6 IBM System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Planning and Implementation Guide
– Survive a processor failure:
The server is designed to recover from a failed processor and restart automatically.
Even if the primary processor (the one used for booting the operating system) fails, the
X6 system is designed so it can boot from another processor using redundant links to
key resources.
– Survive memory failures:
The combination of IBM Chipkill and Redundant Bit Steering (RBS, also known as
Double Device Data Correction or DDDC) allows the server to tolerate two sequential
DRAM memory chip failures without affecting overall system performance.
– Survive an adapter failure and replace it while the server is running:
The new servers have up to six adapter slots that support hot-swapping. This means
the I/O Books can be removed and any failed adapters can be replaced without any
server downtime.
– Swap components easily with the server’s lidless design:
There is no need to pull this server in or out of the rack to service it because all
components can be accessed either from the front or from the rear. This design allows
for faster maintenance by simplifying service procedures. This concept is similar to
what we have with BladeCenter and Flex System.
These built-in technologies drive the outstanding system availability and uninterrupted
application performance needed to host mission-critical applications.
1.3 Positioning
The IBM System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 servers are the next generation of X-Architecture
following on from the highly successful eX5 server. IBM X6 servers include a number of new
features when compared to the previous generation of eX5 including support for more
memory and I/O in a modular design.
When compared to the 4-socket x3750 M4 server, the X6 servers fill the demand for
enterprise workloads that require 4-socket and 8-socket performance, high availability, and
advanced RAS features.
Table 1-1 shows a high-level comparison between the 4 socket x3750 M4, the eX5-based
x3850 and x3950 X5, and the X6-based x3850 and x3950 X6.
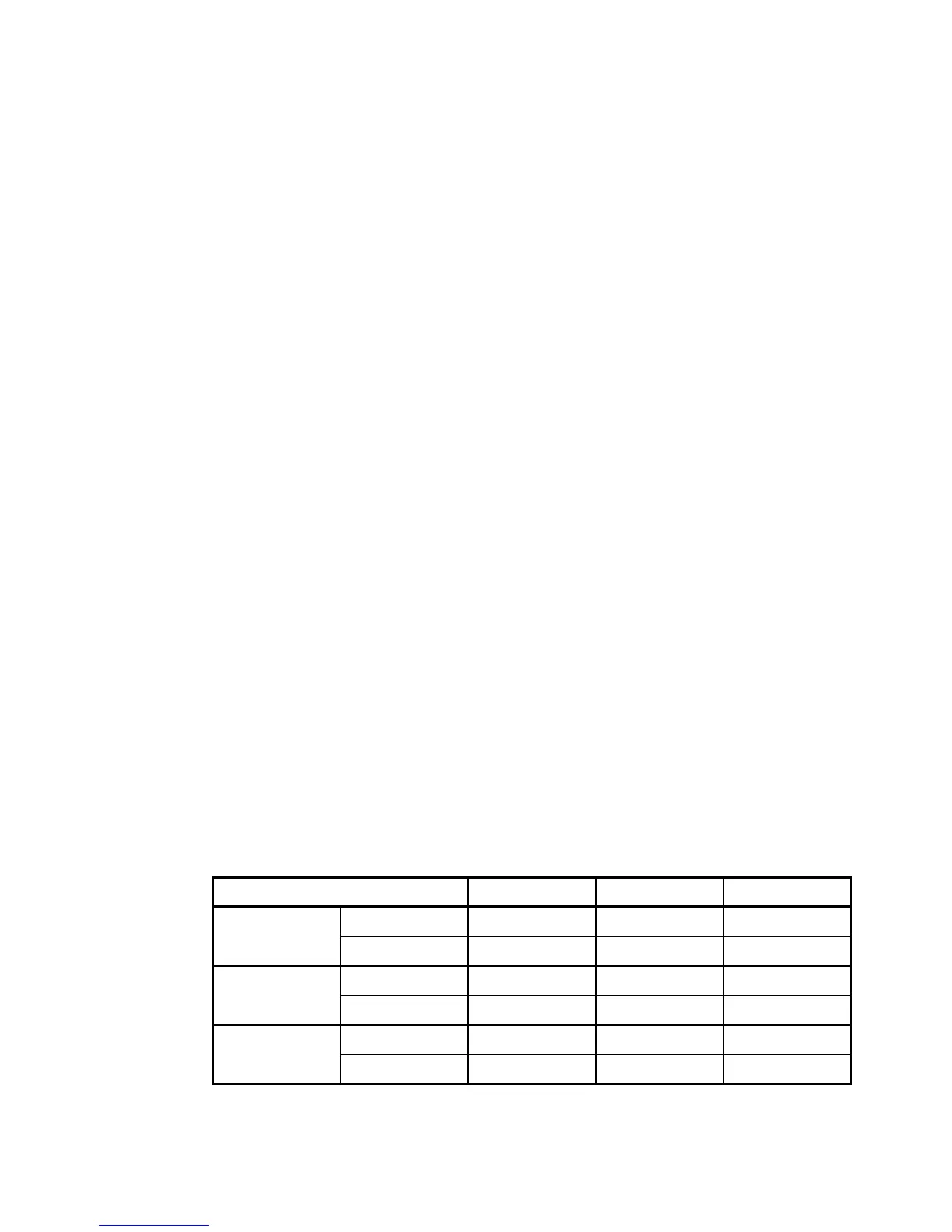
Table 1-1 Maximum configurations for the X6 systems
Maximum configurations x3750 M4 x3850/x3950 X5 x3850/x3950 X6
Form factor 4 socket 2U 4U 4U
8 socket Not available 8U 8U
Processors 1-node 4 4 4
2-node Not available 8 8
Cores 1-node 32 40 60
2-node Not available 80 120

 Loading...
Loading...











