Input/Output setting Input Syntax
MathI/MathO or MathI/DecimalO
d
dx
(f(x))|
x=a
LineI/LineO or LineI/DecimalO
d
dx
(f(x), a, tol)*
* tol specifies tolerance, which becomes 1 × 10
-16
when nothing is input for
tol.
Derivative Calculation Precautions
• When using a trigonometric function in f(x), specify "Radian" as Angle
Unit on the SETTINGS menu.
• A smaller tol value increases precision, but it also increases calculation
time. When specifying tol, use a value that is 1 × 10
-22
or greater.
• Inaccurate results and errors can be caused by the following:
- discontinuous points in x values
- extreme changes in x values
- inclusion of the local maximum point and local minimum point in x
values
- inclusion of the inflection point in x values
- inclusion of undifferentiable points in x values
- differential calculation results approaching zero
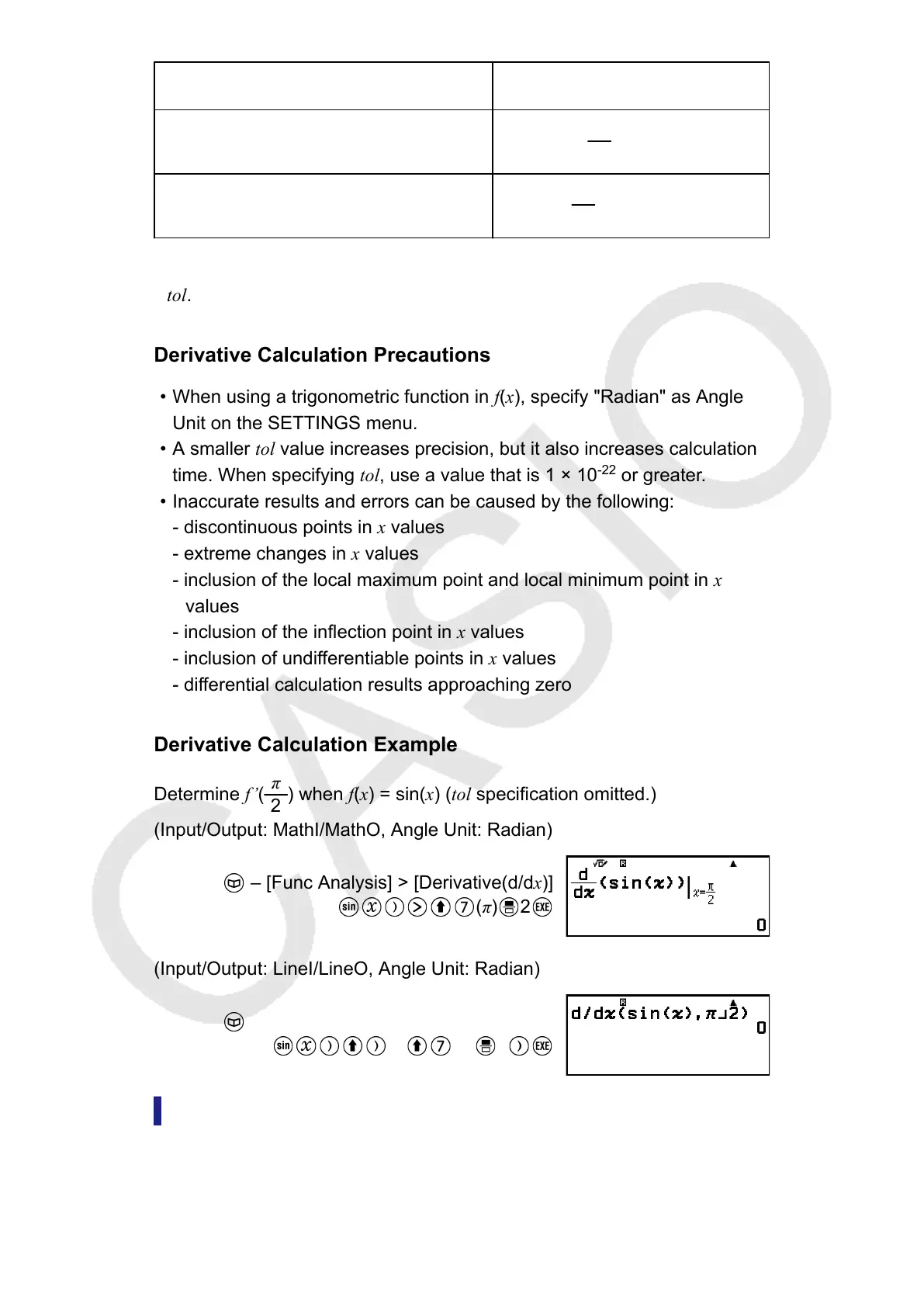
Derivative Calculation Example
Determine f’(
π
2
) when f(x) = sin(x) (tol specification omitted.)
(Input/Output: MathI/MathO, Angle Unit: Radian)
– [Func Analysis] > [Derivative(d/dx)]
(π) 2
(Input/Output: LineI/LineO, Angle Unit: Radian)
– [Func Analysis] > [Derivative(d/dx)]
(,) (π) 2
Integration(∫)
This calculator performs integration using the Gauss-Kronrod method of
numerical integration.
47
 Loading...
Loading...