Analog input modules for temperature acquisition
Temperature values can be acquired with two different sensor technologies: Pt100 resistance
thermometers and thermocouples.
쎲 Pt100 resistance thermometers
These devices measure the resistance of a platinum element, which increases with tem-
perature. At 0°C the element has a resistance of 100쎷C (thus the name Pt100). The resis-
tance sensors are connected in a three-wire configuration, which helps to ensure that the
resistance of the connecting cables does not influence the measurement result.
The maximum measurement range of Pt100 resistance thermometers is from -200°C to
+600°C but in practice it also depends on the capabilities of the temperature acquisition
module being used.
Another metal used for resistance thermometers is nickel (Ni100). In this case the mea-
surement range is smaller (-60쎷C to 180쎷C).
쎲 Thermocouples
These temperature measurement devices take advantage of the fact that a voltage is gen-
erated when heat is applied to an element made of two different metals. This method thus
measures a temperature with the help of a voltage signal.
There are different kinds of thermocouples.They differ in their thermal electromotive force
(thermal e.m.f.) and the temperature ranges they can measure.The material combinations
used are standardized and are identified by a type code.Types J and K are both commonly
used. Type J thermocouples use a combination of iron (Fe) and a copper/nickel alloy
(CuNi), type K thermocouples use a NiCr and Ni combination.In addition to their basic con
-
struction thermocouples also differ in the temperature range they can measure.
Thermocouples can be used to measure temperatures from -200°C to +1,200°C.
3–32 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC
Das MELSEC System Q Special Function Modules
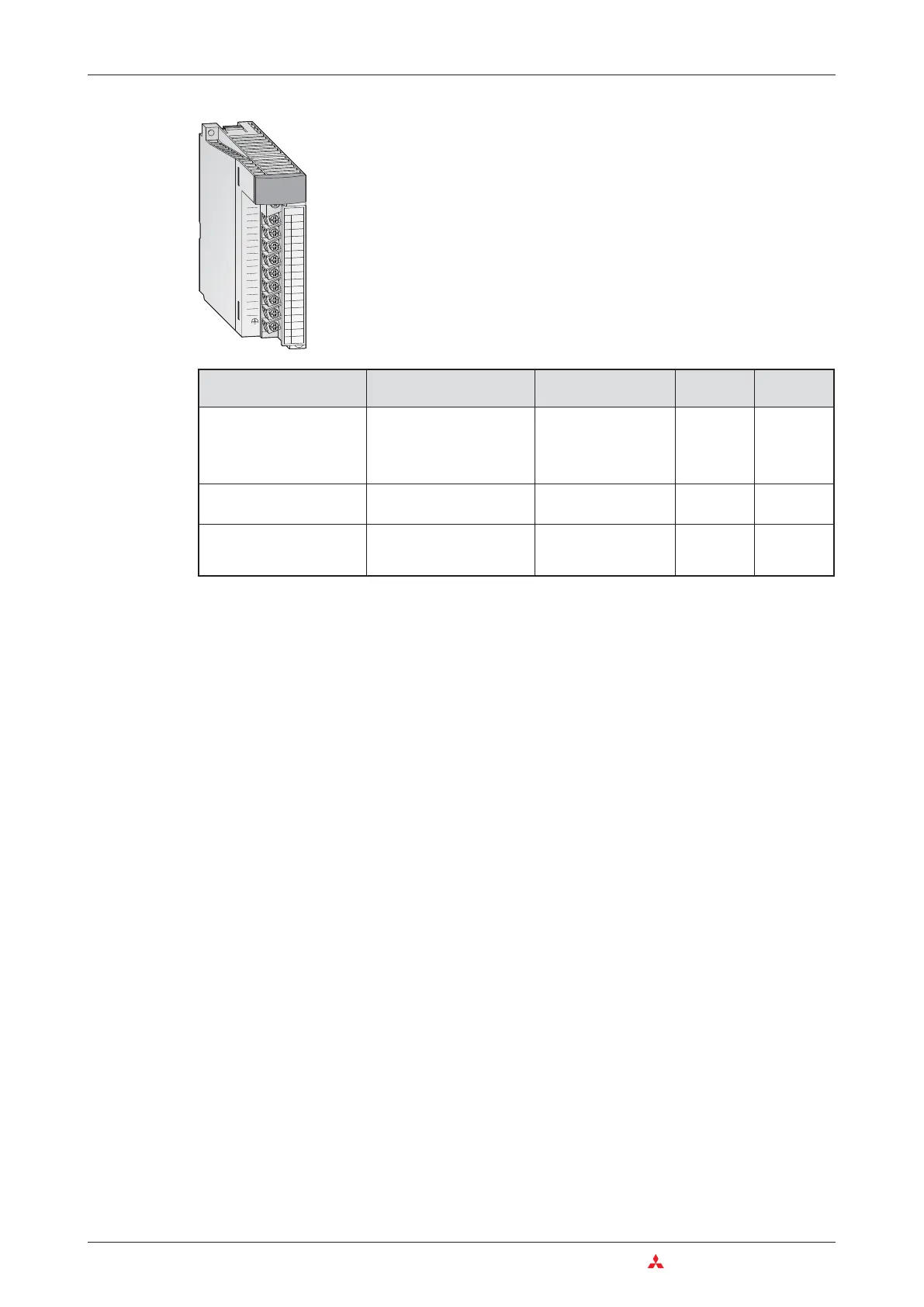
Analog input Analog input range
Selectable input
ranges
Input
channels
Module
Voltage -10 to +10 V
1 to 5 V
0 to 5 V
0 to 10 V
-10 to +10 V
8 Q68ADV
Current 0 to 20 mA
0 to 20 mA
4 to 20 mA
8 Q68ADI
Voltage or current
(can be selected for each
channel)
-10 to +10 V
0 to 20 mA
As for 68ADV and
Q68ADI
4 Q64AD
3
2
1
A/D
0~±10V
0~20mA
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
C
H
1
C
H
2
C
H
3
C
H
4
I+
V+
I+
V+
I+
V+
I+
V-
SLD
V-
SLD
V-
SLD
V-
SLD
A.G.
(FG)
RUN
ERROR
V+
Q
6
4
A
D
The analog input modules of the MELSEC System Q combine a high
resolution (0.333 mV / 1.33 µA) with a high conversion speed (80 µs per
channel).
All modules provide removable screw terminal blocks.

 Loading...
Loading...











