6-52
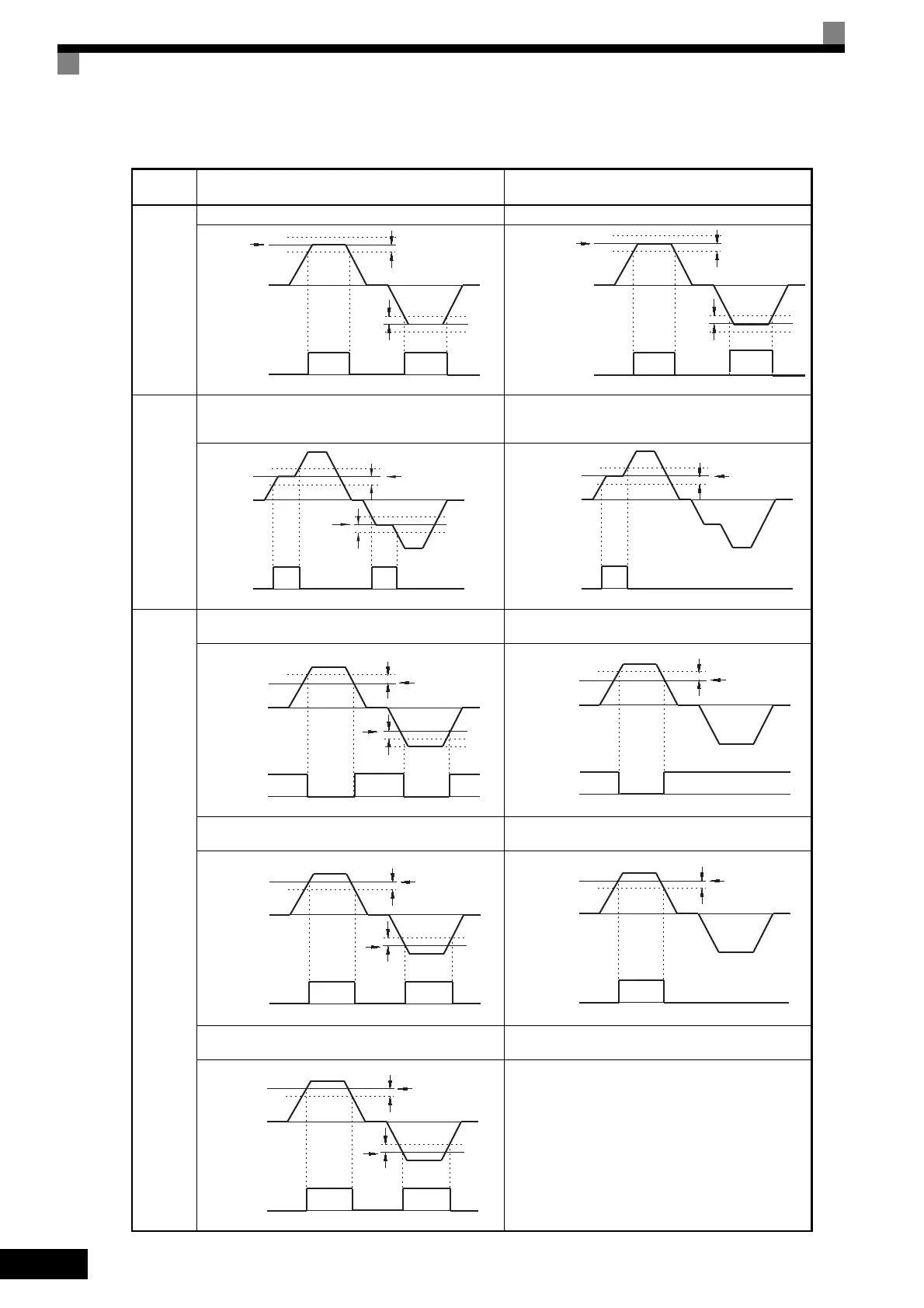
Timing Chart for Frequency Detection Operation
Related
constant
L4-01: Speed Agree Level
L4-02: Speed Agree Width
L4-03: Speed Agree Level +/−
L4-04: Speed Agree Width +/−
Fref/Fout
Agree
Fref/Fout Agree 1 Fref/Fout Agree 2
Fref/Set
Agree
Fref/Set Agree 1
(ON at the following conditions during frequency
agree)
Fref/Set Agree 2 +/−
(ON at the following conditions during frequency
agree)
Fre-
quency
Detection
Frequency (FOUT) Detection 1
(L4-01 > | Output frequency |)
Frequency (FOUT) Detection 3
(L4-03 > Output frequency)
Frequency (FOUT) Detection 2
(L4-01 < | Output frequency |)
Frequency (FOUT) Detection 4
(L4-01 < Output frequency)
Frequency (FOUT) Detection 5
(L4-01 < | Output frequency |)
L4-02
OFF ON
Frequency
reference
L4-02
Output frequency
or motor speed
Fref/Fout Agree 1
(Multi-function output setting = 2)
OFF ON
Frequency
reference
Output frequency
or motor speed
Fref/Fout Agree 2
L4-04
(Multi-function output setting = 13)
OFF ON
tput frequency
motor speed
f/Set Agree 1
L4-02
L4-01
L4-01
L4-02
(Multi-function output setting = 3)
OFF ON
Output frequency
or motor speed
Fref/Set Agree 2
L4-04
L4-03
(Multi-function output setting = 14)
Freq. Detection 1
OFFON
Output frequency
or motor speed
L4-02
L4-02
L4-01
L4-01
(Multi-function output setting = 4)
Freq. Detection 3
OFFON
Output frequency
or motor speed
L4-04
L4-03
(Multi-function output setting = 15)
Freq. Detection 2
OFF ON
Output frequency
or motor speed
L4-02
L4-02
L4-01
L4-01
(Multi-function output setting = 5)
Freq. Detection 4
OFF ON
Output frequency
or motor speed
L4-04
L4-03
(Multi-function output setting = 16)
Freq. Detection 5
OFF ON
Output frequency
or motor speed
L4-02
L4-02
L4-01
L4-01
(Multi-function output setting = 36) OFF during baseblock

 Loading...
Loading...











