40
Oneadvantageofthisinternaldatastructureisthatitdoesnotrequire
toomuchspaceonthememorycard.Ontheotherhand,adisadvan‐
tageisthatthetimelinemaynotalignverywellwhenyouexportthe
datatoanexternalDAWandperformcomplicatedediting.
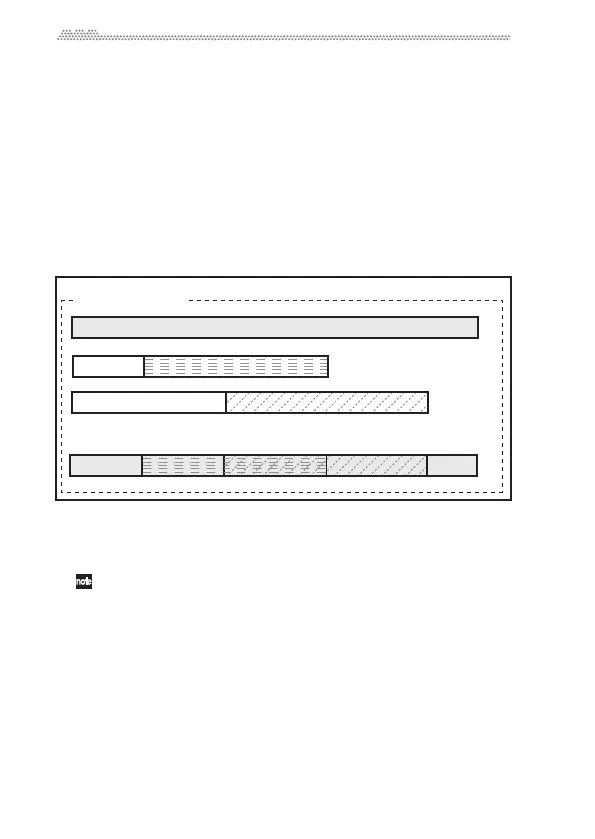
FinalizingthedataontheSO
UNDon
SOUNDwilladdasilentpartat
thetopofeachindividualmaterialfile.Thissilencefillsagapfromthe
topofthefiletotherecordingstartpointsothatthetimelineofall
materialswillalignaccuratelywitheachother.Inthisway,fo
rexam‐
ple,
amixfilewillbecomeacompletestereofilefromwhichyoucan
burnaCD.
Youcanalsospecifywhetheryouwishtofinalizeonlythematerial
files(*1)oronly2‐mixfiles(*2)asafinalizingoption.
Ifyouoverdubbedapartatamodifiedplaybackspe
ed
,thematerial
fileforthispartwillautomaticallybeconvertedbythefinalizeopera‐
tiontoanewfilethatusestheoriginalspeed.
TheSOUNDonSOUNDcreatesaWAVfileinBWF(Broadcast
WaveFile)formatthatcontainstimeinformation.IfyouuseaDAW
thatsupportstheBWFformat,thetimelineofthesefileswillbe
alignedwitheachotherwithoutperformingthefinalizingprocess.
Aboutthespacerequiredforfinalizingonamemorycard
TheSOUNDonSOUNDstoresalloriginalrecordingmaterialfilesand
2‐mixfilesevenafterthefinalizingprocessiscomplete(seepage47).If
youplantoperformthefinalize operation,youshoulduseamem ory
cardwithhighcapacity.Forexample,ifyoufinalizeafileofapproxi‐
mately120
MB(seepa
ge17),afileofuptoapproximately120MBwill
becreated,thususingatotalofapproximately240MBofthememory
cardspace
.
*1
*1
*1
*2
Mix file
Finalized folder
Internal data structure after finalizing
Material file 1
Silence data
Silence data
Material file 2
Material file 3
Material 1+2
Material 1+2+3
Material 1+3
Material 1
Material 1

 Loading...
Loading...











