Chapter 6 ______________________________________________________ Processing Algorithms
VAISALA______________________________________________________________________ 207
This procedure attempts to preserve the noise level and/or overlapped
weather targets. The result is that more accurate estimates of dBZ are
obtained. In extreme cases when the weather spectrum is very narrow,
there can still be some attenuation of weather of a broad filter is selected.
6.2.5.2 Variable Width Clutter Filter
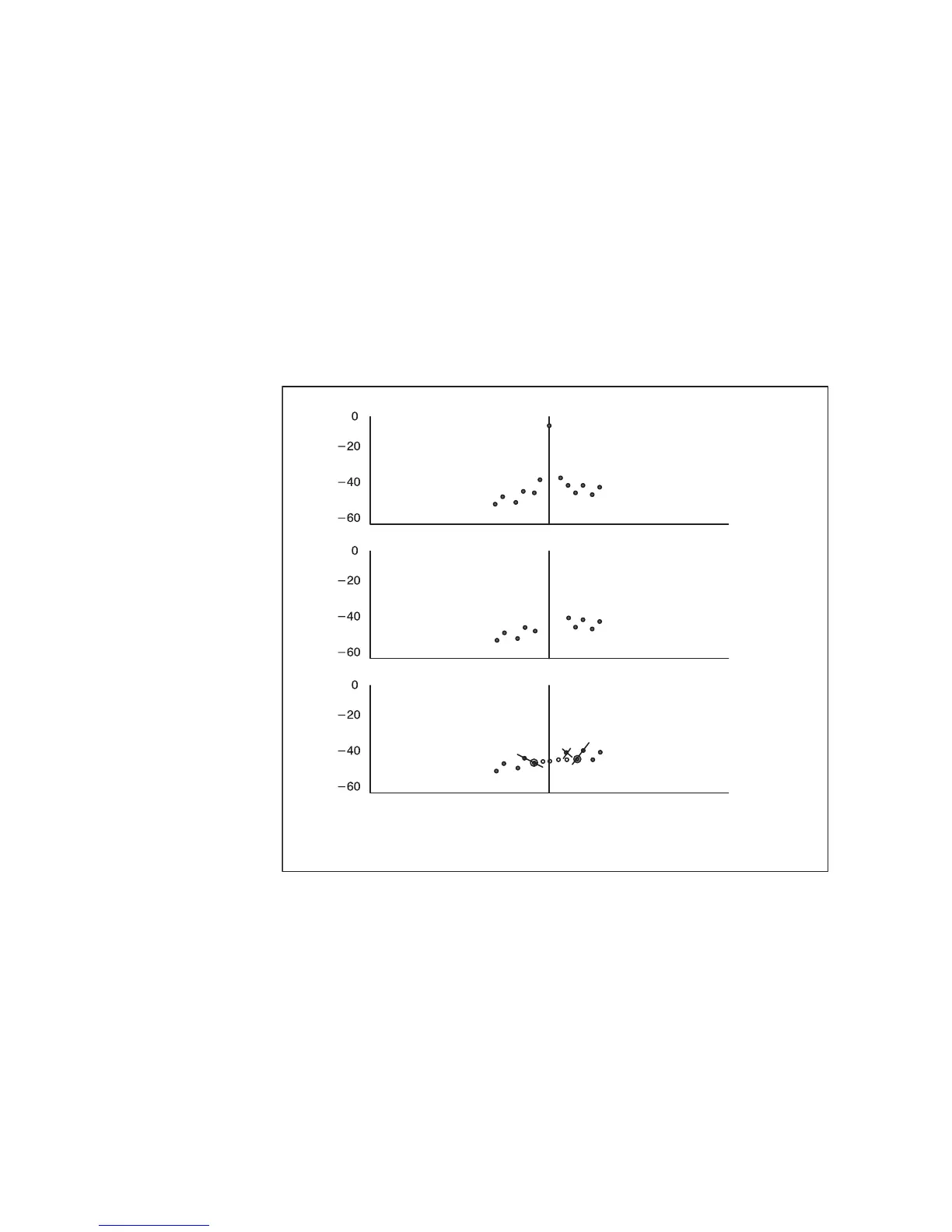
This is similar in many ways to the fixed width filter, except that the
algorithm attempts to extend the boundary of the clutter by determining
which is the first component outside the clutter region to increase in power.
0916-056
Figure 42 Variable Width Clutter Filter
In Figure 42 on page 205, the minimum number of points to reject is set to
3. The filter starts at zero velocity and checks the slope to determine the
point at which the power starts to increase. In the example, this results in
the filter being extended by one point on the right. Note that there is a
selectable maximum number of points that the filter will "hunt". The use
of the edge points for interpolation is identical to the fixed width case.
dB Power
Velocity
dB Power
dB Power
Vu
–
Vu
+
0
Spectrum with ground clutter
Remove 3 interior points
Use slope to extend the clutter bound-
ary. Then find the minimum of the 2
edge points and interpolate.

 Loading...
Loading...