SUMMARY STEPS
1.
configure
2.
router ospf instance-id
3.
segment-routing mpls
4.
segment-routing forwarding mpls
5.
segment-routing prefix-sid-mapadvertise-local
6.
segment-routing sr-preferprefix-list[acl-name]
DETAILED STEPS
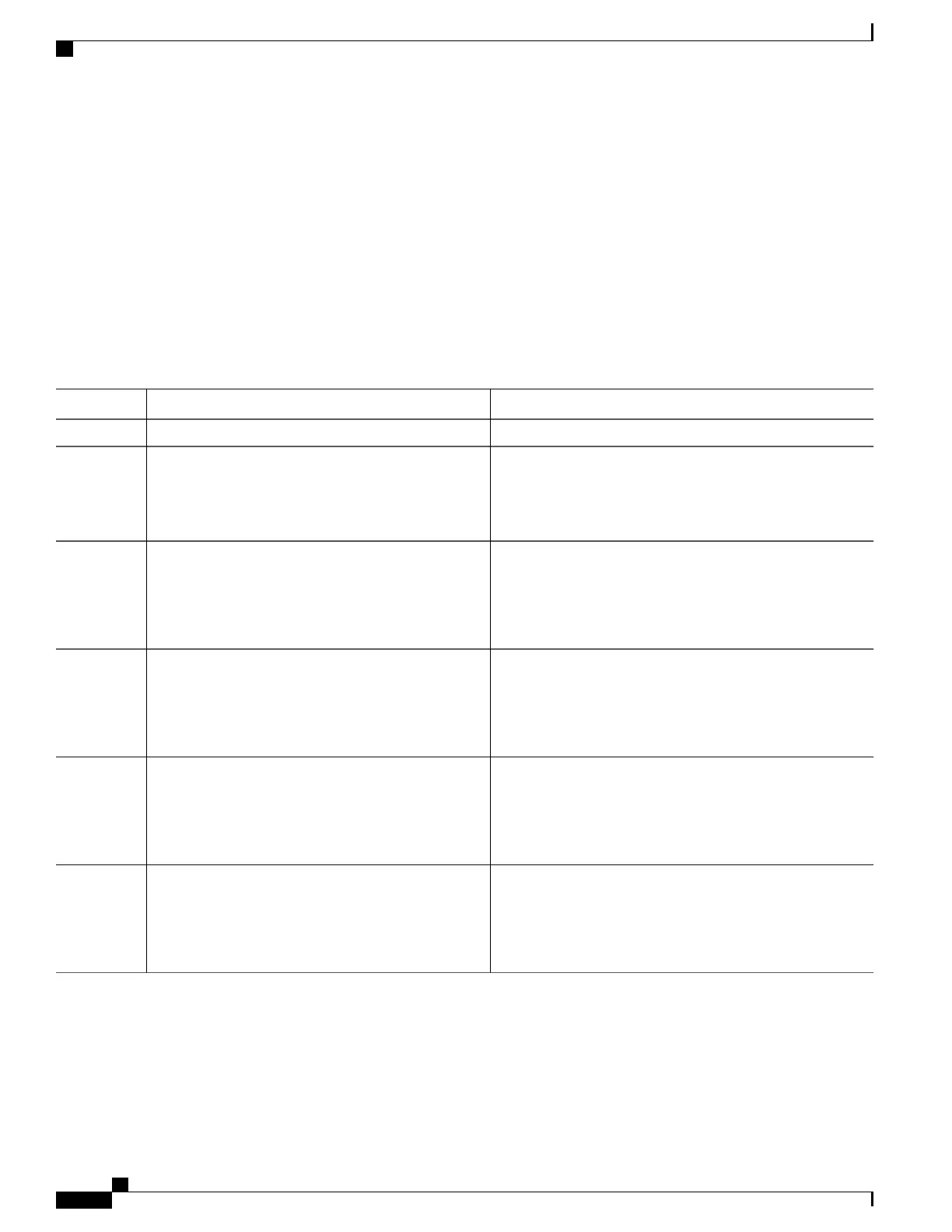
PurposeCommand or Action
configure
Step 1
Enables OSPF routing for the specified routing instance, and
places the router in router configuration mode.
router ospf instance-id
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config)# router ospf isp
Step 2
segment-routing mpls
Step 3
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ospf)#
segment-routing mpls
Enables SR forwarding on all interfaces where this instance
OSPF is enabled.
segment-routing forwarding mpls
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ospf)#
segment-routing forwarding mpls
Step 4
Enables server functionality and allows OSPF to advertise the
local mapping entries using area-scope flooding. The flooding
segment-routing prefix-sid-mapadvertise-local
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ospf)#
segment-routing
prefix-sid-map advertise local
Step 5
is limited to areas where segment-routing is enabled. Disabled
by default.
Enables OSPF to communicate to the routing information base
(RIB) that SR labels are preferred to LDP labels. If ACL is
segment-routing sr-preferprefix-list[acl-name]
Example:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-ospf)#
segment-routing
sr-prefer prefix-list foo
Step 6
used, OSPF signals the preference of SR labels over LDP
labels for prefixes that match ACL. If ACL is not used, OSPF
signals the preference of SR labels for all prefixes.
The following example shows how OSPF advertises local mapping entries using area-flooding scope.
ipv4 prefix-list foo
permit 2.2.2.2/32
!
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.3.x
490
Implementing OSPF
Enabling OSPF Interaction with SRMS Server

 Loading...
Loading...











