150 ULTRA ATA DEVICES
NOTE The industry standard, 1.44-MB diskette drive has its own separate channel and is not included as
a part of the maximum four drives.
Any drive attached to a controller must have a drive designation. If only a single drive is connected to a controller
and its jumper is in the cable-select position, it is designated as the Master Drive (Drive/Device 0) by its attachment
to the Drive/Device 0 cable position. If two cable-selected drives are connected to a single controller, one will be
designated by its attachment to the cable as the Master (Drive/Device 0) and the other as Slave (Drive/Device 1).
For optimal performance of a workstation system, all drives must be attached to the ATA controllers in a specified
sequence. This sequence is determined by the device class of the drives and by specific attach sequence rules.
Device Classes
To determine the best drive attach sequence, ATA/ATAPI drives are segregated into four different classes based on
the bandwidth demands they place on an ATA controller. The most demanding devices are in Class 1 and the least
demanding are in Class 4.
General Attach Guidelines
The lower the device class number, the faster the device and the more bandwidth required.
Drives installed in the Device 0 positions on both the primary and secondary controllers receive the greatest
possible bandwidth.
The bootable ATA hard drive should always be installed on the primary controller in the Device 0 position.
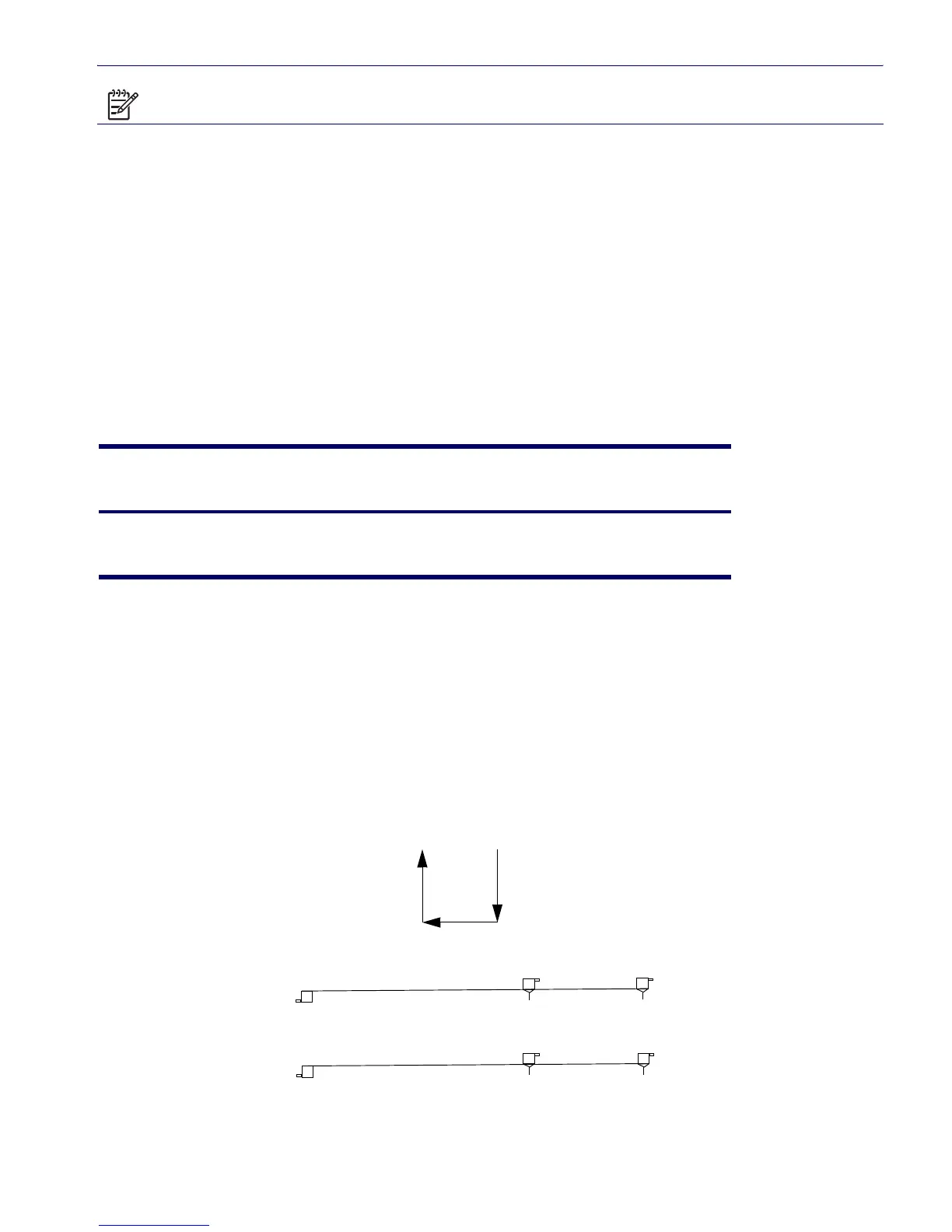
Attach Sequence Rules by Class Priority
Drives should be attached in the sequence shown for optimum performance starting at position 1.
Figure C–1 Installing Drive Order
Table C-1 Device Classes
Class 1
Hard
Drives
Class 2 High Speed
Optical Drives
Class 3 Optical Storage
Drives
Class 4
Magnetic Storage Drives
ATA-100
ATA-66
ATA-33
DVD
DVD-CD R/W
R/W CD-ROM
CD-ROM
LS-120
Tape
Zip
1
2
4
3
Primary
Controller*
41
Secondary
Controller
32
Device 1 Device 0

 Loading...
Loading...









