9
1.2 DESCRIPTION OF SEEDER SYSTEM
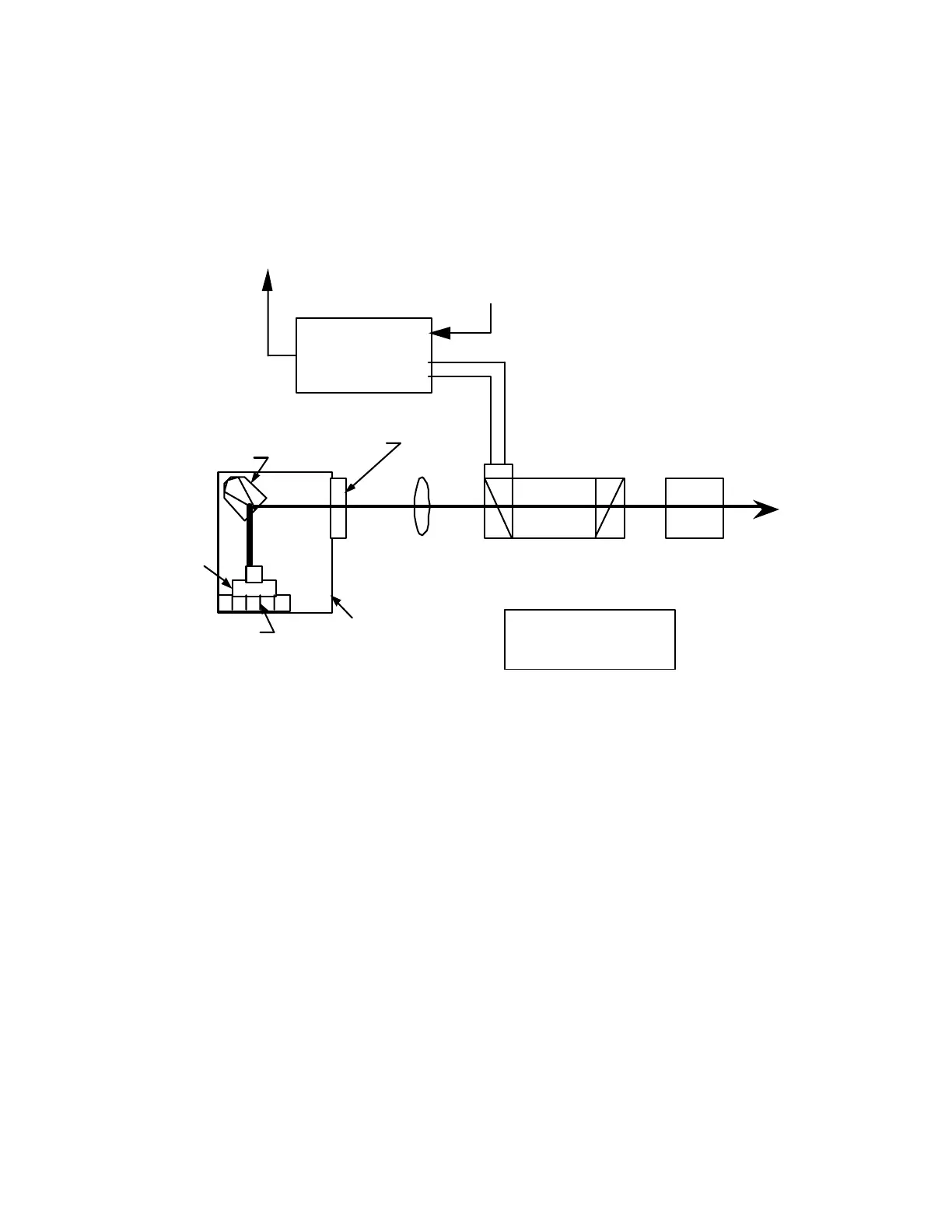
A block diagram of the Series 101 injection seeding system is given in Figure 1-9. The
elements of the system are described below.
Q-Switch Build-up
Time Reduction
Circuit
To Piezoelectric
Frequency Tuning
Element
Q-Switch
Trigger
Half-Wave Plate
Photodiode
Telescope
Assembly
Laser Diode
Thermoelectric Cooler
1 µm, 50 db Isolator
Temperature Control and
Power Supply Circuits
NPRO Crystal on
Thermoelectric Cooler
To Host Laser
Collimating
Lens
Seeder Laser
Housing
Figure 1-9: Injection Seeder Block Diagram
1.2.1 Seed Laser Source
The seed laser employed in the Series 101 is a monolithic, laser diode pumped, unidirectional
ring resonator termed the NPRO (Non-Planar Ring Oscillator) or MISER
(Monolithic, Isolated,
Single mode, End pumped, Ring)
6
. The NPRO is a monolithic structure incorporating an effective
half-wave plate polarization rotator, Faraday rotator, and polarizer. These three optical elements
combine to yield lower losses for a complete transit of the ring resonator in one direction than for
the other. This forces the ring resonator to lase in one direction only. The ring resonator is then a
traveling wave in contrast to a standing wave resonator described previously. Because it is a
traveling wave resonator, the NPRO does not suffer from the effects of spatial hole burning and
consequently will lase in only a single longitudinal mode. See Section 1.1.7 for information on
temperature tuning the NPRO output frequency.
The geometry of the NPRO is shown in Figure 1-10. Polarization takes placed at the curved,
partially transmitting face (point A). At points B, C, and D, total internal reflection occurs. A
magnetic field, H, is applied to establish unidirectional operation. Faraday rotation takes place
along segments AB and DA. The focused pump laser beam enters the crystal at point A, and the
output beam emerges at the same point.

 Loading...
Loading...