36 (55) BRUKER BIOSPIN Technical Manual Version 001
Description
Configuration of the External Memory Interface (EMIF)
The DSP EMIF supports a glue-less interface to a variety of external devices, in-
cluding:
• Pipe-lined synchronous–burst SRAM (SBSRAM).
• Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM).
• Asynchronous devices, including SRAM, ROM and FIFO’s.
If multiple requests arrive simultaneously, the EMIF prioritizes them and performs
the necessary number of operations. The behavior of the EMIF is defined in some
dedicated registers.
Content of EMIF Register and Resulting Memory Allocation
Table 5.25: PLX Controller Interrupts
DSP Interrupt Input Source Signal Function Active Level
LINT 1 HINT DSP to Host interrupt Low
LINT 2 IWR_PLX Logic to Host:
„Read Pipeline Register“
High
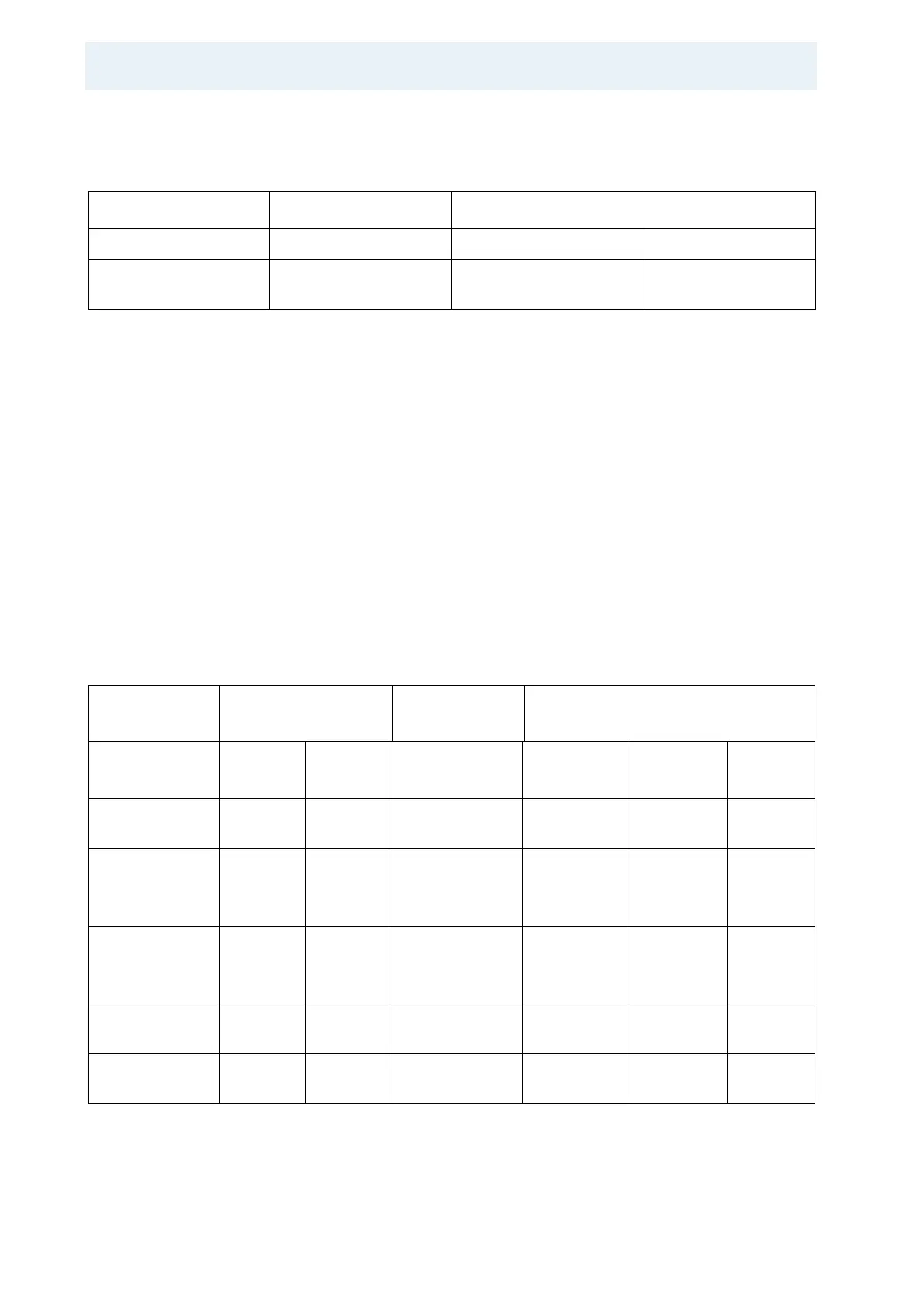
Table 5.26: Configuration Register and Resulting Memory Allocation
Configuration
Register
Memory allocation
Register Name
Hex
Address
Hex
Value
Memory Type
DSP Select
Signal
DSP
Address
Device
Global Control
Register
180 0000 0000
30F8
Space control
reg. CE 0
180 0008 FFFF
FF43
32 bit SBRAM DSP CE 0 80000000
–
8000FFFF
Memory
Space control
reg. CE 1
180 0004 1081
0220
32 bit asyn.
RAM
DSP CE 1 90000000
–
90000008
Control
Register
Space control
reg. CE 2
180 0010 FFFF
FF43
32 bit SBRAM DSP CE 2 A0000000 Receiver
FIFO
Space control
reg. CE 3
180 0014 FFFF
FF43
32 bit SBRAM DSP CE 3 B000 0000 Output
FIFO

 Loading...
Loading...