CHAPTER 4 APPLIED OPERATION
E5CK
4–8
When the number of steps is set to an odd number, the final soak time canĆ
not be set. For example, if we set the number of steps" parameter to 7",
the soak time 3" parameter cannot be set even though the target SP 3"
and rate of rise 3" parameters can be set.
Accordingly, when the number of steps are set to an even number, the final
step is a soak step. When it is set to an odd number, the final step is a ramp
step.
Number of steps = even number Number of steps = odd number
When rate of rise 0 to 7" parameter are set to 0", the ramp step is skipped
and the soak step appears to be continuous.
Step N is skipped.
Step
Ramp step Soak step
N N-1
Soak step
N+1
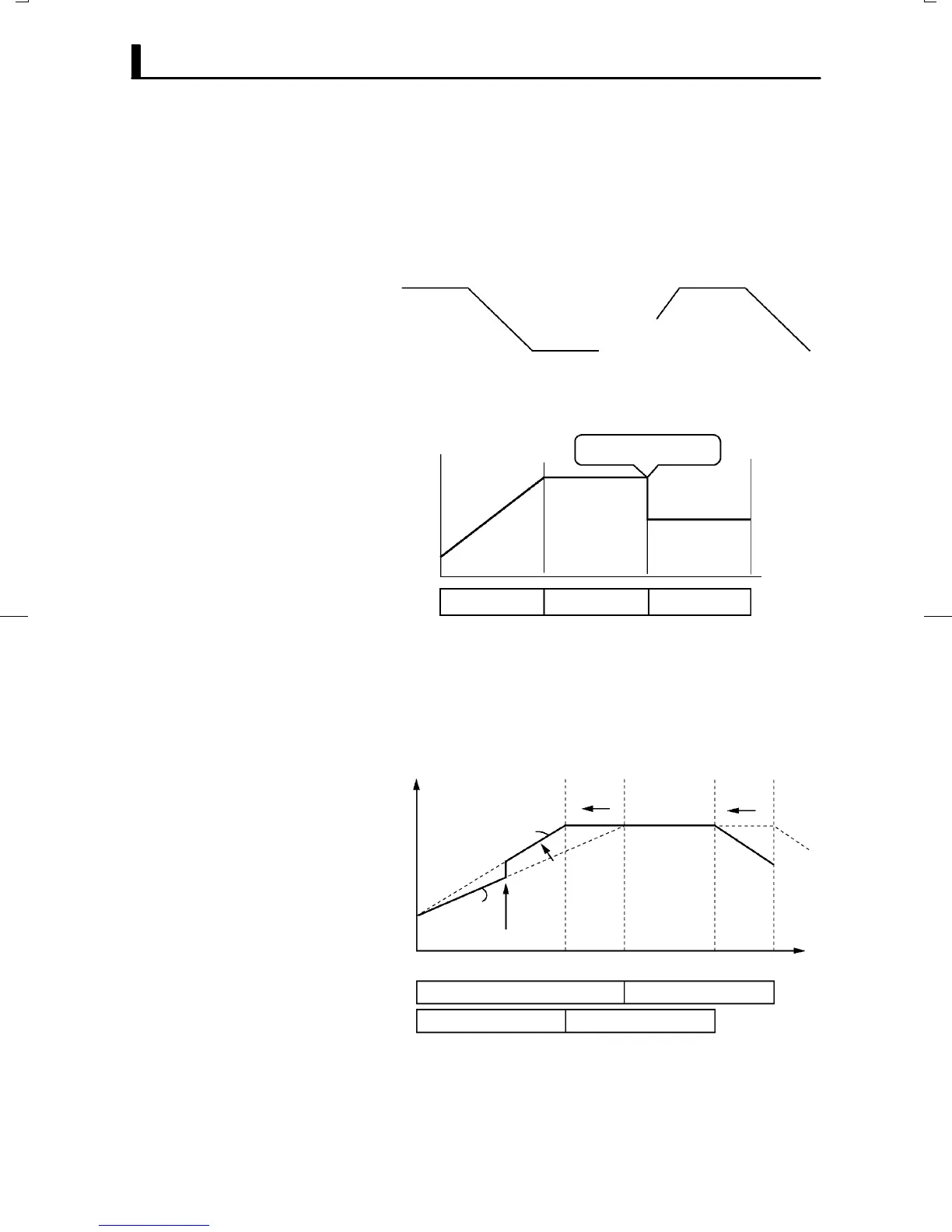
Ramp rise rate setup programs take the PV at start of program operation
as the SP (PV start) when they are started.
When the rate of rise is changed midway during operation, the SP rate of
rise and the step time in the ramp cycle both change.
After change
Before
change
Switching point
Time
Before change
After change
Step N Step N+1
Step N Step N+1
Ă• In the above figure, increasing the rate of rise results in a shorter target
step time. Likewise, when the SP is changed, the step time of the ramp
cycle also changes.
Ă• When the soak time is changed, only the step time in the soak cycle
changes.
F Relationship with
the number of
steps
F When the rate of
rise is set to “0”
JRunning the ramp
rise rate setup
program
F Changing
parameters
 Loading...
Loading...