A-29
Appendix A Maintenance and Troubleshooting of this Device
A4-4-4 Judging the possibility of diagnosis
Whether or not clogging can be diagnosed can be judged according to the index and its maximum
and minimum values collected under normal operating conditions (section A4-4-2) and under a
simulated clogged condition (section A4-4-3).
Judgment criteria
The upper range limit of the clog simulated condition is
smaller than the lower range value during normal condition.
The difference between the minimum under normal operating
conditions and the maximum with simulated clogging is
equivalent to or larger than the difference between the
minimum and maximum under normal operating conditions.
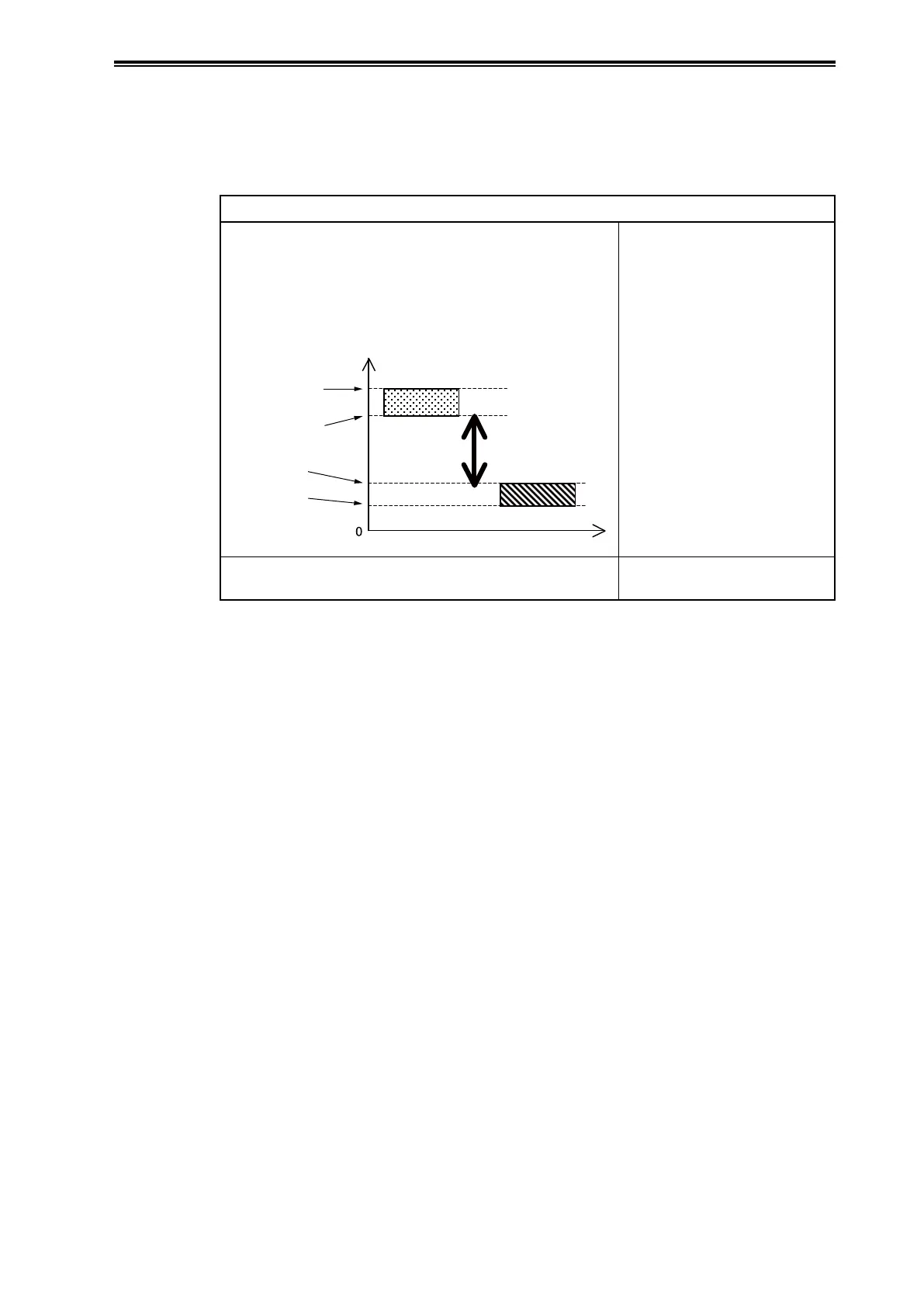
Index value
Maximum value
under normal
operating conditions
Minimum value
under normal
operating conditions
Maximum value
under simulated
clogging
Minimum value
under simulated
clogging
Normal condition Simulated clogging
The larger the dierence
between the minimum
under normal operating
conditions and
the maximum with
simulated clogging
Diagnosis is possible.
The above conditions are not satisfied.
Diagnosis is not possible or
difficult.
The minimum condition for diagnosis is that the maximum with simulated clogging is smaller
than the minimum under normal conditions. If this condition is not satisfied, the index value may
decrease to the value with simulated clogging even when the connecting pipe is operating normally.
Therefore, the conditions are not suitable for diagnosis. In cases where the index value under
normal conditions varies depending on the operating conditions, judgment should be based on the
values when the minimum index value is at its smallest.
The larger the difference between the minimum under normal operating conditions and the
maximum with simulated clogging, the easier diagnosis is. Therefore, this value is important.
A reference for judging whether diagnosis is possible is that this difference is equivalent to or
larger than the difference between the minimum value and maximum value under normal
operating conditions. If this difference is less than half of the difference between the minimum
and maximum under normal conditions, diagnosis will probably be difficult. The reason for this
is that the index will be close to its value with clogging even under normal conditions, so it will be
difficult to distinguish between normal and abnormal states. In this case, conditions are probably
inappropriate for diagnosis.
If diagnosis is judged to be possible, go on to section A4-4-5 and set the diagnostic alarm. If
diagnosis is judged to be not possible, go to section A4-4-6 and consider parameter adjustment.
[CAUTION]
The position of a clog may affect the amount of variation of the pressure frequency
index. In particular, if the fluid is a compressible fluid, the effect can be significant.
In such a case, if clogging is closer to the process side, the amount of variation will be
greater. Therefore, when the position where clogging actually occurs is closer to the
transmitter than the position of the simulated clogging, changes in the index value
will be small or almost zero in comparison to those in the simulation test. Likewise,
when the position where clogging actually occurs is closer to the process as compared
to the position of the simulated clog, changes in the index will be greater than in the
simulation test.
 Loading...
Loading...