Chapter 1. Introduction 7
1.4 Storage versus in-memory data
Main memory (RAM) is the fastest storage type that can hold a significant amount of data.
Data in main memory can be accessed more than a hundred thousand times faster than data
on a spinning hard disk, and even flash technology storage is about a thousand times slower
than main memory.
Main memory is connected directly to the processors through a high-speed bus, whereas
hard disks are connected through a chain of buses (QPI, PCIe, SAN) and controllers (I/O hub,
RAID controller or SAN adapter, and storage controller).
Compared to keeping data on disk, keeping the data in main memory can dramatically
improve database performance just by the advantage in access time. However, there is one
potential drawback. In a database transaction that has been committed, the transaction
cannot stay committed.
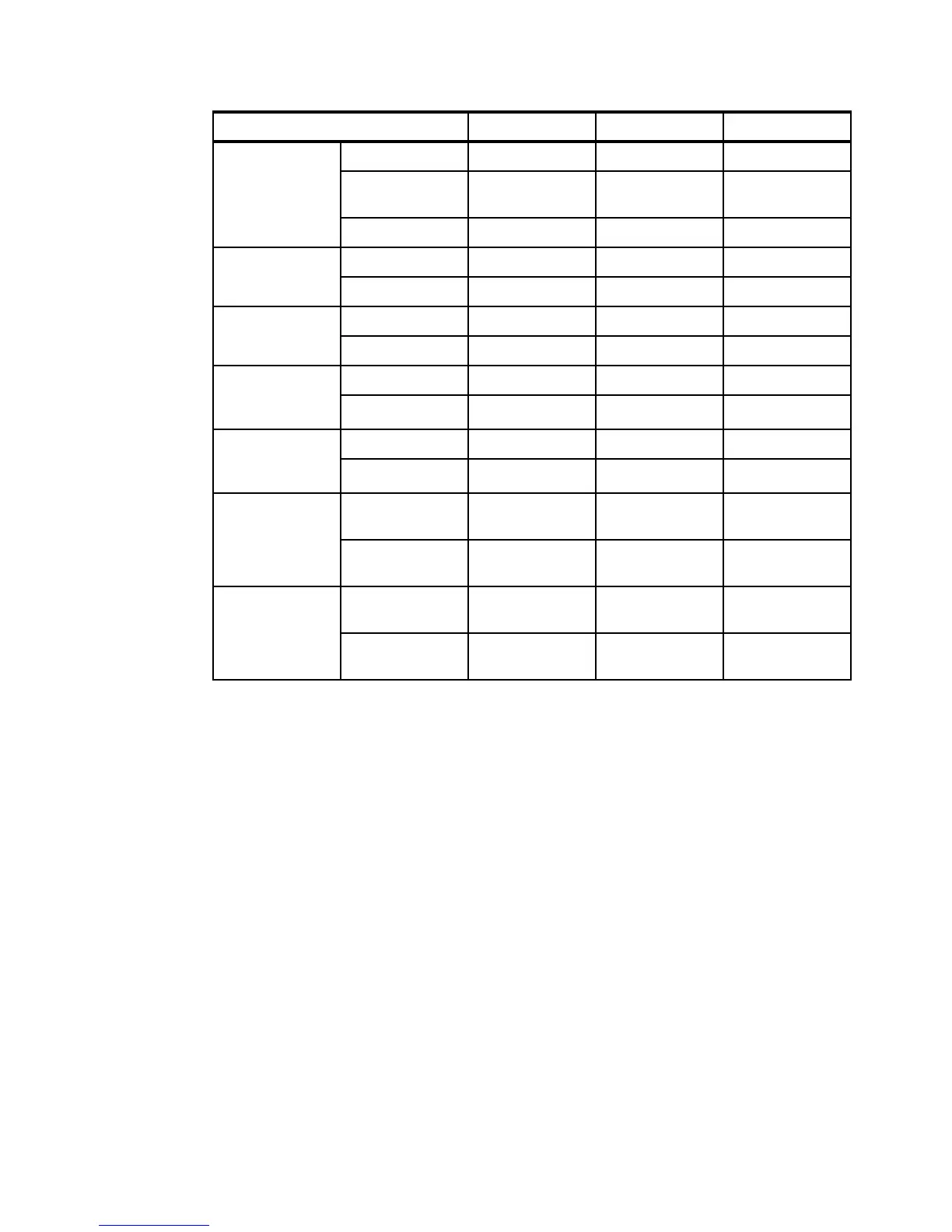
Memory 1-node 48 DIMM slots
a
64 DIMM slots
a
96 DIMM slots
a
1-node with
MAX5
Not available 96 DIMM slots
a
Not available
2-node Not available 128 DIMM slots
a
192 DIMM slots
a
2.5-inch drive
bays
1-node 16 8 8
2-node Not available 16 16
1.8-inch SSDs
drive bays
1-node 32 16 16
2-node Not available 32 32
Standard 1Gb
Ethernet
interfaces
1-node 2 2
b
4 (Optional)
2-node Not available 4 8 (Optional)
Standard 10Gb
Ethernet
interface
1-node 2 (Optional) 2 2 (Optional)
2-node Not available 4 4 (Optional)
USB ports 1-node 4 USB 2.0 8 USB 2.0 6 USB 2.0, 2 USB
3.0
2-node Not available 16 USB 2.0 12 USB 2.0, 4
USB 3.0
Power supplies 1-node 2 x 1400W 2 x 1975W 4 x 900W or
1400W
c
2-node Not available 4 x 1975W 8 x 900W or
1400W
c
a. Requires all processors to be installed in order to use all memory slots.
b. Model dependent.
c. Mixing of power supplies in pairs is supported.
Maximum configurations x3750 M4 x3850/x3950 X5 x3850/x3950 X6

 Loading...
Loading...











