Rockwell Automation Publication 440R-UM013G-EN-P - December 2022 25
Chapter 3 Power, Ground, and Wire
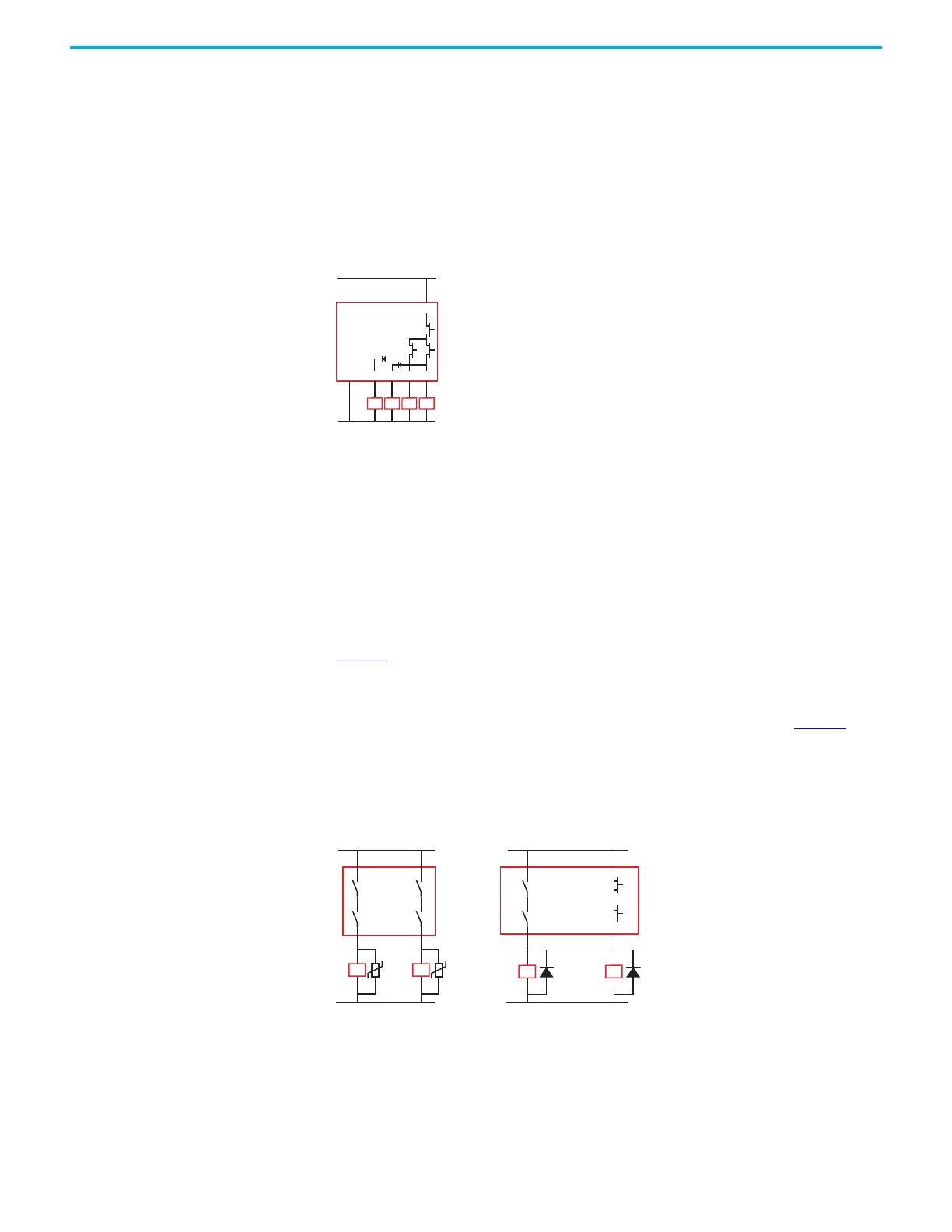
The pulse-tested outputs check for short circuits between the following:
• Each terminal.
• Each terminal and the 24V supply.
• Each terminal and 24V common. The load must connect to the same voltage reference
as terminal A2.
The load must connect to the same voltage reference as terminal A2. All four OSSD outputs are
short-circuit protected.
Figure 17 - OSSD Output Connections
Surge Suppressors
Because of the potentially high current surges that occur when switching inductive load
devices, such as motor starters and solenoids, the use of surge suppression to help protect
and extend the operating life of the safety relays is required. By adding a suppression device
directly across the coil of an inductive device, you prolong the life of the outputs. You also
reduce the effects of voltage transients and electrical noise from radiating into adjacent
systems.
Figure 18
shows an output with a suppression device. We recommend that you locate the
suppression device as close as possible to the load device.
For outputs that use 24V DC, we recommend 1N4001 (50V reverse voltage) to 1N4007 (1000V
reverse voltage) diodes for surge suppression for the OSSD safety outputs (see Figure 18
). The
diode must connect as close as possible to the load coil.
For outputs that use 120V AC or 240V AC, we recommend metal oxide varistors.
Figure 18 - Surge Suppressors
Example surge suppressors include the following catalog numbers:
• 100-FSD250 for Bulletin 100S contactors
• 1492-LD4DF terminal block with built-in 1N4007 diode
• 1492-JD3SS terminal block with built-in varistor
34 44 14 24
A1
A2
K4K3K2K1
24V common
24V DC supply
DIS
K2K1
K2K1
V common V common
Metal Oxide Varistors
for VAC Supply
Diodes for
VDC Supplies

 Loading...
Loading...









