13.10 Calculation Formula
199
10
13
Chapter 13 Specifications
Note) c: measured channel, M: number of samples per period, s: number of sampling points
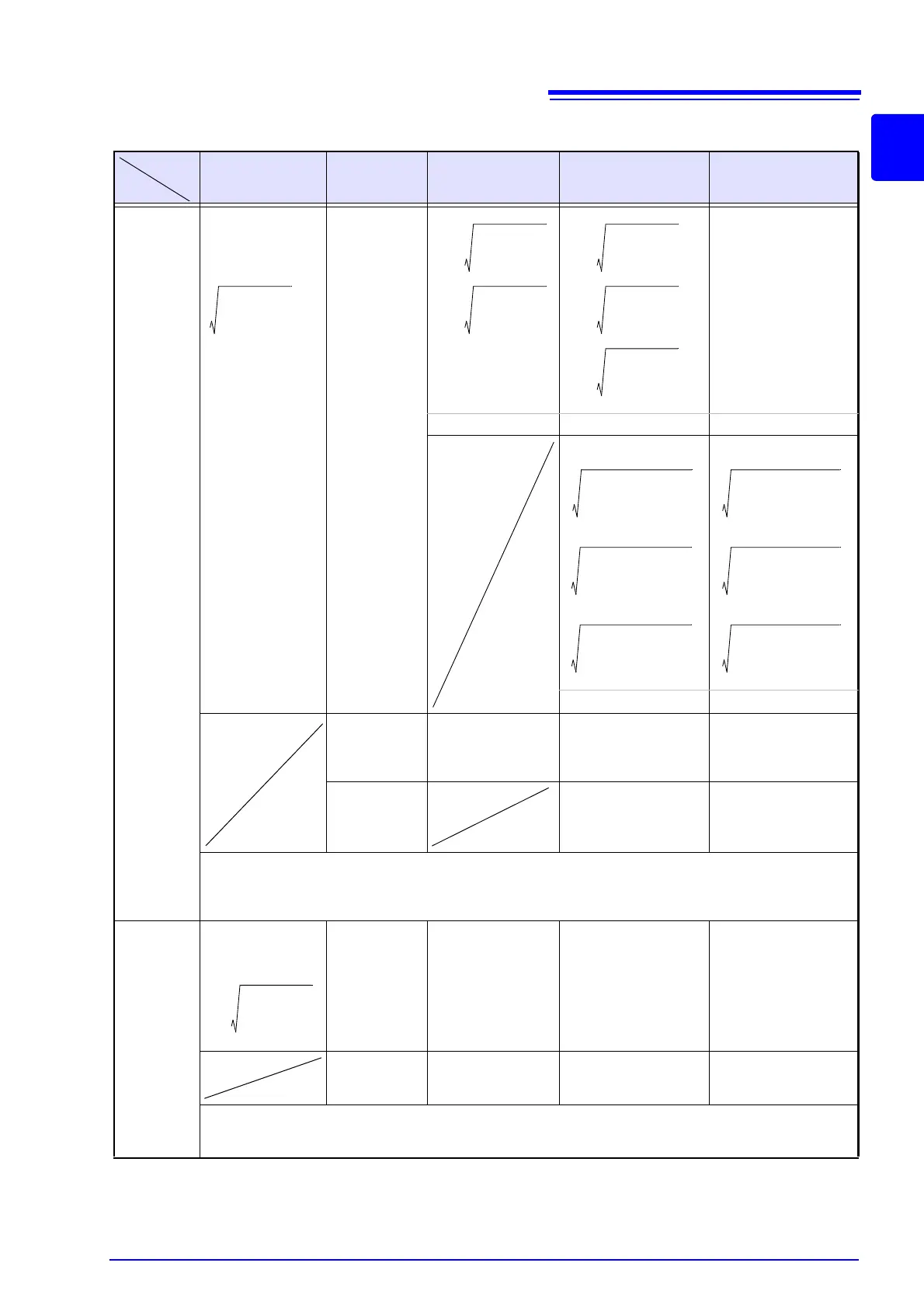
RMS Voltage (Urms), RMS Current (Irms)
Single Phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single Phase
3-wire
1P3W
3-Phase, 3-Wire,
2-Measurement
3P3W2M
3-Phase, 3-Wire,
3-Measurement
3P3W3M
3-Phase, 4-Wire
3P4W
Urms U
1
U
4
Uc=
U
1
U
2
U
4
Line-to-line voltage
U
12
=
U
32
=
U
31
is calculated from
the RMS value for
(U3s=U2s-U1s).
Line-to-line voltage
U
12
=
U
23
=
U
31
=
Phase voltage
U
1
U
2
U
3
U
4
U
4
U
4
Phase voltage
U
1
=
U
2
=
U
3
=
Line-to-line voltage
U
12
=
U
23
=
U
31
=
U
4
U
4
Uave=
Line-to-line voltage
Uave=
Line-to-line voltage
Uave=
Phase voltage
Uave=
Phase voltage
Uave=
Line-to-line voltage
Uave=
• Calculated with 10 waveforms (50 Hz measurement) or 12 waveforms (60 Hz measurement). For 400 Hz measurement,
the calculation is performed with 80 waveforms.
• For 3-phase 3-wire connections, the phase voltage is calculated so that the neutral point is at the center. The CH4 RMS
voltage can be calculated regardless of the connection type.
Irms I
1
I
4
Ic=
I
1
I
2
I
4
I
1
I
2
I
3
is calculated from
the RMS value for
(I3s=-I1s-I2s).
I
4
I
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
Iave= Iave= Iave= Iave=
• Calculated with 10 waveforms (50 Hz measurement) or 12 waveforms (60 Hz measurement). For 400 Hz measurement,
the calculation is performed with 80 waveforms.
• The CH4 RMS current can be calculated regardless of the connection type.
1
M
-- -
U1sU3s–
3
-------------------------
2
s 0=
M 1–
1
M
-- -
U2sU1s–
3
-------------------------
2
s 0=
M 1–
1
M
-- -
U3sU2s–
3
-------------------------
2
s 0=
M 1–
1
M
-- -
U1sU2s–
2
s 0=
M 1–
1
M
-- -
U2sU3s–
2
s 0=
M 1–
1
M
-- -
U3sU1s–
2
s 0=
M 1–

 Loading...
Loading...