Chapter 4. API Guides
When the target dumps code coverage data, the .gcda files are stored in the project’s build direc-
tory. For example, if gcov_example_main.c of the main component was compiled with the -
-coverage option, then dumping the code coverage data would generate a gcov_example_main.
gcda in build/esp-idf/main/CMakeFiles/__idf_main.dir/gcov_example_main.c.gcda
(or build/main/gcov_example_main.gcda if using the legacy Make build system). Note that the .gcno
files produced during compilation are also placed in the same directory.
The dumping of code coverage data can be done multiple times throughout an application’s life time. Each dump
will simply update the .gcda file with the newest code coverage information. Code coverage data is accumulative,
thus the newest data will contain the total execution count of each code path over the application’s entire lifetime.
ESP-IDF supports two methods of dumping code coverage data form the target to the host:
• Instant Run-Time Dumpgit
• Hard-coded Dump
Instant Run-Time Dump An Instant Run-Time Dump is triggered by calling the ESP32-S2 gcov OpenOCD
command (via a telnet session). Once called, OpenOCD will immediately preempt the ESP32-S2’s current state
and execute a builtin IDF Gcov debug stub function. The debug stub function will handle the dumping of data to the
Host. Upon completion, the ESP32-S2 will resume it’s current state.
Hard-coded Dump A Hard-coded Dump is triggered by the application itself by calling esp_gcov_dump()
from somewhere within the application. When called, the application will halt and wait for OpenOCD to connect and
retrieve the code coverage data. Once esp_gcov_dump() is called, the Host must execute the esp gcov dump
OpenOCD command (via a telnet session). The esp gcov dump command will cause OpenOCD to connect to
the ESP32-S2, retrieve the code coverage data, then disconnect from the ESP32-S2 thus allowing the application to
resume. Hard-coded Dumps can also be triggered multiple times throughout an application’s lifetime.
Hard-coded dumps are useful if code coverage data is required at certain points of an application’s lifetime by placing
esp_gcov_dump() where necessary (e.g., after application initialization, during each iteration of an application’
s main loop).
GDB can be used to set a breakpoint on esp_gcov_dump(), then call mon esp gcov dump automatically
via the use a gdbinit script (see Using GDB from Command Line).
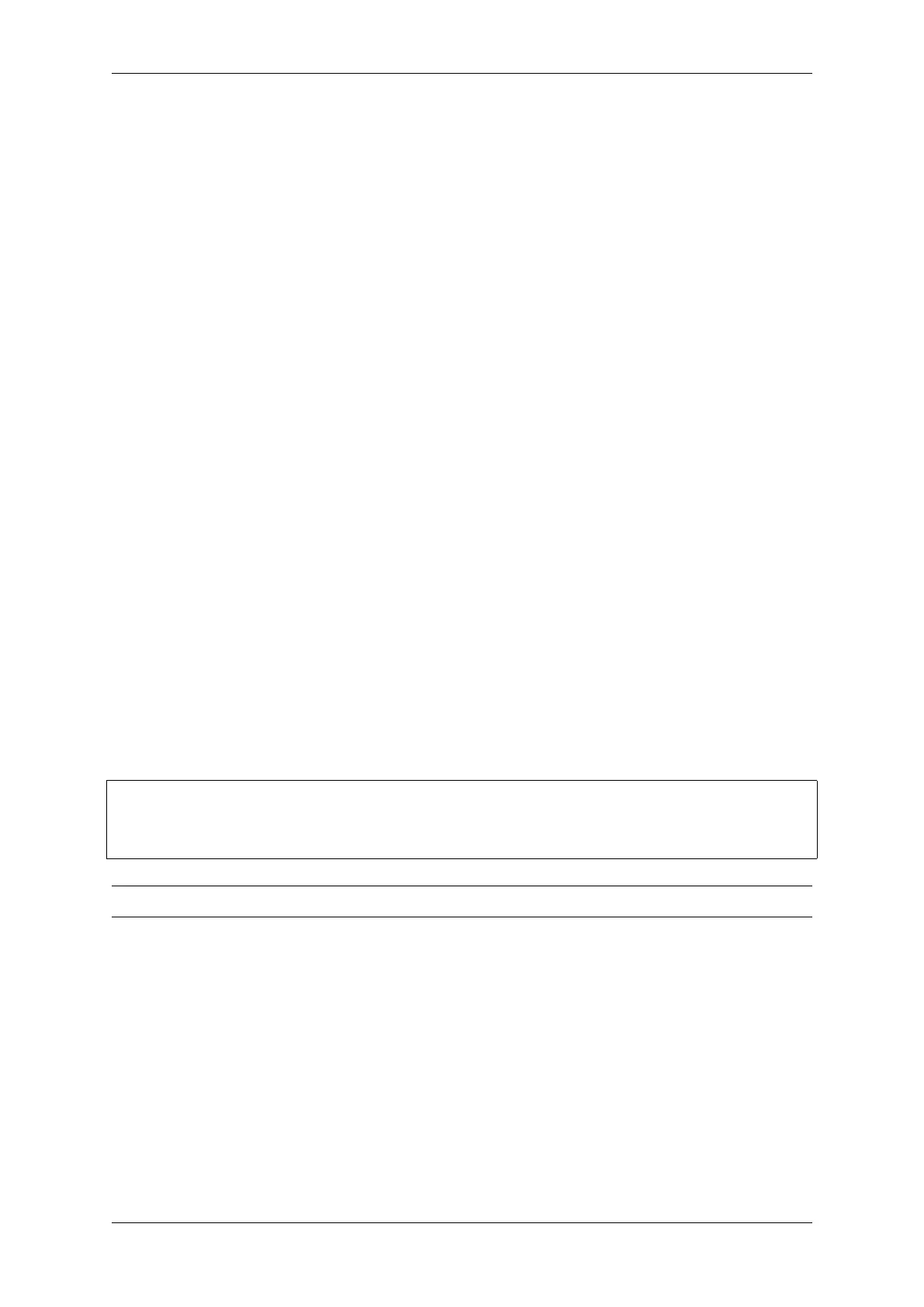
The following GDB script is will add a breakpoint at esp_gcov_dump(), then call the mon esp gcov dump
OpenOCD command.
b esp_gcov_dump
commands
mon esp gcov dump
end
Note: Note that all OpenOCD commands should be invoked in GDB as: mon <oocd_command>.
Generating Coverage Report Once the code coverage data has been dumped, the .gcno, .gcda and the source
files can be used to generate a code coverage report. A code coverage report is simply a report indicating the number
of times each line in a source file has been executed.
Both Gcov and Gcovr can be used to generate code coverage reports. Gcov is provided along with the Xtensa
toolchain, whilst Gcovr may need to be installed separately. For details on how to use Gcov or Gcovr, refer to
Gcov documentation and Gcovr documentation.
Adding Gcovr Build Target to Project To make report generation more convenient, users can define additional
build targets in their projects such report generation can be done with a single build command.
Espressif Systems 1262
Submit Document Feedback
Release v4.4
 Loading...
Loading...