6-1
IM WT3001E-51EN
Delta Computation
6
6.1 Delta Computation Function
Functional Overview
The sum or difference of the instantaneous values (sampled data) of the voltage or
current between the elements in a wiring unit can be used to determine various types
of data such as the differential voltage and phase voltage. This operation is called delta
computation.
Delta computation enables the following computations.
• The differential voltage and differential current between two elements
can be computed on a single-phase, three-wire system or a three-phase,
three-wire system (using two elements).
• The line voltage and phase current that are not measured on a single-
phase, three-wire system or a three-phase, three-wire system (using 2
elements) can be computed.
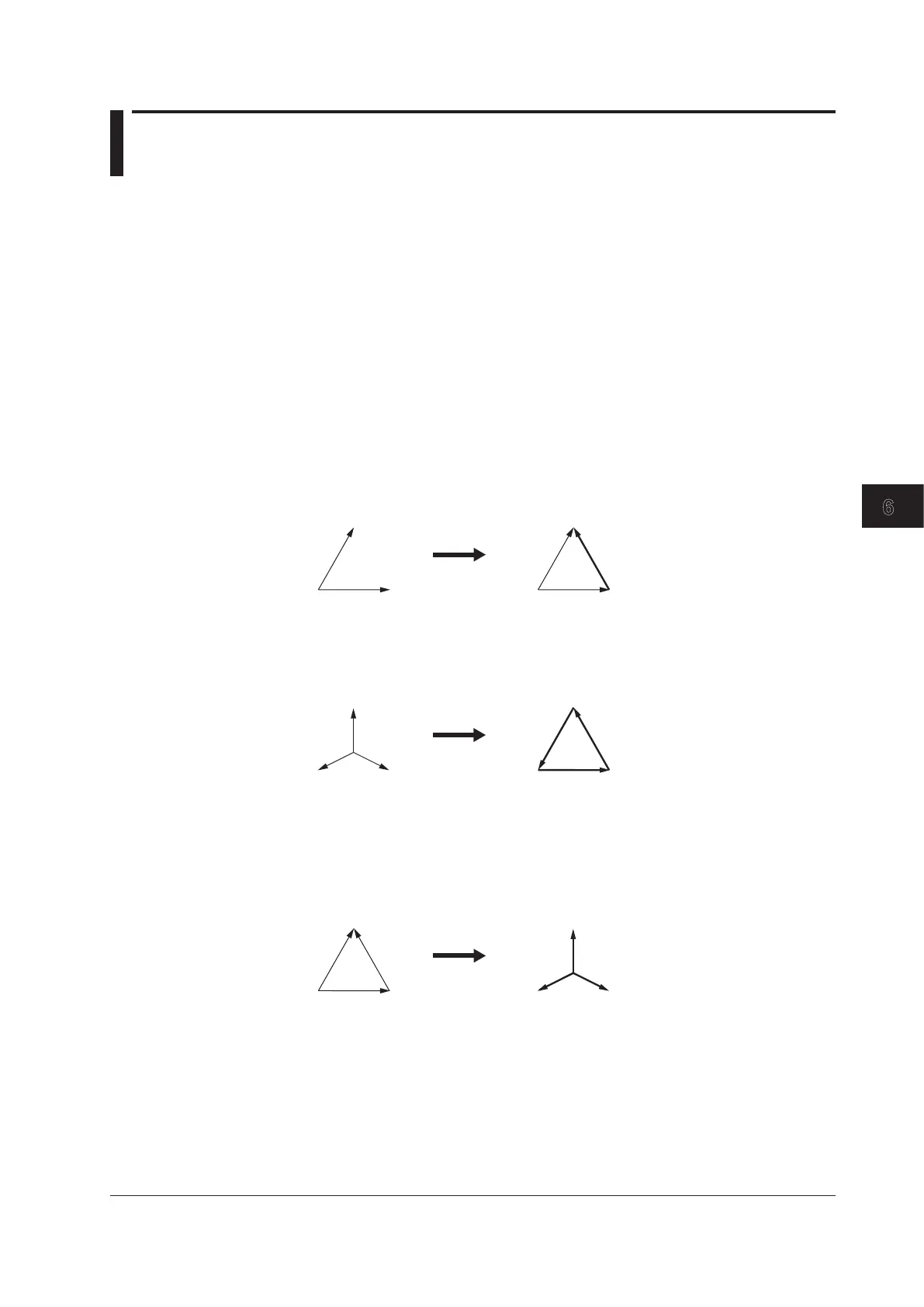
• Using the data from a three-phase, four-wire system, various data of a
delta connection can be computed from the data of a star connection
(star-delta transformation).
• Using the data from a three-phase, three-wire (three-voltage, three-
current) system, various data of a star connection can be computed
from the data of a delta connection (delta-star transformation). This
function is effective when you wish to observe the phase voltage of an
object that has no neutral line such as a motor.
For the equations, see section 6.3.
Limitations by Measurement Modes
Delta computation cannot be performed in the following measurement modes.
• Wide bandwidth harmonic measurement mode
• IEC harmonic measurement mode
• Voltage fluctuation and flicker measurement mode
• Cycle-by-cycle measurement mode
Chapter 6 Delta Computation

 Loading...
Loading...