154 Chapter 4
Basic Digital Operation
Using Waveform Clipping
Using Waveform Clipping
Waveforms with high power peaks can cause intermodulation distortion, which generates spectral regrowth
(a condition that interferes with signals in adjacent frequency bands). The clipping function enables you to
reduce high power peaks by clipping the I and Q data to a selected percentage of its highest peak.
The clipping feature is available only with the dual ARB mode.
How Power Peaks Develop
To understand how clipping reduces high power peaks, it is important to know how the peaks develop as the
signal is constructed.
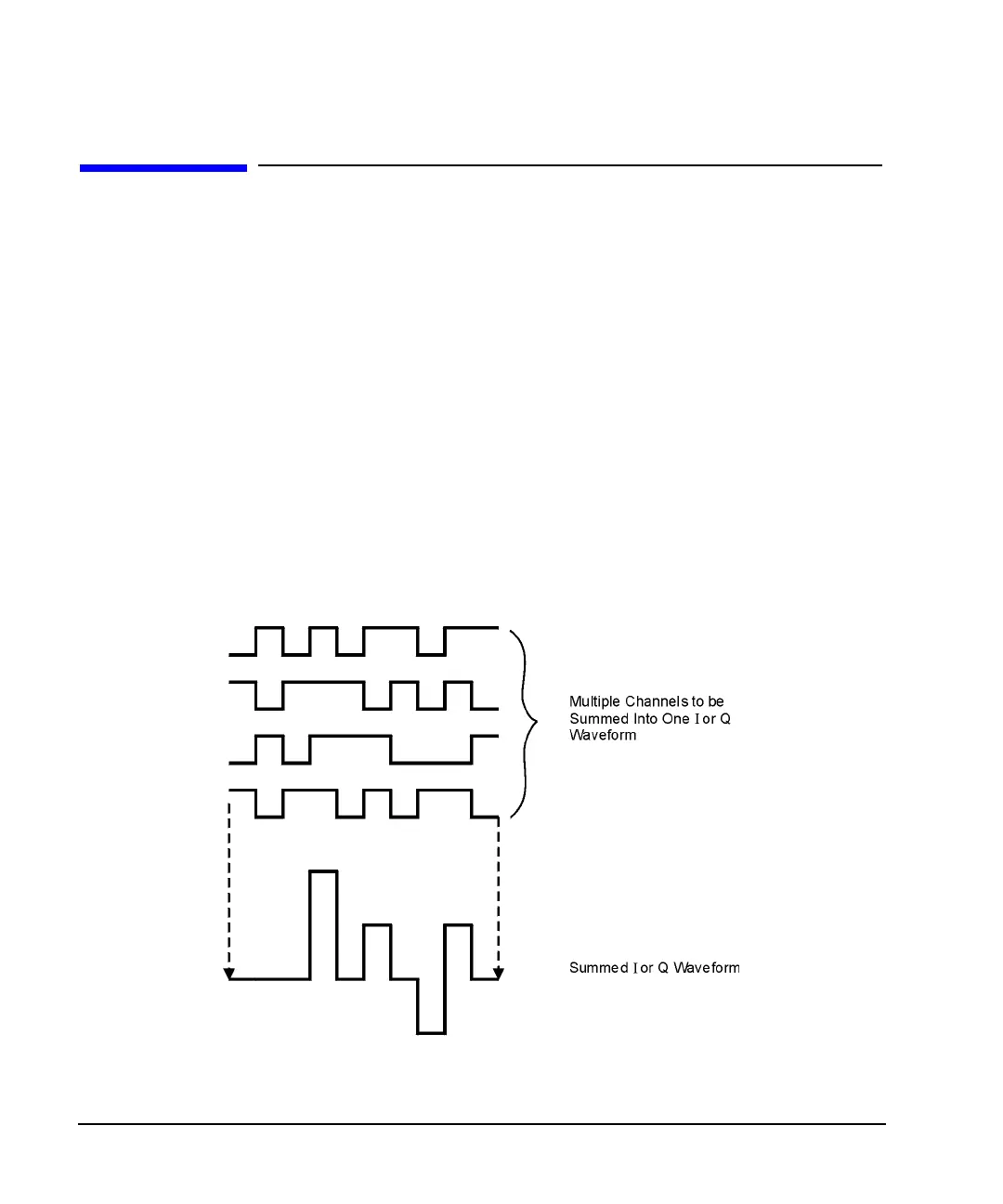
I/Q waveforms can be the summation of multiple channels (see Figure 4-17). Whenever most or all of the
individual channel waveforms simultaneously contain a bit in the same state (high or low), an unusually
high power peak (negative or positive) occurs in the summed waveform. This does not happen frequently
because the high and low states of the bits on these channel waveforms are random, which causes a
cancelling effect.
Figure 4-17 Multiple Channel Summing

 Loading...
Loading...