HELIOS LED Processing Platform - USER GUIDE 9
Dual Input Cards
If the total number of pixels will not t any single input raster, the system can be fed video from multiple input cards. A
HELIOS Processor with the necessary hardware (dual DisplayPort or dual HDMI cards) can receive dual video signals of the
same type of signal. When HELIOS is outtted with two of the same card type (DisplayPort or HDMI) it will stitch the two
rasters together into one continuous output to tiles. Please see the Input Setup section in Chapter 5 for more information
on conguring this mode.
Figure 9: Dual DisplayPort Input Card Conguration
Data Distribution
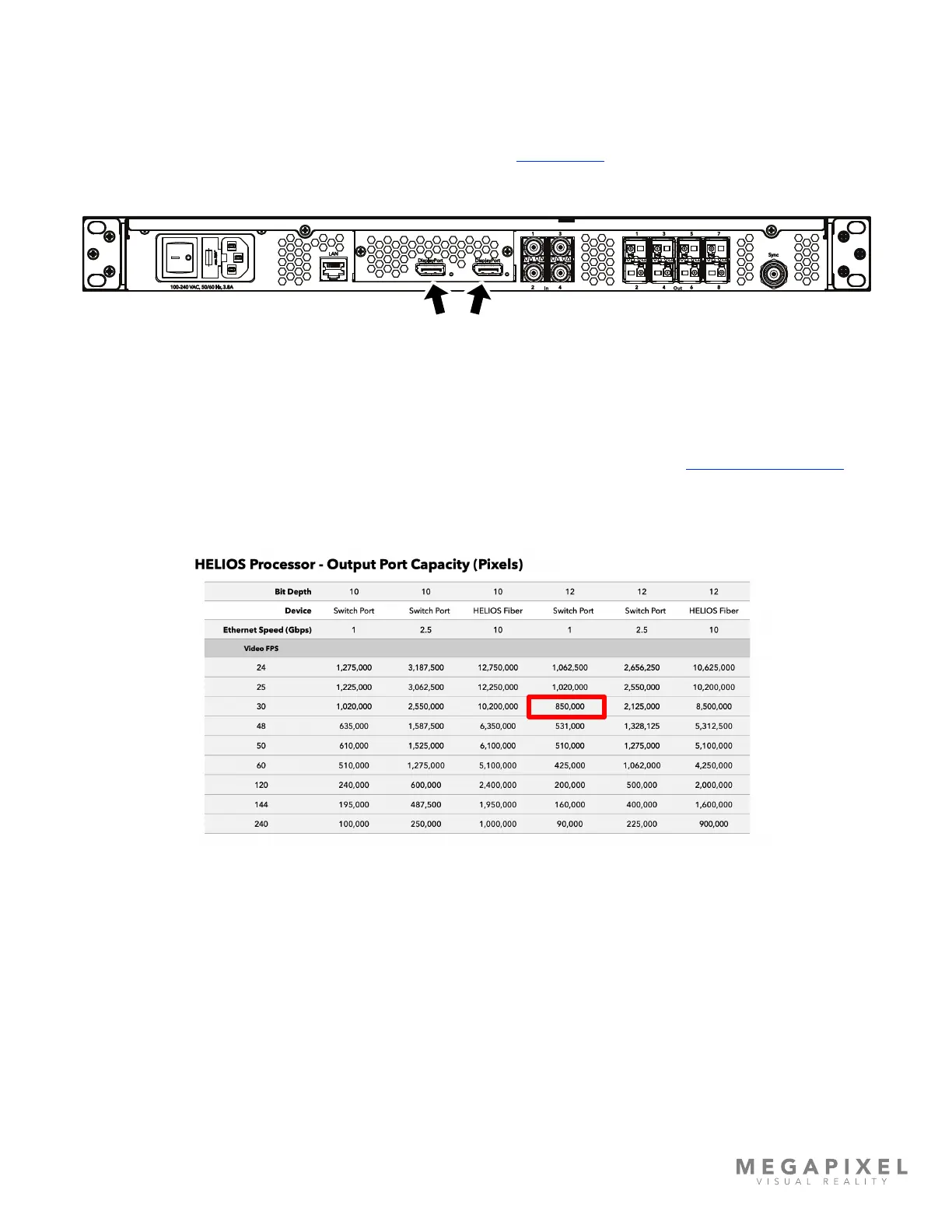
At this point it can be helpful to draw out the data topology (gure 10). Decide if the display will be cabled vertically or
horizontally. Calculate the number of network switches it will take to distribute data to the display. In the system example
below we use a tile with the pixel dimensions 480 x 270 (tiles are 129,600 pixels). From the Output Port Capacity table in
Appendix G we see that a 1Gbps switch port running a color bit depth of 12 at 30Hz can support up to 850,000 pixels
(850,000 / 129,600 = 6.5). If bit depth and frequency requirements change, the system bandwidth must be recalculated.
This tells us we can safely put 6 of these tiles on a 1Gb link.
Figure 10: Output capacity table
Check to make sure the entire data load on each network switch is within the limits of 10Gb ber. In this case, we are
using a color bit depth of 12 at 30Hz. So, the 10Gb link can support 8,500,000 pixels / 129,000 = 65.58 tiles per 10Gb link.
With only 24 tiles in the example system we know we are well within the limits. Always aim to distribute data evenly, spread
the load across switches and switch ports as evenly as possible.
 Loading...
Loading...