The ensuing section provides an example of the CLI configuration of how flowspec works. First, on the
Flowspec router you define the match-action criteria to take on the incoming traffic. This comprises the PBR
portion of the configuration. The service-policy type defines the actual PBR policy and contains the
combination of match and action criteria which must be added to the flowspec. In this example, the policy is
added under address-family IPv4, and hence it is propagated as an IPv4 flowspec rule.
Flowspec router CLI example:
class-map type traffic match-all cm1
match source-address ipv4 100.0.0.0/24
policy-map type pbr pm1
class type traffic cm1
drop
flowspec
address-family ipv4
service-policy type pbr pm0
Transient router CLI:
flowspec
address-family ipv4
service-policy type pbr pm1
For detailed procedural information and commands used for configuring Flowspec, see How to Configure
BGP Flowspec, on page 212.
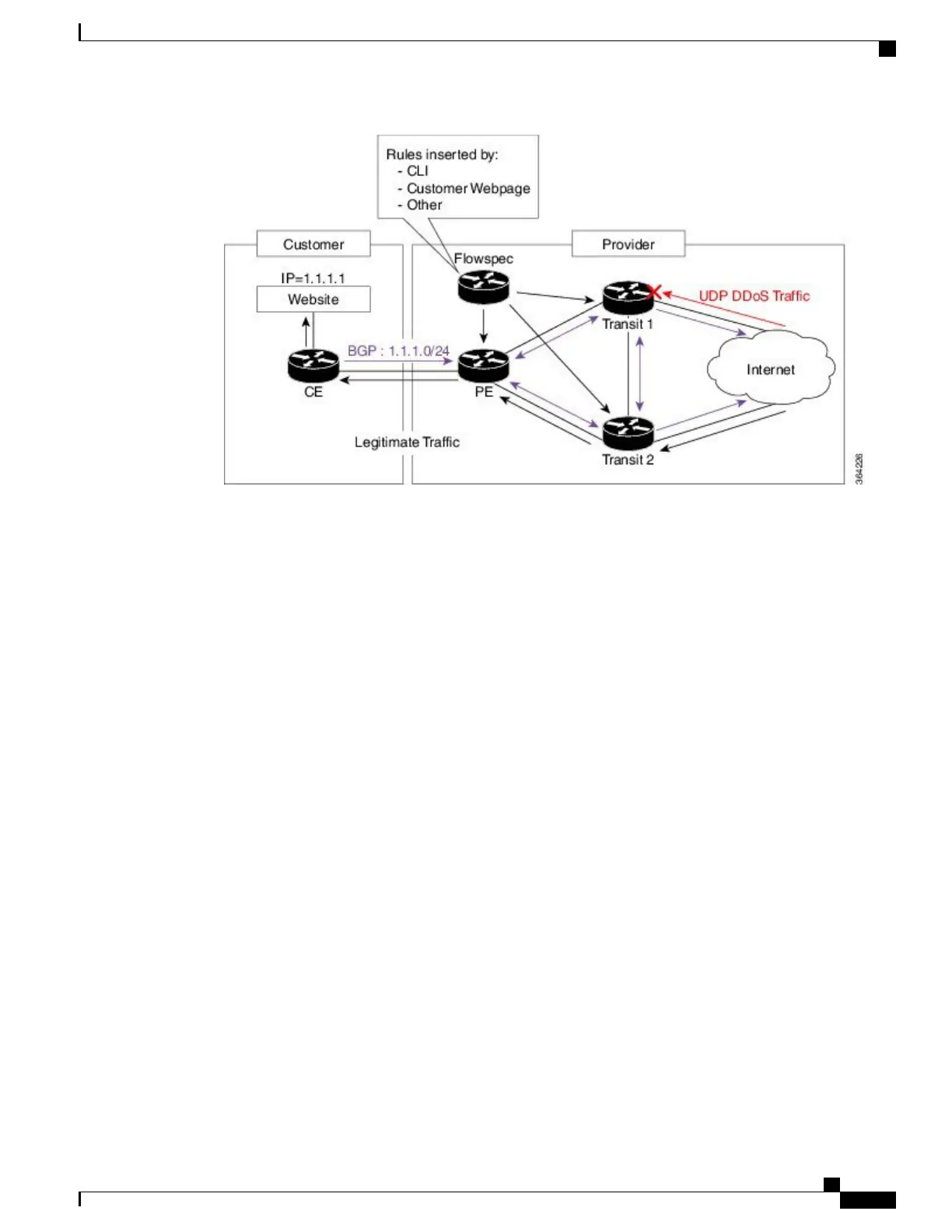
Information About Implementing BGP Flowspec
To implement BGP Flowspec, you need to understand the following concepts:
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.3.x
205
Implementing BGP Flowspec
Information About Implementing BGP Flowspec

 Loading...
Loading...











