2 Functions
120
7UT613/63x Manual
C53000-G1176-C160-2
Figure 2-34 Example of a single-phase transformer with current definition
Like with three-phase power transformers, the currents are matched by programmed
coefficient matrices which simulate the difference currents in the transformer wind-
ings. The common form of these equations is:
Since the phase displacement between the windings can only be 0° or 180°, matching
is relevant only with respect to the treatment of the zero sequence current (besides
magnitude matching). If a „Starpoint“ of the protected transformer winding is not
earthed (left in figure 2-34), the phase currents can directly be used.
If the „starpoint“ is earthed (figure 2-34 right side), the zero sequence current must be
eliminated unless it can be compensated by considering the „starpoint current“. By
eliminating the zero sequence current, fault currents which flow through the transform-
er during earth faults in the network in case of an earth point in the protected zone
(transformer starpoint) are rendered harmless without any special external measures.
The matrices for the left and the right winding as per figure 2-34 are:
The disadvantage of elimination of the zero sequence current is that the differential
protection becomes less sensitive (by factor
1
/
2
because the zero sequence current
amounts to
1
/
2
in case of an earth faults in the protected zone). Higher earth fault sen-
sitivity can be achieved if the „starpoint“ current is available, i.e. if a CT is installed in
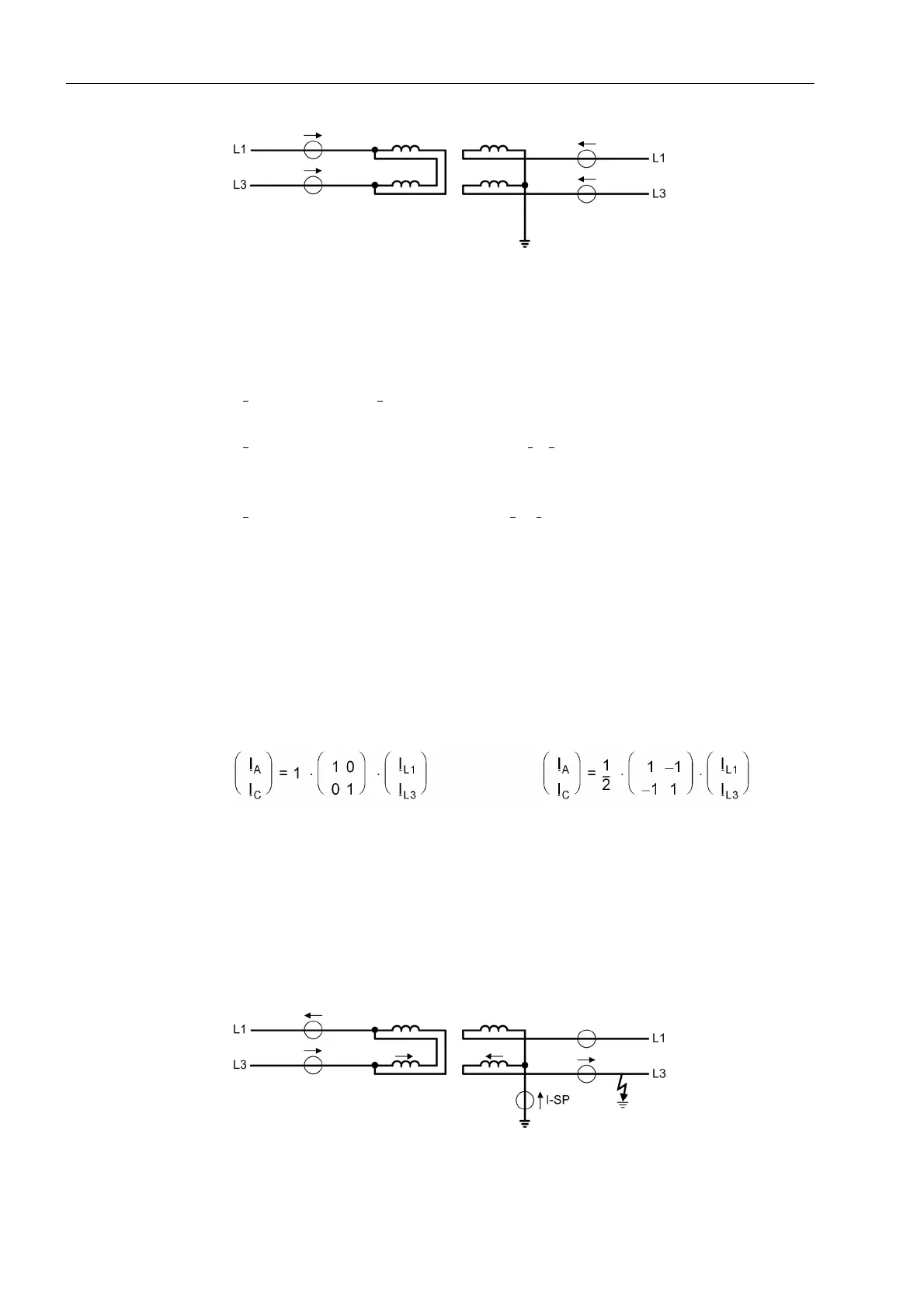
the „starpoint“ connection to earth and this current is fed to the device (figure 2-35).
For consideration of the earth fault current, the advanced parameter diff protection
with measured earth current, side x must be switched on (addresses 1211
DIFFw.IE1-MEAS to 1215 DIFFw.IE5-MEAS = YES).
Figure 2-35 Example of an earth fault outside a single-phase transformer with current distri-
bution
(I
m
) = k· (K)· (I
n
)
with
(I
m
) - matrix of the matched currents I
A
, I
C
,
k - constant factor for magnitude matching,
(K) - coefficient matrix,
(I
n
) - matrix of the phase currents I
L1
, I
L3
.
 Loading...
Loading...











