67
Packet formats
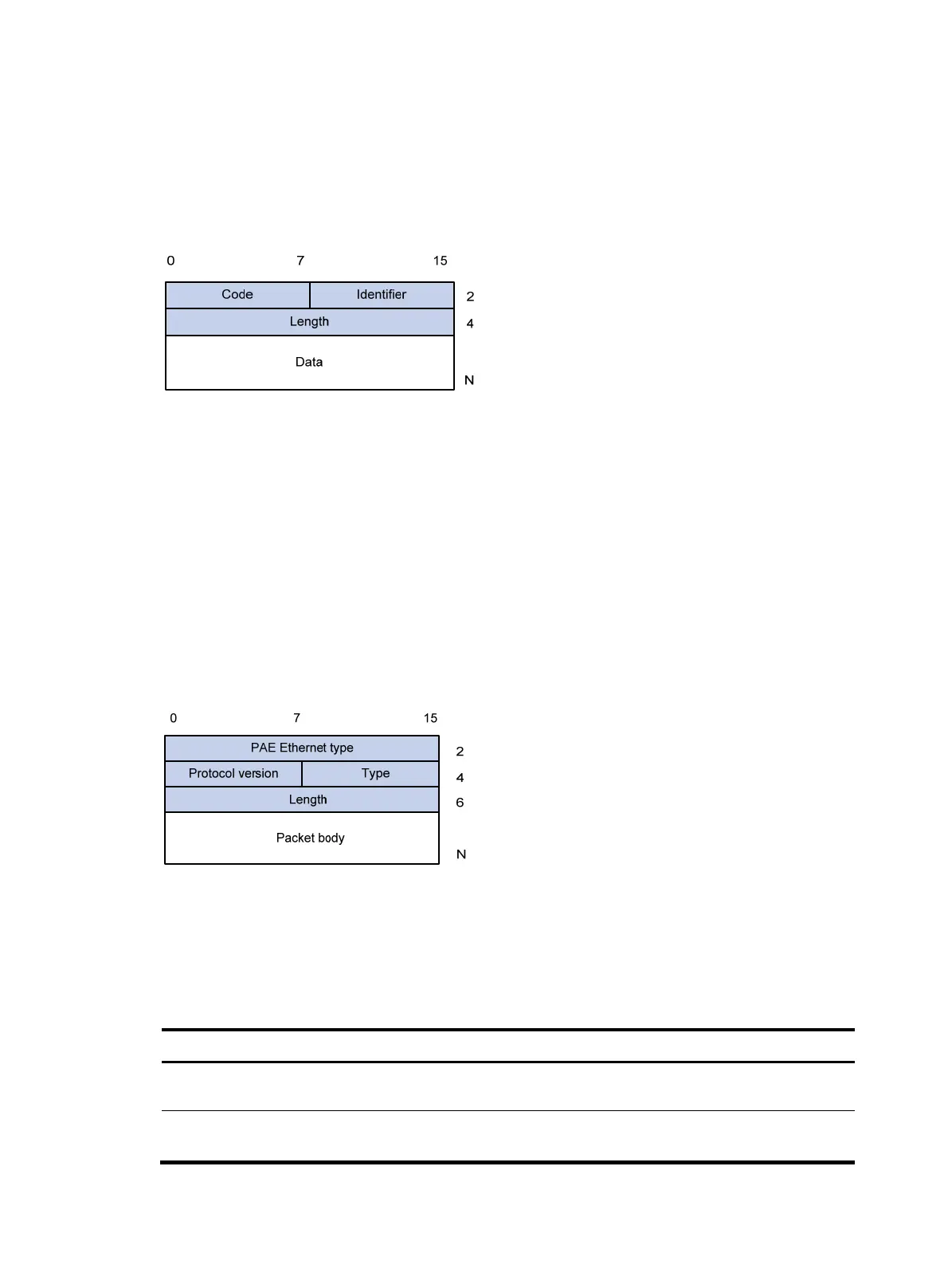
EAP packet format
Figure 21 shows the EAP packet format.
Figure 21 EAP packet format
• Code—Type of the EAP packet. Options include Request (1), Response (2), Success (3), or Failure
(4).
• Identifier—Used for matching Responses with Requests.
• Length—Length (in bytes) of the EAP packet. The EAP packet length is the sum of the Code, Identifier,
Length, and Data fields.
• Data—Content of the EAP packet. This field appears only in a Request or Response EAP packet. The
field comprises the request type (or the response type) and the type data. Type 1 (Identify) and type
4 (MD5-challenge) are two examples for the type field.
EAPOL packet format
Figure 22 shows the EAPOL packet format.
Figure 22 EAPOL packet format
• PAE Ethernet type—Protocol type. It takes the value 0x888E for EAPOL.
• Protocol version—The EAPOL protocol version used by the EAPOL packet sender.
• Type—Type of the EAPOL packet. Table 5 lists the t
ypes of EAPOL packets supported by HP
implementation of 802.1X.
Table 5 EAPOL packet types
Value Type Description
0x00 EAP-Packet
The client and the network access device uses
EAP-Packets to transport authentication information.
0x01 EAPOL-Start
The client sends an EAPOL-Start message to initiate
802.1X authentication to the network access device.
 Loading...
Loading...















