2 Functions
110
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C155-3
Figure 2-37 Pickup characteristic for the power swing detection for the MHO circle
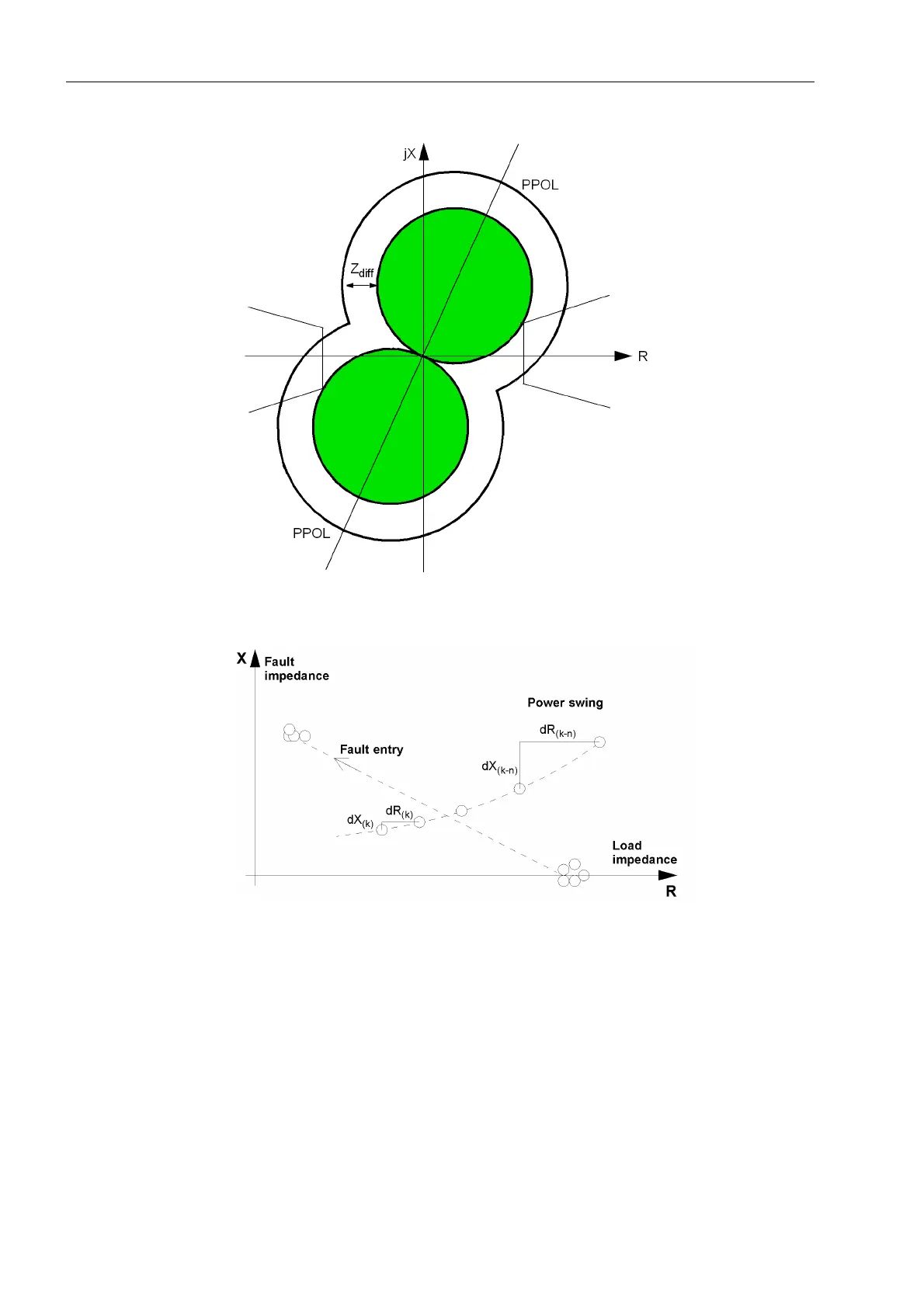
Figure 2-38 Impedance vector during power swing
Trajectory
Continuity and
Monotony
The rate of change of the impedance vector is very important for the differentiation
between faults and power swing conditions. This is shown in Figure 2-38. During the
power swing the measured impedance from one sample to the next has a defined
change in R and X, referred to as dR(k) and dX(k). Important is also the fact that from
one sample to the next the difference is small: i.e. |dR(k) – dR(k+1)| < threshold.
During a fault entry there is a rapid change that will not cause the power swing detec-
tion function to pick up.
Trajectory Stability When the impedance vector enters the impedance characteristic during a power
swing this is at a point of the elliptical curve that corresponds to a steady state insta-

 Loading...
Loading...











