System Control
ARM DDI 0363G Copyright © 2006-2011 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. 4-49
ID073015 Non-Confidential
c5, Instruction Fault Status Register
The IFSR characteristics are:
Purpose Holds status information regarding the source of the last instruction abort.
Usage constraints The IFSR is:
• a read/write register
• accessible in Privileged mode only.
Configurations Available in all processor configurations.
Attributes See Table 4-29.
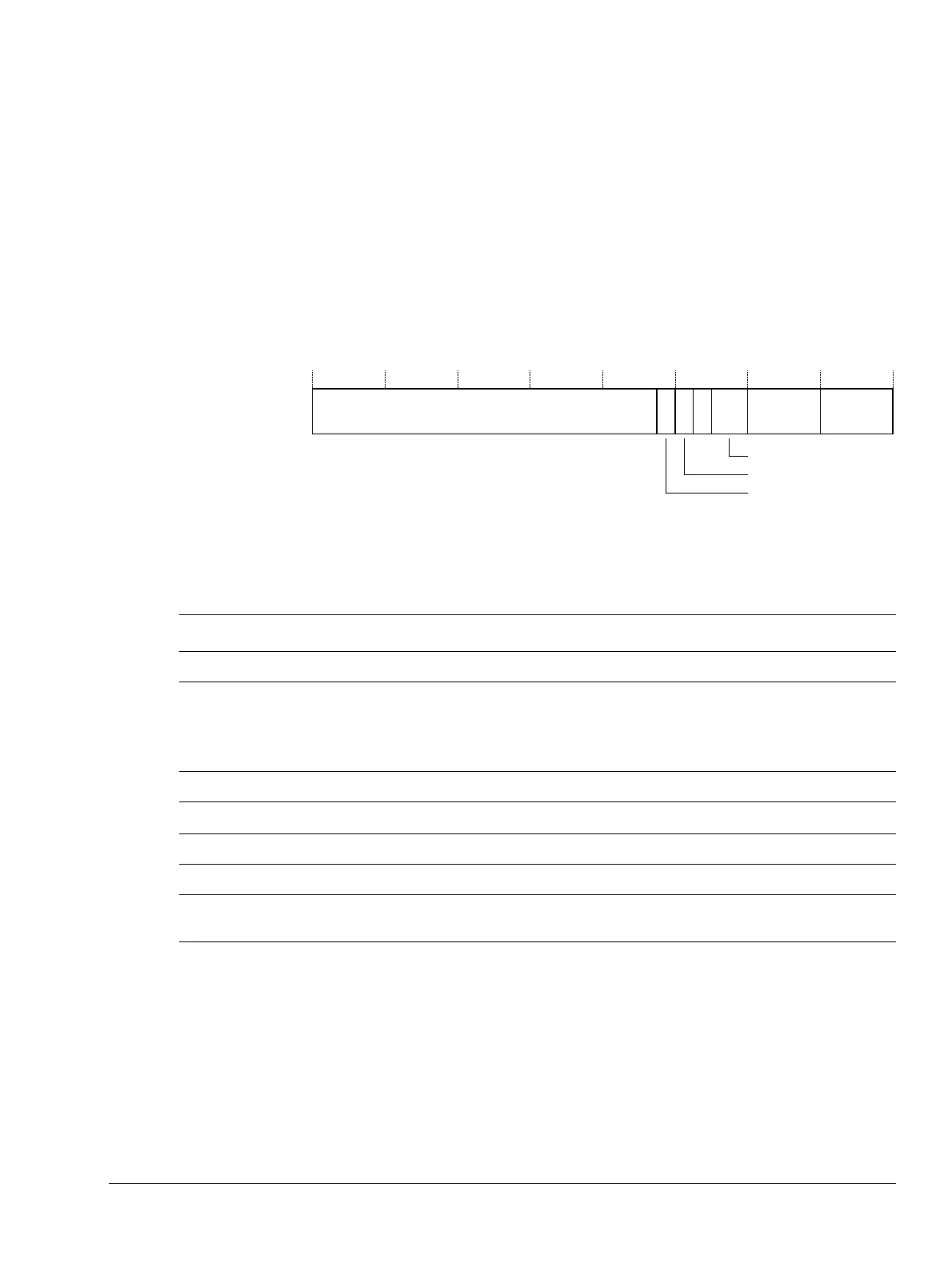
Figure 4-31 shows the IFSR bit assignments.
Figure 4-31 IFSR Register bit assignments
Table 4-29 shows the IFSR bit assignments.
To access the IFSR read or write CP15 with:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c5, c0, 1 ; Read IFSR
MCR p15, 0, <Rd>, c5, c0, 1 ; Write IFSR
c5, Auxiliary Fault Status Registers
The processor has two auxiliary fault status registers:
• the Auxiliary Data Fault Status Register (ADFSR)
SReserved
31 30
StatusDomain
4
910111213
Reserved
SD
87
Reserved
Table 4-29 IFSR Register bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:13] - SBZ.
[12] SD Distinguishes between an AXI Decode or Slave error on an external abort. This bit is only valid for
external aborts. For all other aborts types of abort, this bit is set to zero:
0
= AXI Decode error (DECERR) caused the abort
1
= AXI Slave error (SLVERR) caused the abort.
[11] - SBZ.
[10]
a
S Part of the Status field.
[9:8] - SBZ.
[7:4] Domain SBZ. This is because domains are not implemented in this processor.
[3:0]
a
Status Indicates the type of fault generated. To determine the instruction fault, bit [12] and bit [10] must
be used in conjunction with bits [3:0].
a. For more information on how these bits are used in reporting faults, see Table 4-27 on page 4-47.
 Loading...
Loading...