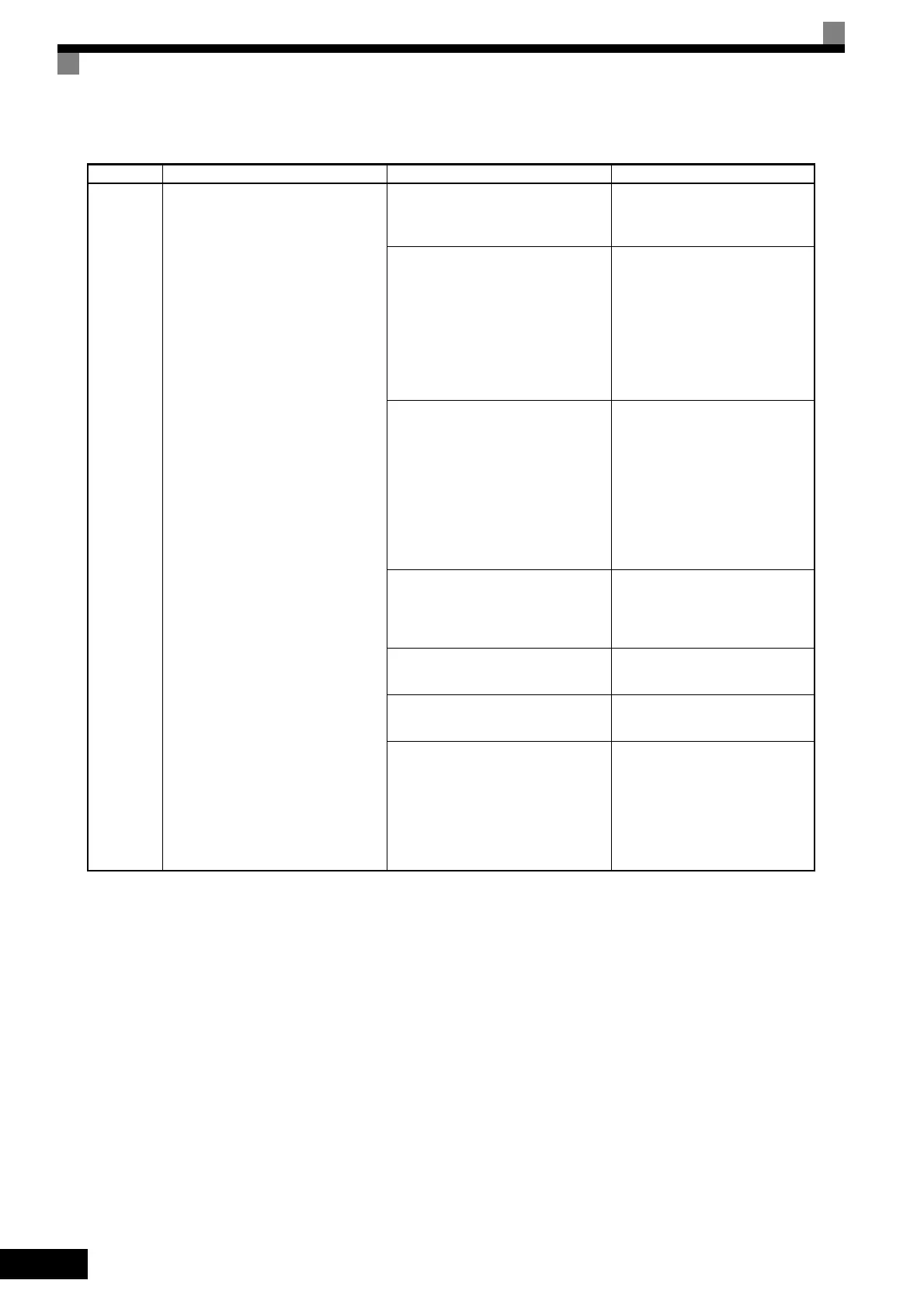
7-6
OL1
电机过载
Motor Overload
The motor overload protection func-
tion has operated based on the internal
electronic thermal value.
The load is too heavy. The accelera-
tion time, deceleration time, and cycle
time are too short.
Check the size of the load and the
length of the acceleration, deceler-
ation, and cycle times.
The constant setting for speed search
is incorrect.
(Motor overload occurred due to
motor hunting and vibration.)
• Use the speed search function.
• Adjust the settings of the Speed
search operating current (b3-02)
and Speed search deceleration
time (b3-03).
• Use the estimated speed search
function. (Perform stationary
autotuning for line-to-line resis-
tance only.)
• Motor overload occurred when run-
ning at low speed. (If a general-pur-
pose motor is used, motor overload
can occur when running at low
speed even if running within the
rated current.)
• Motor protection selection (L1-01)
is set to general-purpose motor pro-
tection (1) when an Inverter duty
motor is used.
• Check the size of the load.
• Check the setting of L1-01.
• Increase the frame size of the
Inverter.
The directions of the motor and PG
are different. (Only in flux vector con-
trol)
• Correct the PG wiring.
• Correct the motor wiring.
• Change the setting of PG rota-
tion (F1-05).
The V/f characteristics voltage is too
high.
Check the V/f characteristics.
The Motor Rated Current (E2-01) is
incorrect.
Check the Motor Rated Current
(E2-01).
• A short-circuit between +V, −V, and
AC terminals occurred.
• Overload in the control circuit ter-
minal.
• Make sure that incorrect wiring
has not been done.
• Check the resistance and wir-
ing for the frequency setting
potentiometer, etc. (Check that
the current for terminals +V and
–V is 20 mA or less.)
Table 7.1 Fault Displays and Processing (Continued)
Display Meaning Probable Causes Corrective Actions

 Loading...
Loading...











