Chapter 2. Technology 31
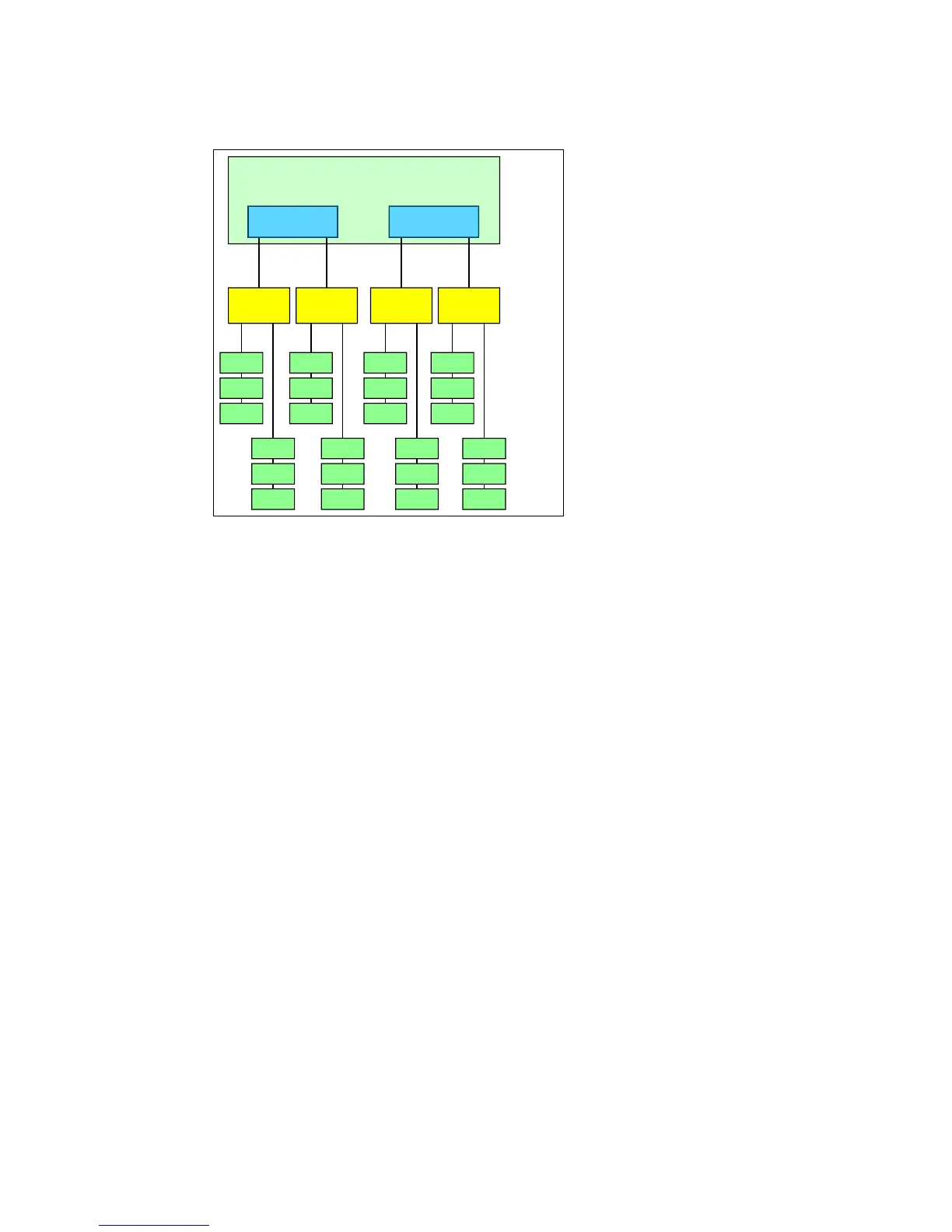
Figure 2-23 shows the processor’s memory architecture.
Figure 2-23 Intel Xeon processor E7-4800/8800 v2 memory architecture
2.4.1 Operational modes
Two memory modes are supported by the Intel Xeon processor E7-4800 v2/8800 v2 product
families:
Performance mode:
In this operation mode, each DDR3 channel works independently and it is addressed
individually via burst lengths of 8 bytes (64 bits). The Intel SMI2 channel operates at twice
the DDR3 speed. All channels can be populated in any order and modules have no
matching requirements. All memory modules may run at different DIMM timings, but all
DIMMs must run at the same speed.
Chipkill (Single Device Data Correction or SDDC) is supported in Performance mode.
Redundant Bit Steering (RBS) is not supported.
Although in this mode DIMMs can be populated in any order, for best performance
memory modules should be placed based on round robin algorithm between SMI2
channels and alternating between DDR channels. For more information about DIMMs
population order, see 3.8.2, “Memory population order” on page 71.
RAS (Lockstep) mode:
RAS stands for reliability, availability, and serviceability. In this operation mode (also
known as Lockstep mode), the memory controller operates two DDR3 channels behind
one memory buffer as single channel.
In RAS mode, the SMI2 channel operates at the DDR3 transfer rate. DIMMs must be
installed in pairs.
Intel Xeon processor
DIMM
Memory
controller
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
controller
SMI2 links
DDR3 links
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer

 Loading...
Loading...











