' $ ! $!& #$"&&"! Ċ (%& !' $$ !"
4 - 1
Siemens AG ⋅ January 1999
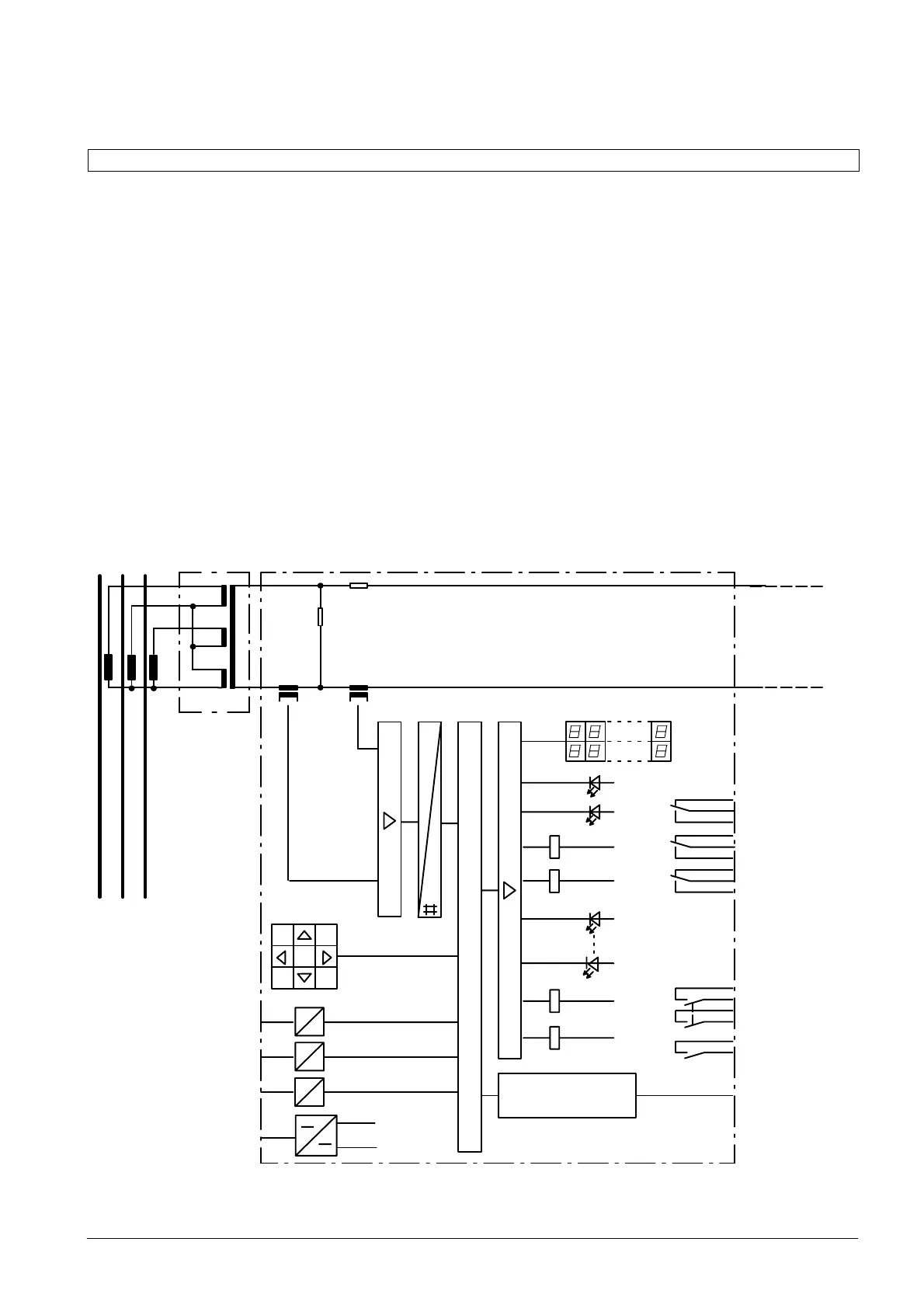
The numerical line differential protection 7SD600 is
equipped with a powerful 16-bit microprocessor
which enables full digital processing of all tasks, from
the acquisition of measured values through to trip
command initiation to the circuit-breaker.
Figure 4.1 shows the basic structure of the device.
In the case of symmetrical nominal current flow, the
summation transformer MT creates a single-phase
equivalent current of 20 mA from the currents coming
from the current transformer. Due to the unbalanced
number of turns of the input windings, with the ratio
of 2 : 1 : 3, each type of fault produces a defined sinĆ
gle-phase AC current which decisively influences the
protection functions of the device.
MT
AI
Ɛ
L1 L2 L3
+
2 indications
(marshallable)
4 LEDs
(marshallable)
2 trip commands
(marshallable)
PC
Setting via
control panel
3 binary inputs
(marshallable)
Power supply
Isolated serial interface
Fault
Operation
LCD display
(2x8 characters)
Pilot wire link
with remote end
2
MI
I1
Rb
Ia
7SD600
1
3
-
Y/J
N
E
Ra
Fail signal
(not marshallable)
Figure 4.1 Hardware structure of the line differential protection 7SD600

 Loading...
Loading...











