Chapter 8 Logic Instructions
In1~InN are allowed to be the variables of different data types when none of the data types of input
variables are BOOL.
When In1 to InN are the variables of different data types, take the data type which can include all
ranges of the values of In1~InN for the operation.
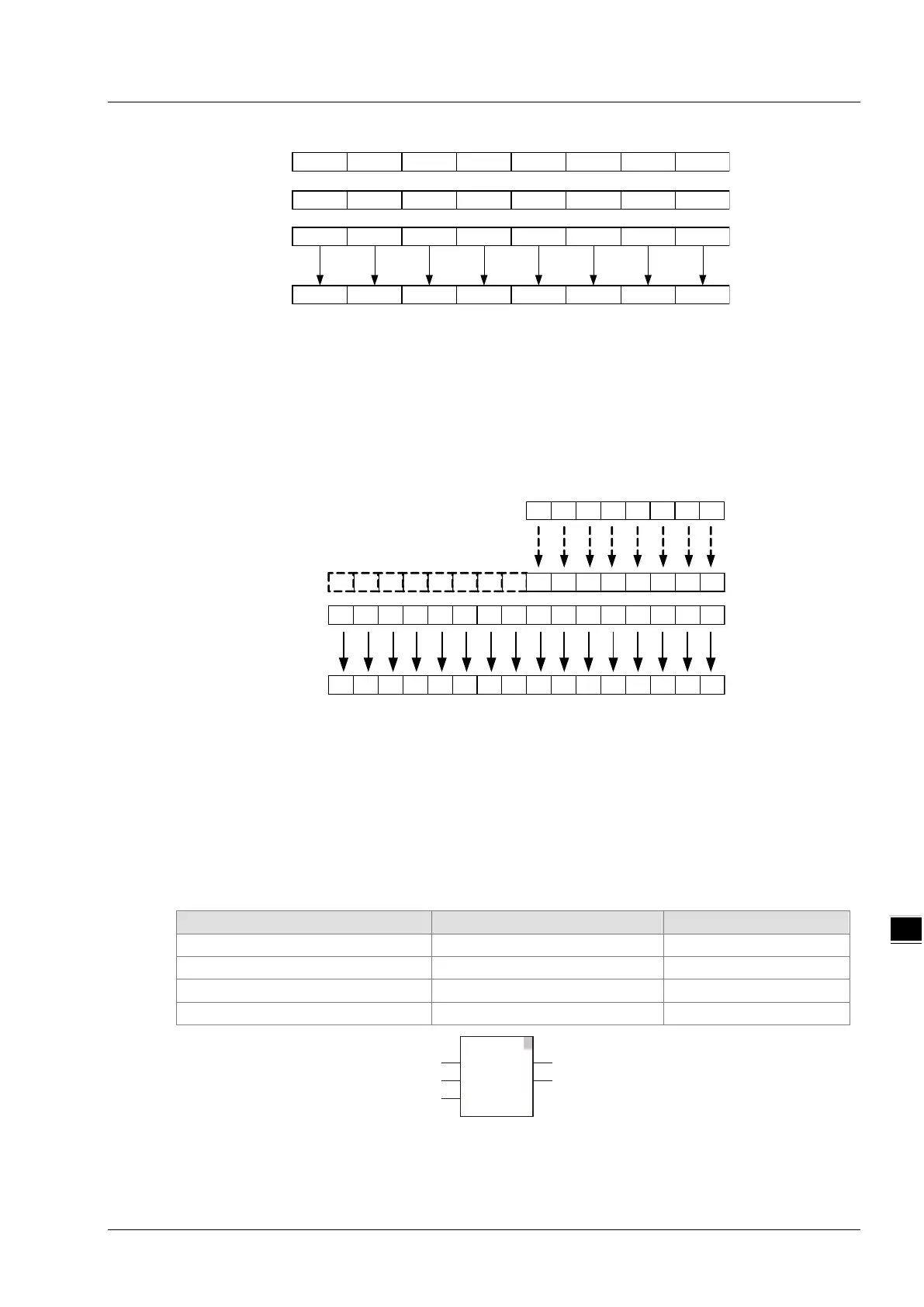
For example, if the data type of In1 is BYTE and In2 is WORD, the data type of Out is WORD. In
operation, the value of In1 is converted from BYTE to WORD as shown in the following figure. Bit8~
Bit 15 are complemented and their values are all 0. And then the logical AND of the bit values of In1
and In2 is conducted as below.
If the data type of an input variable is BOOL, the data types of all input and output variables are
required to be BOOL. Otherwise, an error will occur in the compiling of the software.
Precautions for Correct Use
The input variables are not allowed to omit. An error will occur during the compiling of the software if any
input variable is omitted. But the output variable is allowed to omit.
Programming Example
The data types of AND_In1, AND_In2 and Out1 are all BYTE. The values of AND_In1 and AND_In2
are 10 and 50 respectively and the value of Out1 is 2 when AND_EN is TRUE.
The variable table and program
The data types of AND_In1, AND_In2 and Out1 are BYTE, WORD and WORD respectively. The
values of AND_In1 and AND_In2 are 255 and 256 respectively and the value of Out1 is 0 when
AND_EN is TRUE.
00101100
01111001
00
10110
0
00101000
Bit0Bit7
In 1
In 2
In 3
Out
00101100
Bit0Bit7
In1
0000
0000
1010010100101100
In1_WORD
In2
Bit8
Bit15
0010010
0
00000000
Out
00
101100
1
AND
EN ENO
In1 Out
AND_EN
AND_In1 Out1
In2
AND_In2
8-111
 Loading...
Loading...











