A-30
Appendix A Maintenance and Troubleshooting of this Device
A4-4-5 Setting of the diagnosis alarm
If diagnosis is judged to be possible, set the alarm. If you do not want to activate the alarm, omit the
steps in this section.
[CAUTION]
The procedures described in this document do not guarantee the detection of clogging
or the elimination of false indications. The pressure frequency index may change due
to causes other than clogging, and may also depend on the degree of clogging or the
material of the clog. Adjusting the settings should be done with the realization that
there is no threshold value setting that can eliminate misinformation and securely
detect clogging only.
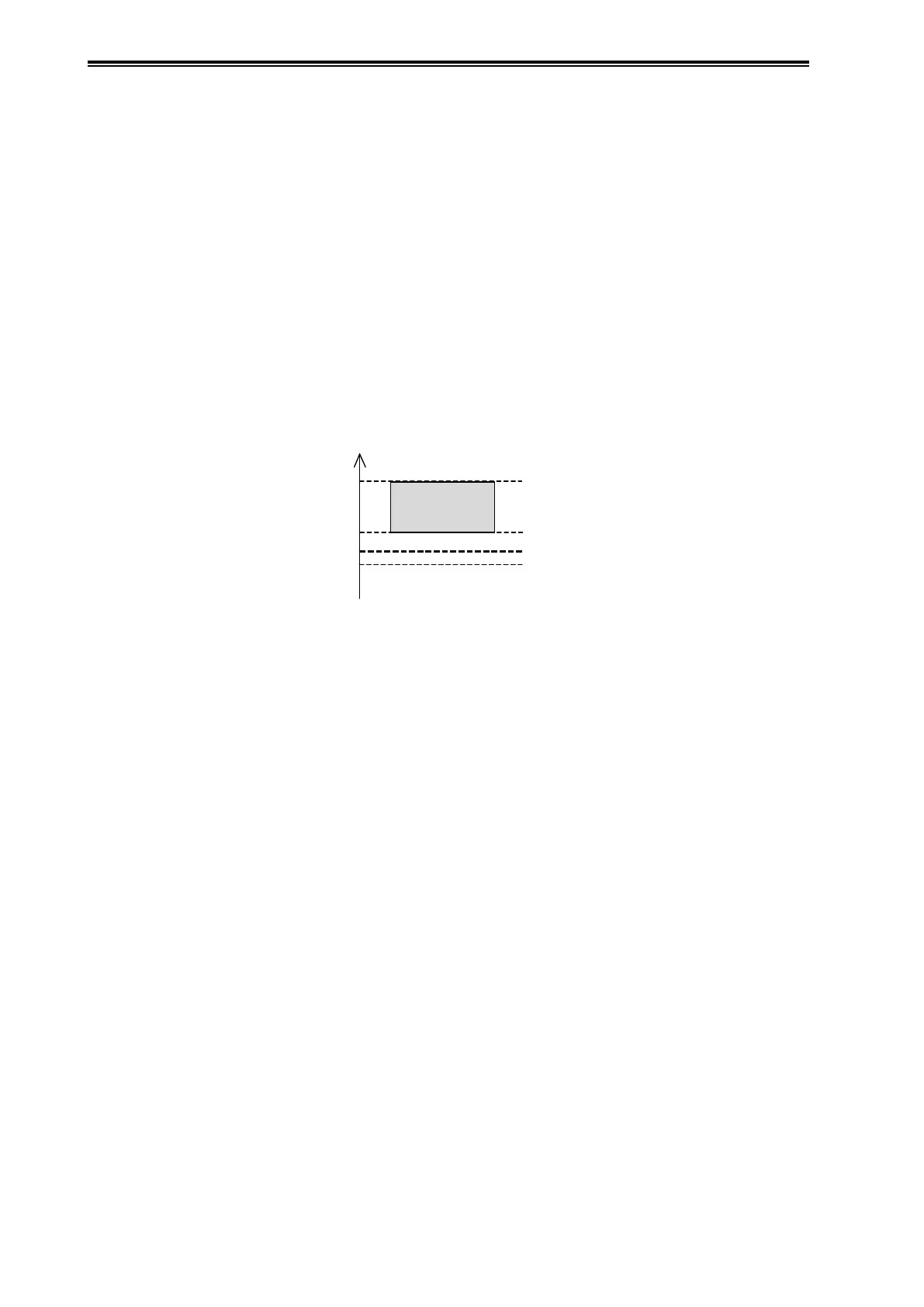
First, determine the alarm threshold value. This threshold should be between the minimum index
value under normal conditions and the maximum with simulated clogging. If the threshold is put
close to the minimum under normal operating conditions, the alarm will be activated earlier, but
the possibility of a false alarm is also higher. Put the threshold at a certain distance away from the
minimum under normal operating conditions, leaving a margin.
Index value
Index value range
under the normal
operating conditions
Minimum value
under normal
operating conditions
Maximum value
under simulated clogging
Threshold
value
After determining the threshold value, follow the steps below to set the alarm and start the
diagnosis.
Procedure
(1) Execute Reset Press Freq Index.
(2) Set Press Freq Index Low Limit to the determined threshold value.
(3) Set Press Freq Index Alarm Use “Enabled (Low)” (lower limit only).
With these settings, when the index value is outside the normal range and approaches the value
with simulated clogging, the alarm is activated.
A4-4-6 Parameter adjustment
If diagnosis is judged to be not possible, the data collected under normal operating conditions
(section A4-4-2) and when there is simulated clogging (section A4-4-3) can be analyzed and the
parameters adjusted. The reason why diagnosis cannot be performed is that the index value—even
under normal operating conditions—is similar to or smaller than that when there is clogging, so
the normal and clogged states cannot be distinguished. There are two primary causes leading for
this situation.
• A large amount of variation of the index under normal conditions
• A small variation of the index when there is clogging
This situation may be improved by adjusting the parameters of the pressure frequency index
diagnosis. The following describes the two cases.

 Loading...
Loading...