30 |
Navigating with the NSO-II | NSO-II Operator Manual
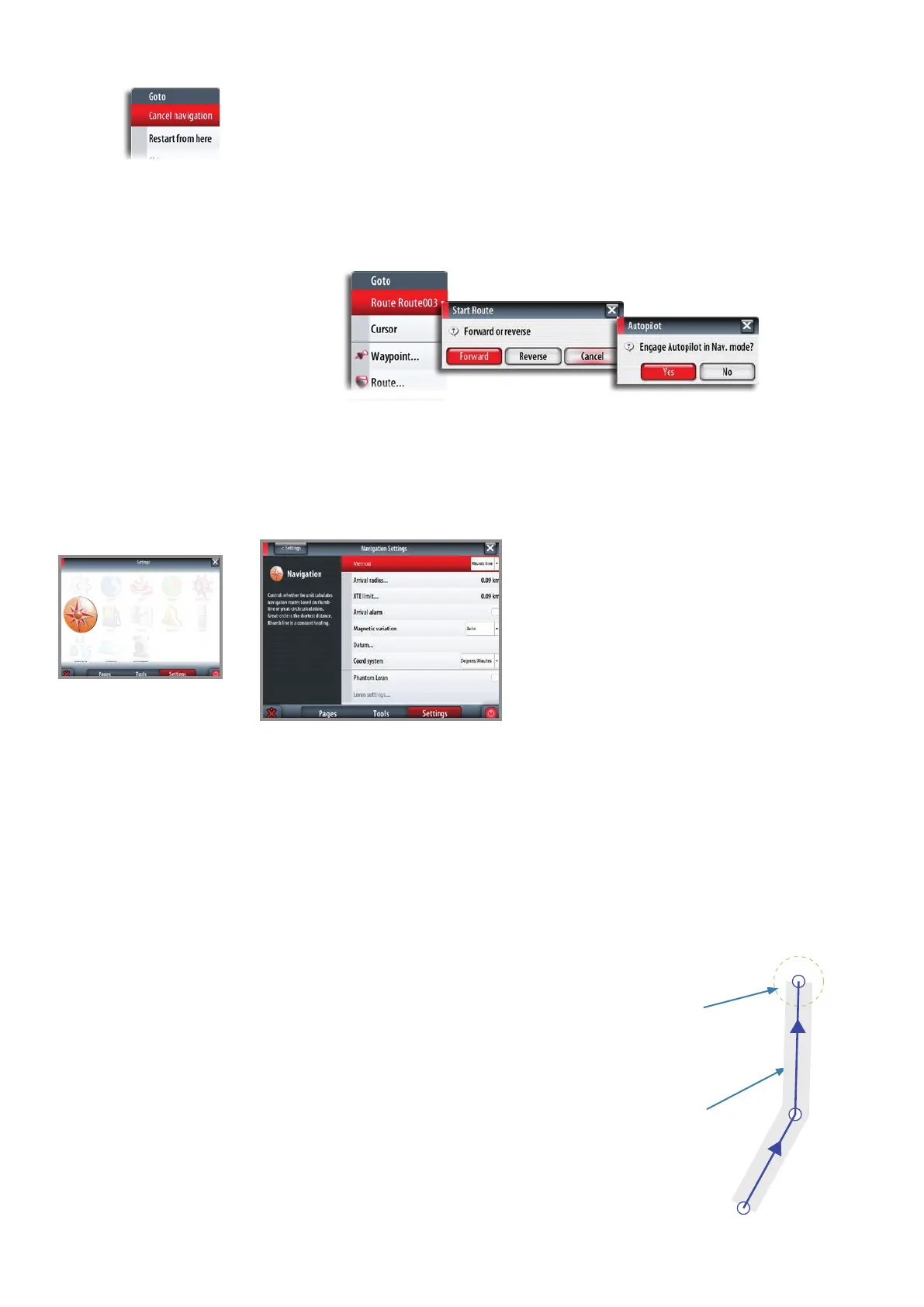
Cancel navigation
You cancel navigation from the Goto menu or the chart panel menu.
Navigating with the autopilot
If an AC12, AC42 or an SG05 autopilot computer is connected to the system, autopilot
functionality will be included in the NSO-II.
When you start navigation on a system with autopilot functionality, you will be prompted
to set the pilot to navigation mode.
If you choose not to engage the autopilot, the pilot can later on still be set to navigation
mode from the pilot menu.
For more information about autopilot functionality see “Autopilot” on page 33.
Navigation settings panel
Navigation method
Dierent methods are available for calculating the distance and bearing between any two
points on a chart.
The great-circle route is the shortest path between two points. However, if you are to
travel along such a route, it would be dicult to steer manually as the heading would
constantly be changing (except in the case of due north, south, or along the equator).
Rhumb lines are tracks of constant bearing. It is possible to travel between two locations
using Rhumb line computation, but the distance would usually be greater than if Great
circle is used.
Steering alarm limits
Arrival radius
Sets an invisible circle around the destination waypoint.
The vessel is considered arrived at the waypoint when it is within this
radius.
O course (XTE) limit
This parameter denes the vessel’s accepted oset distance from the
leg. If the vessel goes beyond this limit an alarm will be activated.
Arrival alarm
When the arrival alarm is enabled, an alarm will be activated when
the vessel reaches the waypoint or when it is within the specied
arrival radius.
 Loading...
Loading...