3-59
Chapter 3 Starting and Stopping this Device
3-11 Advanced Diagnostics (optional )
The advanced diagnostics include the pressure frequency index, the standard deviation, and
calculation of the out-of-range pressure event count.
The diagnosis also determines whether the pressure frequency index, standard deviation, and the
out-of-range pressure event count exceed the threshold values. Users can check alarms on the self-
diagnostics status screen in the communicator if the results exceed a threshold. Alarms can also be
checked on the built-in indicator of the transmitter.
3-11-1 Pressure Frequency Index
The pressure frequency index quantifies how often the input pressure goes up and down
(fluctuation) with a number between 0 and 1. The index is calculated from data on the number
of fluctuations during a time period of several minutes. It is possible to detect a change in process
conditions by monitoring changes in this value. For example, the pressure frequency index can be
used for diagnosis of clogged connecting pipes.
For information about diagnosis of clogged connecting pipes, see Appendix B.
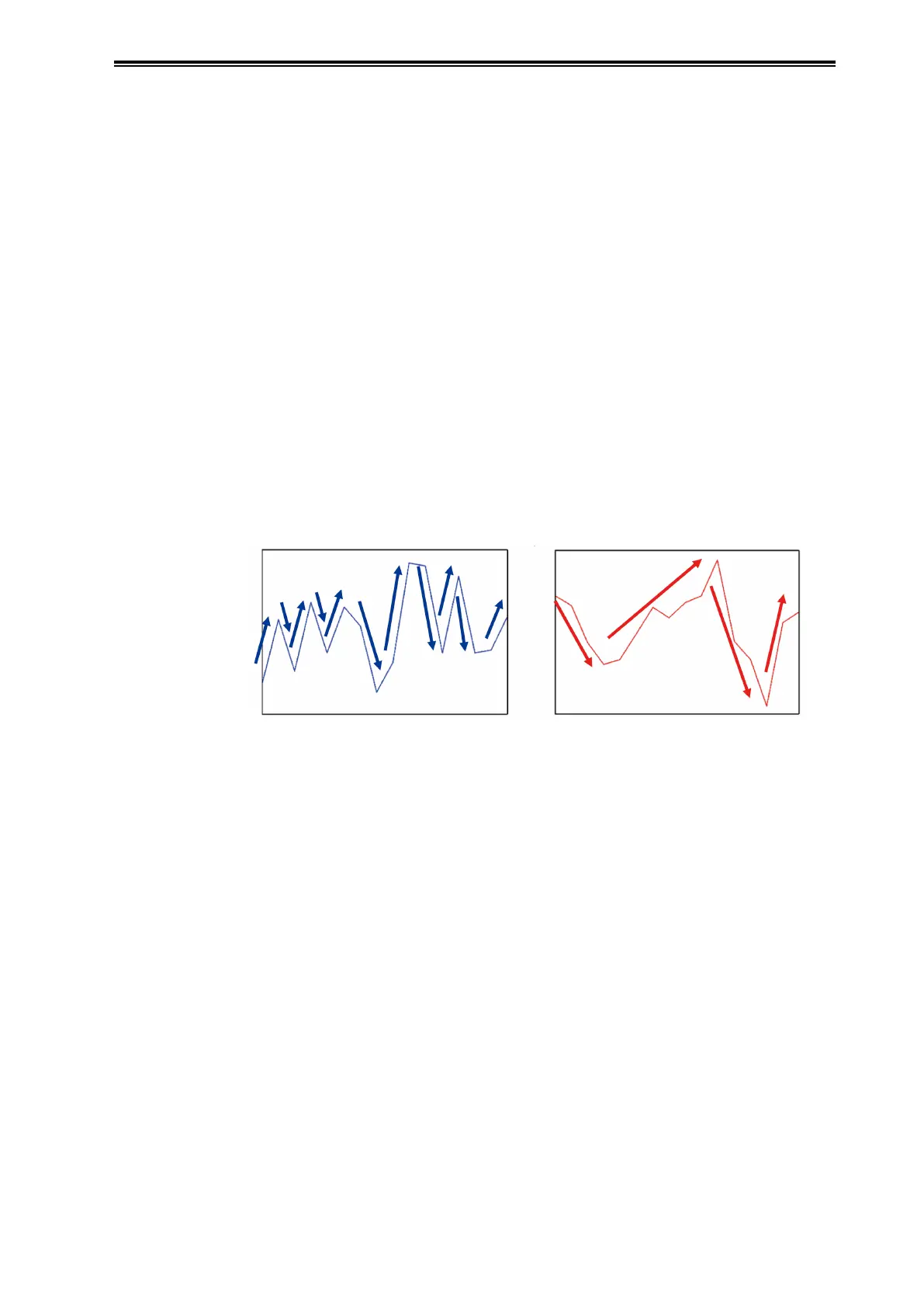
In the practical example shown below, a change in the number of fluctuations of the input pressure
when the process is operating normally and when conditions have changed can be easily seen.
normal conditions changed conditions
(1) Points to note
When using the pressure frequency index, note the following:
The pressure frequency index changes depending on a combination of factors. Thus, it may be
difficult to detect a single abnormality or phenomenon by this index alone.
If the process is in an abnormal state from the beginning, it is not possible to detect a change
caused by abnormal conditions. Carry out the steps described below in (3), “Preparation,” under
normal conditions.
Even if an unexpected abnormality occurs, the pressure frequency index does not necessarily
change immediately. This is because it takes a few minutes to calculate the frequency of the
pressure fluctuation with a high level of accuracy. If an abnormality occurs briefly and conditions
quickly return to normal, the change in the index will be small, and an alarm may not be activated.
If the transmitter is installed in an environment subject to excessive vibration, the pressure
frequency index will be affected. As a result, an error may not be detected or there may be a false
alarm. If the pressure frequency index is used to diagnose clogging of connecting pipes, problems
may not be detected correctly, depending on the process conditions.

 Loading...
Loading...