A-9
Appendix A Maintenance and Troubleshooting of this Device
A2-4-6 Parameter adjustment
If diagnosis is judged to be not possible, the data collected under normal operating conditions
(section A2-4-2) and when there is simulated clogging (section A2-4-3) can be analyzed and the
parameters adjusted.
The reason why diagnosis cannot be performed is that the index value—even under normal
operating conditions—is similar to or smaller than that when there is clogging, so the normal and
clogged states cannot be distinguished. There are two primary causes leading for this situation.
• A large amount of variation of the index under normal conditions
• A small variation of the index when there is clogging
This situation may be improved by adjusting the parameters of the pressure frequency index
diagnosis. The following describes the two cases.
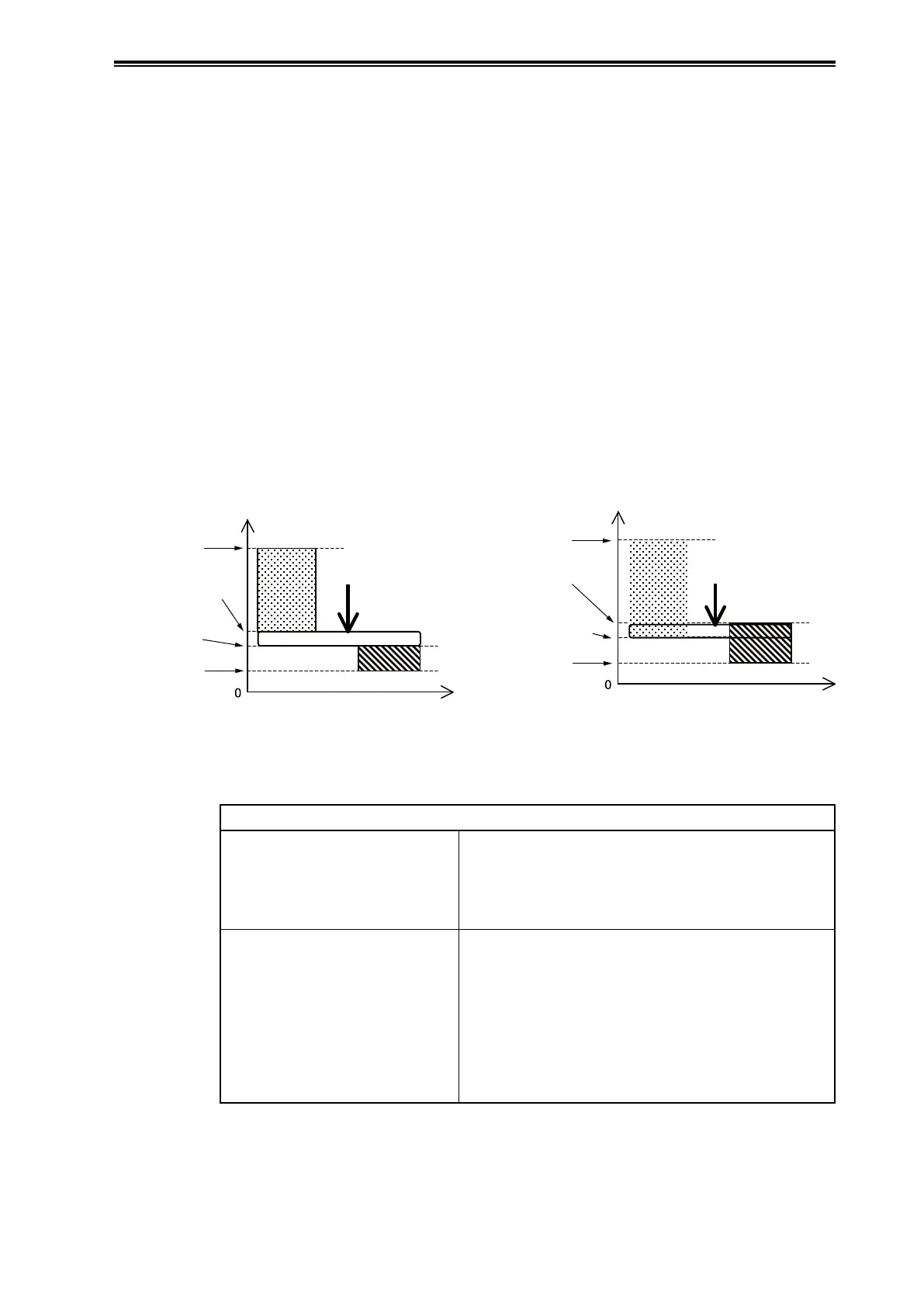
(A) Variation of the index under normal operating conditions is large.
In this case, although the value of the index is small with simulated clogging, variation in the index
is large under normal conditions, so the index value can be close to or equivalent to its value with
clogging even when there is no clogging, as shown in the figure below.
Index value Index value
Maximum value
under normal
operating conditions
Minimum value
under normal
operating conditions
Maximum value
under simulated
clogging
Minimum value
under simulated
clogging
Maximum value
under normal
operating conditions
Minimum value
under normal
operating conditions
Maximum value
under simulated
clogging
Minimum value
under simulated
clogging
Normal condition Simulated clogging
Normal condition Simulated clogging
condition
Slight dierence Value being overlapping
In this case, it is necessary to examine the cause of the large variation that occurs under normal
conditions, and to reduce this effect. Use the following the guidelines for adjustment.
Guidelines for parameter adjustment
The index value sometimes
decreases significantly under normal
operating conditions. At this time,
the process variable changes or the
standard deviation becomes large.
Increase the Press Freq Filter Constant in steps of 0.02–
0.05.
The index value under normal
operating conditions changes
significantly depending on the
operating conditions.
Check whether the operating conditions are related to the
process variable. If there is a PV range where the difference
between the maximum index value and the minimum is
relatively small, or a PV range where the minimum under
normal conditions is not small, set Press Freq Calc PV
High Limit and Press Freq Calc PV Low Limit to the values
of this range. When these parameters are used, diagnosis
should be carried out only when pressure is applied, and
should be stopped when no pressure is applied.
 Loading...
Loading...