One of the applications of BGP Accept Own is auto-configuration of extranets within MPLS VPN networks.
In an extranet configuration, routes present in one VRF is imported into another VRF on the same PE. Normally,
the extranet mechanism requires that either the import-rt or the import policy of the extranet VRFs be modified
to control import of the prefixes from another VRF. However, with Accept Own feature, the route-reflector
can assert that control without the need for any configuration change on the PE. This way, the Accept Own
feature provides a centralized mechanism for administering control of route imports between different VRFs.
BGP Accept Own is supported only for VPNv4 and VPNv6 address families in neighbor configuration mode.
Route-Reflector Handling Accept Own Community and RTs
The ACCEPT_OWN community is originated by the InterAS route-reflector (InterAS-RR) using an outbound
route-policy. To minimize the propagation of prefixes with the ACCEPT_OWN community attribute, the
attribute will be attached on the InterAS-RR using an outbound route-policy towards the originating PE. The
InterAs-RR adds the ACCEPT-OWN community and modifies the set of RTs before sending the new Accept
Own route to the attached PEs, including the originator, through intervening RRs. The route is modified via
route-policy.
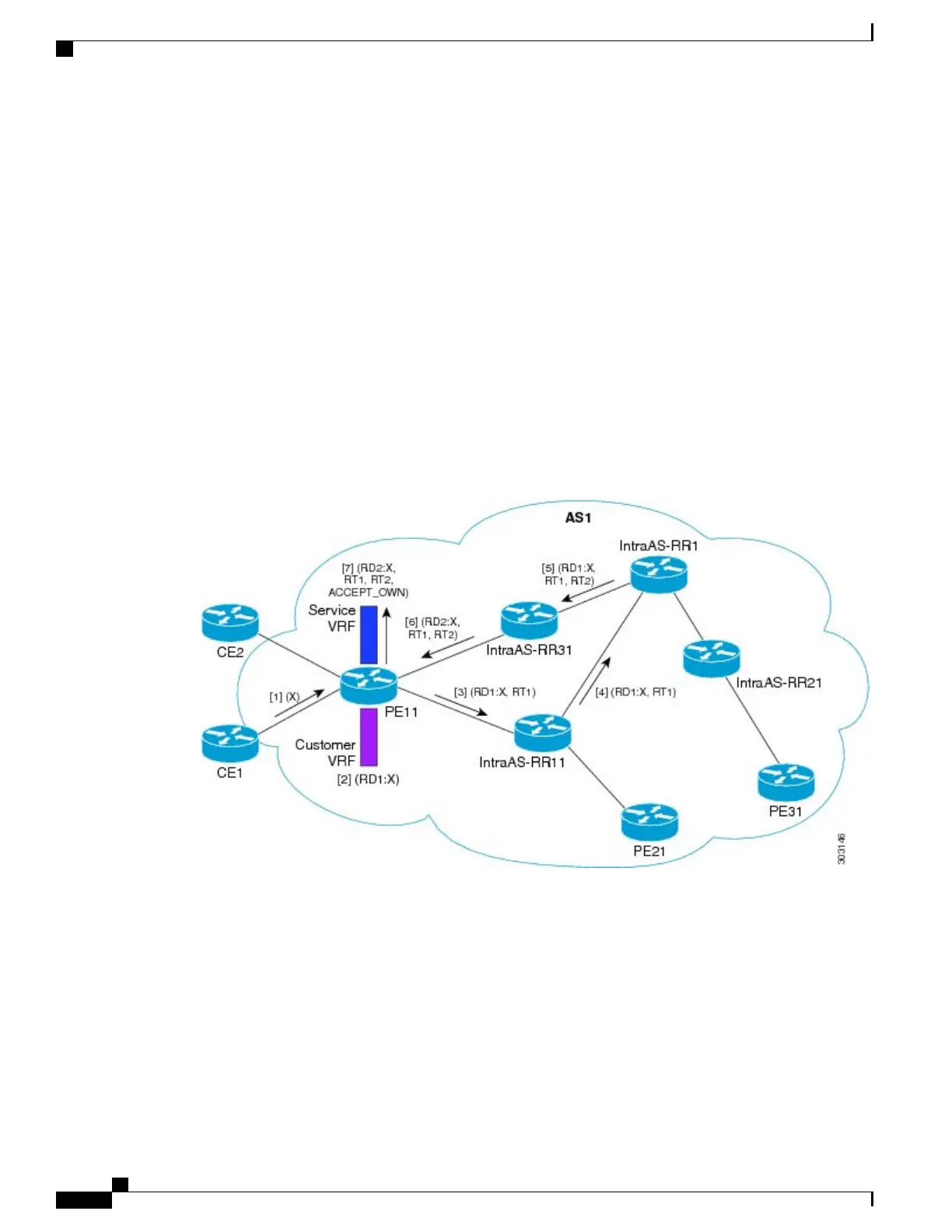
Accept Own Configuration Example
In this configuration example:
•
PE11 is configured with Customer VRF and Service VRF.
•
OSPF is used as the IGP.
•
VPNv4 unicast and VPNv6 unicast address families are enabled between the PE and RR neighbors and
IPv4 and IPv6 are enabled between PE and CE neighbors.
The Accept Own configuration works as follows:
1
CE1 originates prefix X.
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.3.x
64
Implementing BGP
BGP Accept Own

 Loading...
Loading...











