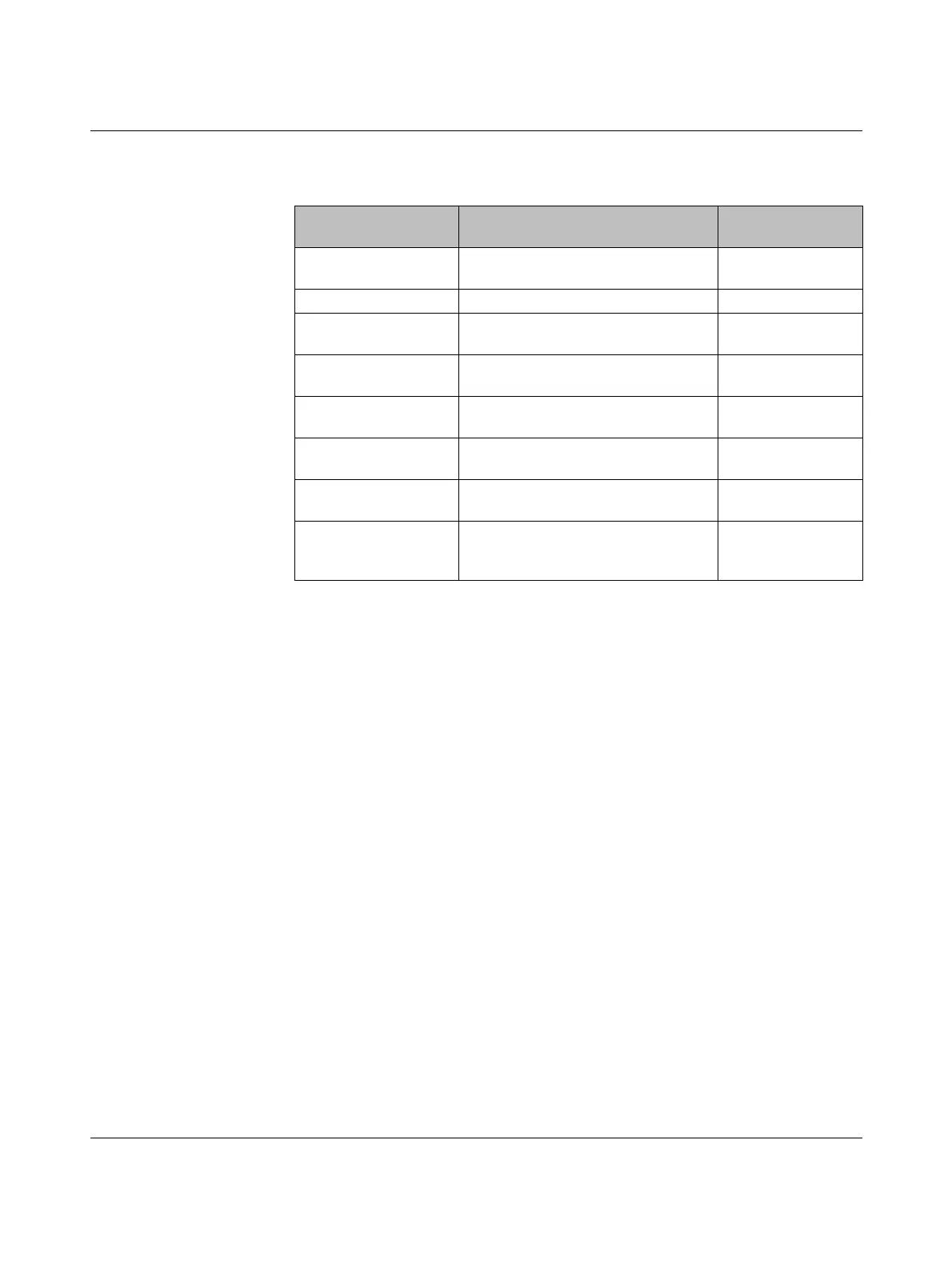
Table 2-1 Functional blocks that support a startup inhibit/restart inhibit
Functional block
name
Function Available inhibit
EmergencyStop Emergency stop monitoring Startup inhibit
Restart inhibit
EDM External device monitoring Startup inhibit
EnableSwitch Evaluation of a three-position enable
switch
Restart inhibit
ESPE Monitoring of electrosensitive
protective equipment (e.g., light grid)
Startup inhibit
Restart inhibit
GuardLocking Monitoring of safety door with four-state
interlocking
Startup inhibit
Restart inhibit
GuardMonitoring Monitoring of safety door with two-state
interlocking
Startup inhibit
Restart inhibit
MutingPar_2Sensor Monitoring of two muting sensors and
light grid
Startup inhibit
TestableSafetySensor Monitoring of a connected
optoelectronic protective device
(e.g., light curtain) with test function
Startup inhibit
Restart inhibit

 Loading...
Loading...