Measurement Concepts 2-19
Measurement considerations
There are a variety of factors to consider when making low level measurements. These con-
siderations are listed and summarized in Table 2-6. For comprehensive information on all mea-
surement considerations, refer to the Low Level Measurements handbook, which is available
from Keithley Instruments.
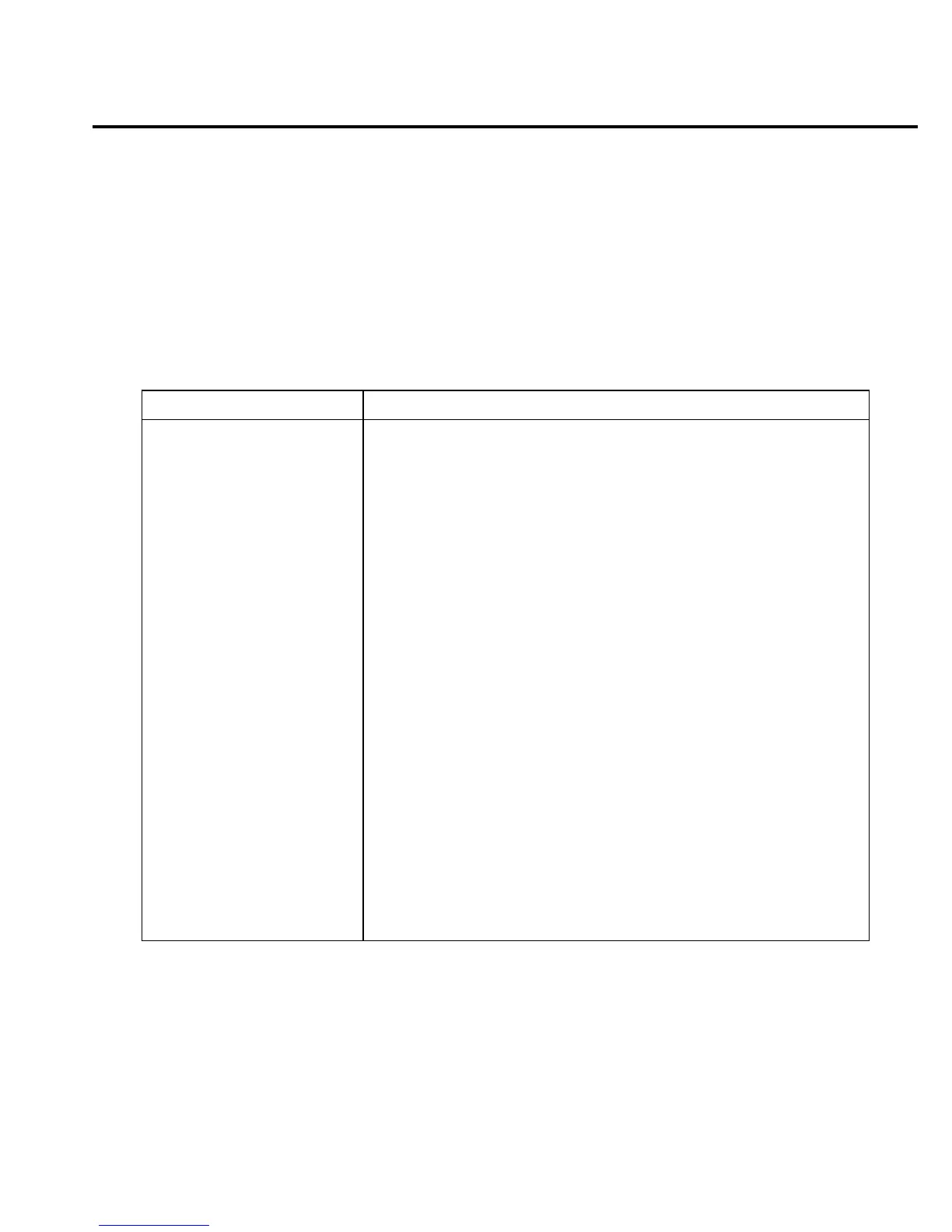
Table 2-6
Summary of measurement considerations
Considerations Description
For V and
Ω
measurements: See Section 3 for details
Loading effects Circuit loading caused by a high impedance voltage source.
Cable leakage resistance For unguarded measurements, leakage resistance in the triax cable
(between HI and LO) shunts the voltage to be measured.
Input capacitance (settling
time)
At very high resistance levels, effects of cable capacitance can slow
down measurement response time.
Guarding input cable Eliminates the effects of leakage resistance for high impedance
measurements and input capacitance when using a long input cable.
For I measurements: See Section 4 for details
Input bias current Offset current of Model 6514 could affect low current
measurements.
Voltage burden Offset voltage of Model 6514 could cause errors if it is high in
relation to the voltage of the measured circuit.
Noise Noise generated by source resistance and source capacitance.
For Q measurements: See Section 5 for details
Input bias current Offset current of Model 6514 is integrated along with the input
signal, affecting the final reading.
External voltage source Input current to Model 6514 should be limited to <1mA.
Zero check hop Sudden change in the charge reading when zero check is turned off.
Auto-discharge hop Sudden change in the charge reading when auto-discharge resets the
charge reading to zero.

 Loading...
Loading...