182 Chapter 4
Basic Digital Operation
Differential Encoding
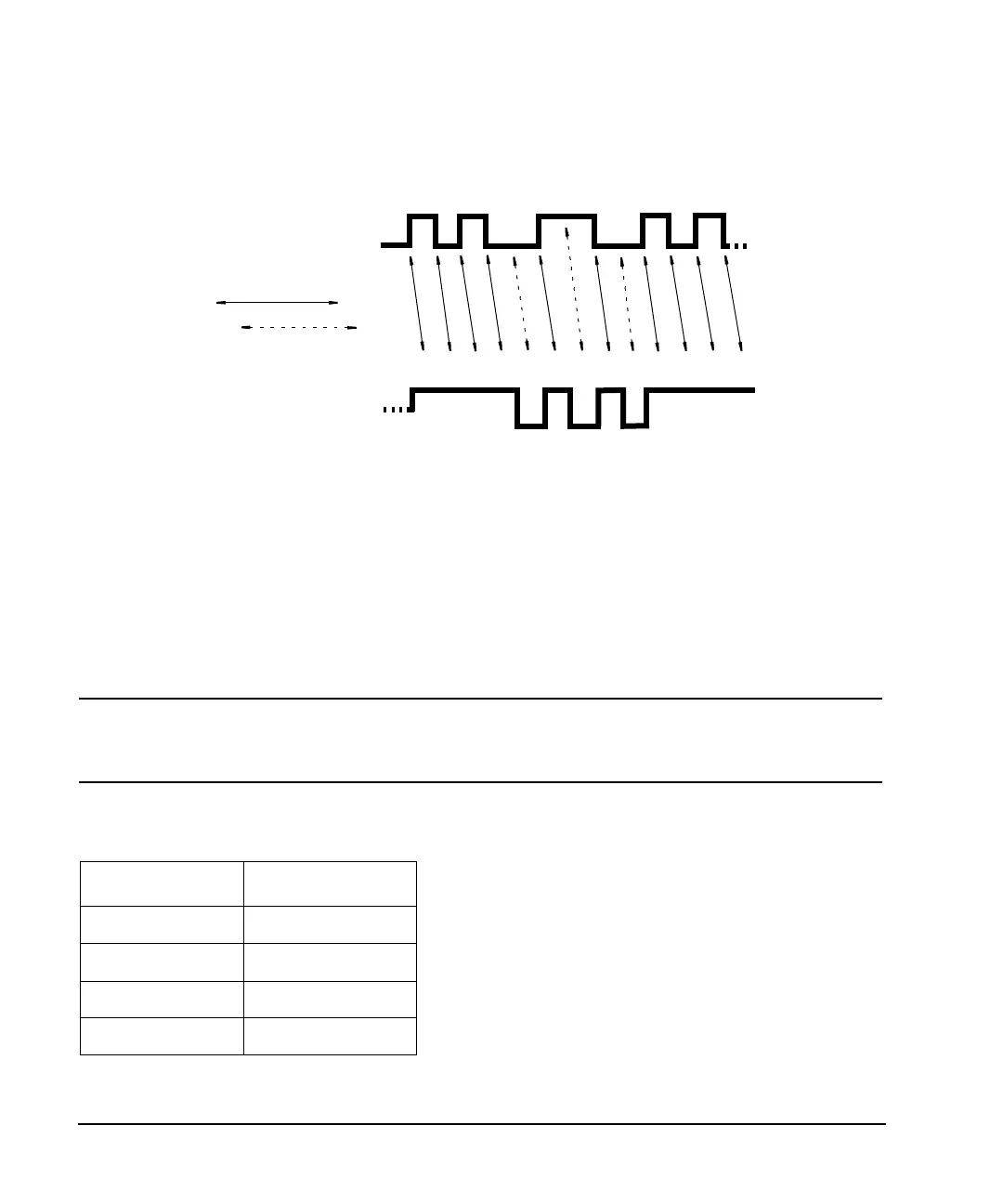
For a bit-by-bit illustration of the encoding process, see the following illustration.
How Differential Encoding Works
Differential encoding employs offsets in the symbol table to encode user-defined modulation schemes. The
Differential State Map table editor is used to introduce symbol table offset values which in turn
cause transitions through the I/Q State Map based on their associated data value. Whenever a data value is
modulated, the offset value stored in the Differential State Map is used to encode the data by transitioning
through the I/Q State Map in a direction and distance defined by the symbol table offset value.
Entering a value of +1 will cause a 1-state forward transition through the I/Q State Map, as shown in the
following illustration.
NOTE The following I/Q State Map illustrations show all of the possible state transitions using a
particular symbol table offset value. The actual state-to-state transition would depend upon
the state in which the modulation had started.
As an example, consider the following data/symbol table offset values.
Tabl e 4-3
Data Offset Value
00000000 +1
00000001 -1
00000010 +2
00000011 0
1
01 00 1 1 00
1
1
0
raw (unencoded) data
differentially encoded data
11
11
1
1
1
111
0
0
0
change =
no change =
0
 Loading...
Loading...