95
Gateway: Type in the correct IPv6 Gateway address for the IPv6 Static Route.
Interface: Select the Interface from the drop-down list.
Status: Select Enabled or Disabled from the drop-down list.
3. Click Sav e to save your settings.
To modify or delete an existing entry:
1. Find the desired entry in the table.
2. Click Edit as desired on the Edit column.
Click the Enable/ Disabled Selected button to make selected entries enabled/ disabled.
Click the Delete Selected button to delete the selected entries.
4.14 Forwarding
There are four submenus under the Forwarding menu: Virtual Servers, Port Triggering, DM Z
and UPnP. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
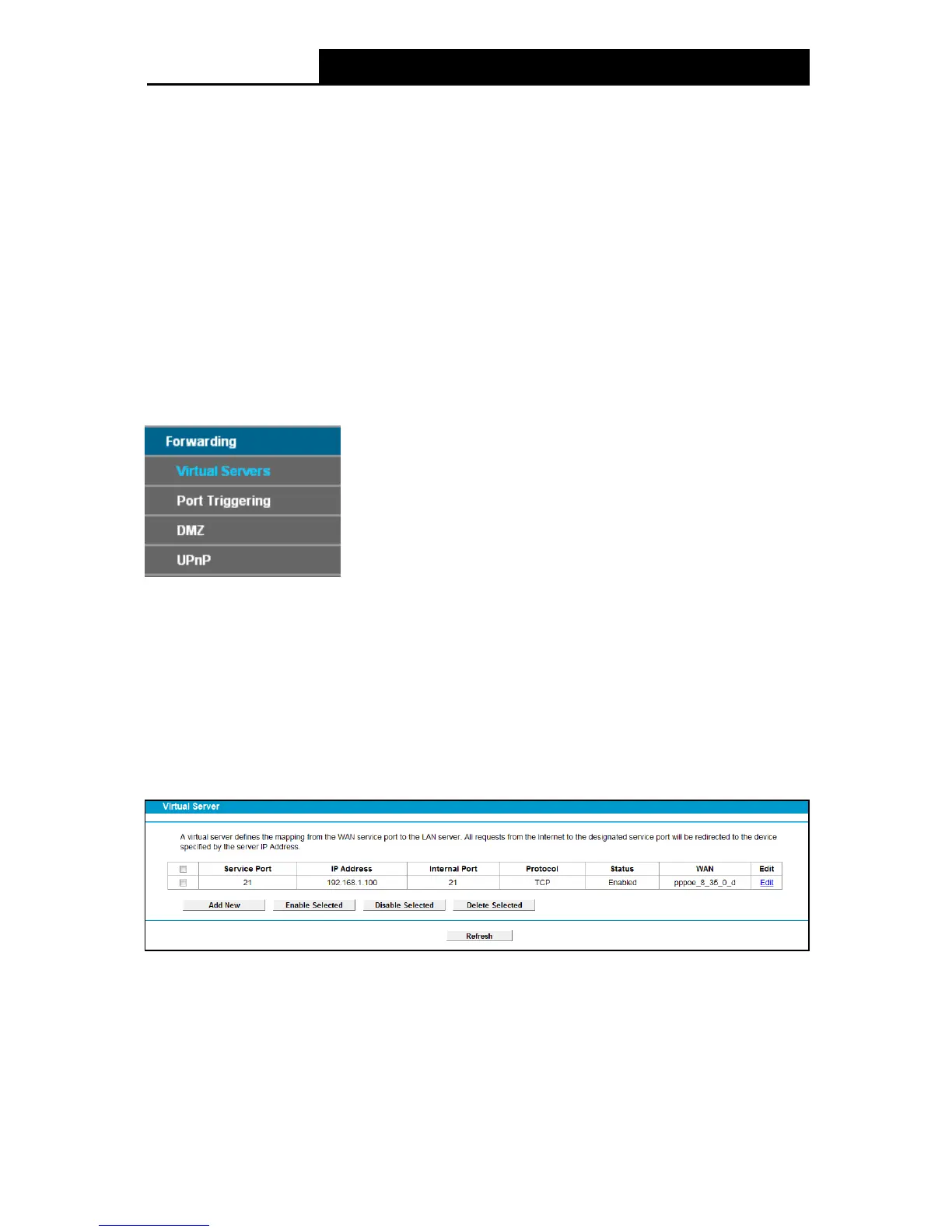
4.14.1 Virtual Servers
Choose menu “Forwarding” → “Virtual Servers”, and then you can view and add virtual servers
in the next screen (shown in Figure 4-92). Virtual servers can be used for setting up public
services on your LAN. A virtual server is defined as a service port, and all requests from Internet
to this service port will be redirected to the computer specified by the server IP. Any PC that was
used for a virtual server must have a static or reserved IP address because its IP address may
change when using the DHCP function.
Figure 4-92
Se rvice Port: The numbers of External Service Ports. You can enter a service port or a
range of service ports (the format is XXX – YYY; XXX is the Start port and YYY is the End
port).
IP Address: The IP address of the PC running the service application.
Internal Port: The Internal Service Port number of the PC running the service application.

 Loading...
Loading...