Chapter 2. Technology 35
When this threshold is reached, the content is copied to its spare rank. The failed rank is then
taken offline, and the spare counterpart is activated for use.
In rank sparing mode, one rank per memory channel is configured as a spare. The spare rank
must have identical or larger memory capacity than all the other ranks (sparing source ranks)
on the same channel.
For example, If dual-rank DIMMs are installed, all of the same capacity, then there are 6 ranks
total for each memory channel (three DIMMs per channel). This means that 1 of the 6 ranks
are reserved and 5 of the 6 are usable for operating system use.
Memory sparing is independent of the operating system. There is a slight memory
performance trade-off when memory sparing is enabled.
The rank sparing feature can be used in addition to performance or RAS modes:
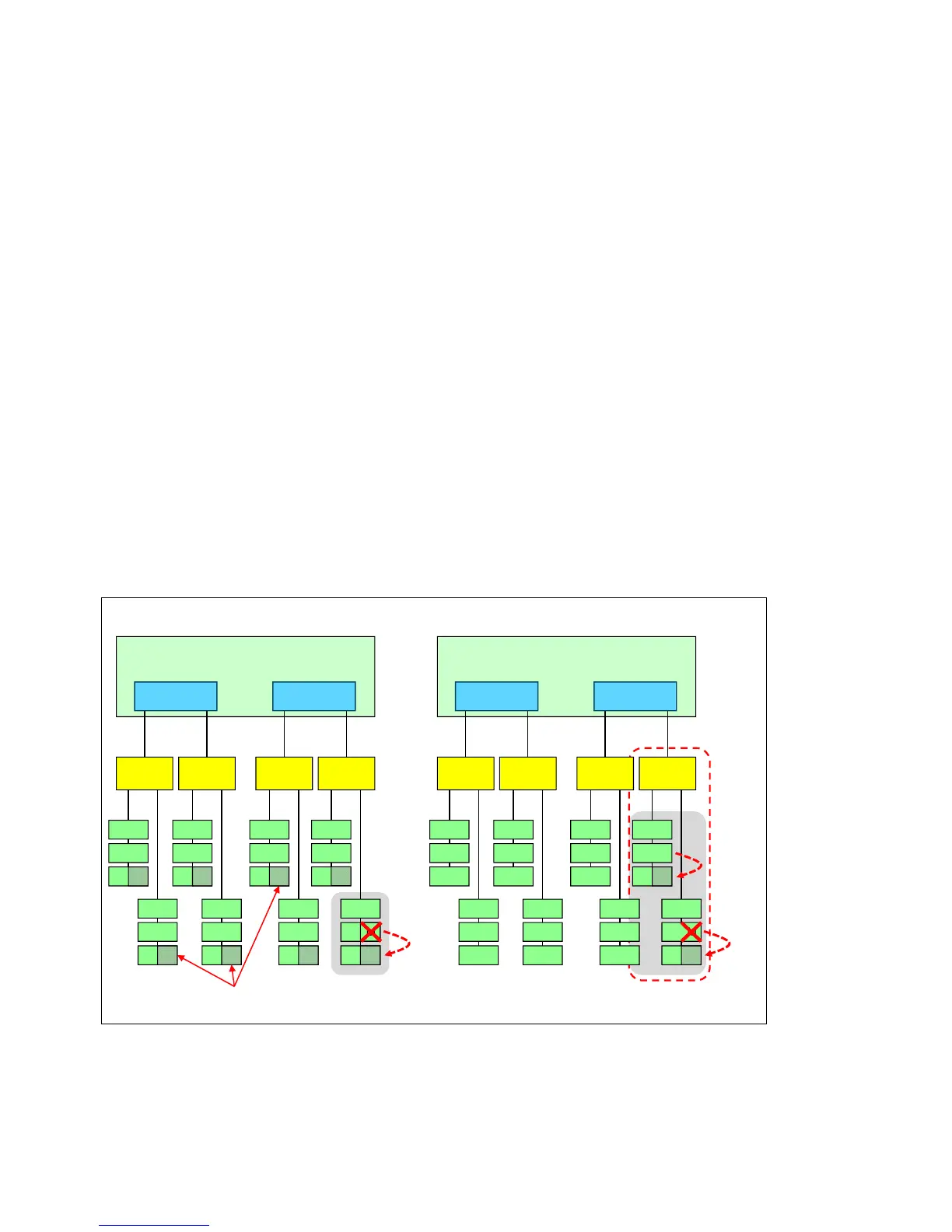
When Performance mode is used, rank sparing duplicates data between memory modules
of same channel of one memory buffer. In the event of an imminent failure (red X in
Figure 2-26), that rank is taken offline and the data is copied to the spare rank.
When RAS (Lockstep) mode is used, rank sparing duplicates data between memory
channels of one memory buffer. In the event of an imminent failure (red X in Figure 2-26),
that rank is taken offline and the data is copied to the spare rank. In addition, the partner
rank on the other channel connected to the same memory buffer is also copied over.
Figure 2-26 shows the rank sparing usage in conjunction with Performance mode (left) and
RAS mode (right).
Figure 2-26 Rank sparing: Performance mode (left) and RAS mode (right)
Intel Xeon processor
DIMM
Memory
controller
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
controller
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Intel Xeon processor
DIMM
Memory
controller
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
controller
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
DIMM
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Memory
buffer
Lockstep
channel
Memory performance mode
+ rank sparing
Memory RAS mode
+ rank sparing
Spare ranks (1 for each of the 8 channels)
(assuming dual-rank DIMMs)
Forced
failover
Failover
Failover

 Loading...
Loading...











