158 IBM System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Planning and Implementation Guide
PCIe performance
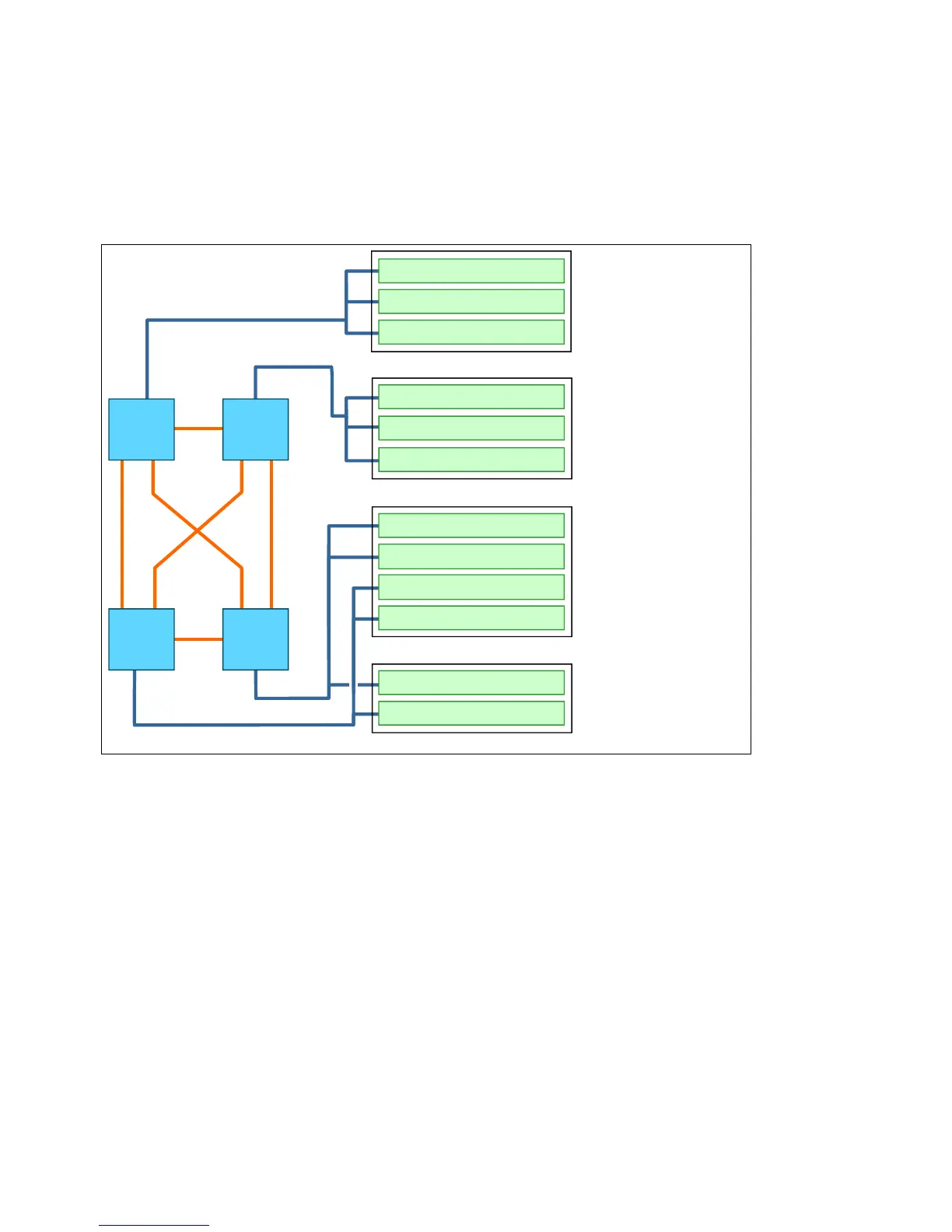
The x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 offer a large quantity of PCIe slots. To ensure the best possible
performance, it is important to understand the design of the servers and how the PCIe slots
connect to each processor.
Figure 5-34 shows processor-to-slot PCIe connectivity for the x3850 X6.
Figure 5-34 PCIe slot connectivity in the x3850 X6
For best performance, consider these suggestions:
Ensure that the slot used for an adapter has the necessary bandwidth. For example, slot 8
(in the Primary I/O Book) is an x8 wired slot, but can physically accept an x16 adapter.
Performance will be negatively impacted if an x16 adapter is installed in that slot.
Balance the PCIe load across all processors. This ensures a distributed workload and
reduces the chance of performance bottlenecks.
Use processor affinity in the operating system to tie application threads that use PCIe
resources the most to the processor that connects to that PCIe device.
QPI links
Intel
Xeon
CPU 1
Slot 7: PCIe 3.0 x16 (x16)
Slot 9: PCIe 3.0 x16 (x16)
Slot 10: Mezz LOM (x8)
Slot 12: PCIe 3.0 x16 (x8)
Intel
Xeon
CPU 2
Slot 8: PCIe 3.0 x16 (x8)
Slot 11: PCIe 3.0 x16 (x8)
Intel
Xeon
CPU 4
Intel
Xeon
CPU 3
Slot 1
Slot 2
Slot 3
Slot 4
Slot 5
Slot 6
Storage Book
Primary I/O Book
Optional I/O Book in Bay 2
Optional I/O Book in Bay 1
PCIe 3.0 lanes
Optional I/O Books can be either:
Half-length I/O Book
• PCIe 3.0 x16 slot (x16 wired)
• PCIe 3.0 x8 slot (x8 wired)
• PCIe 3.0 x8 slot (x8 wired)
Full-length I/O Book
• PCIe 3.0 x16 (x16 wired)
• PCIe 3.0 x16 (x16 wired)
• PCIe 2.0 x8 slot (x4 wired)

 Loading...
Loading...











