2-18SectionMathematical Function
279
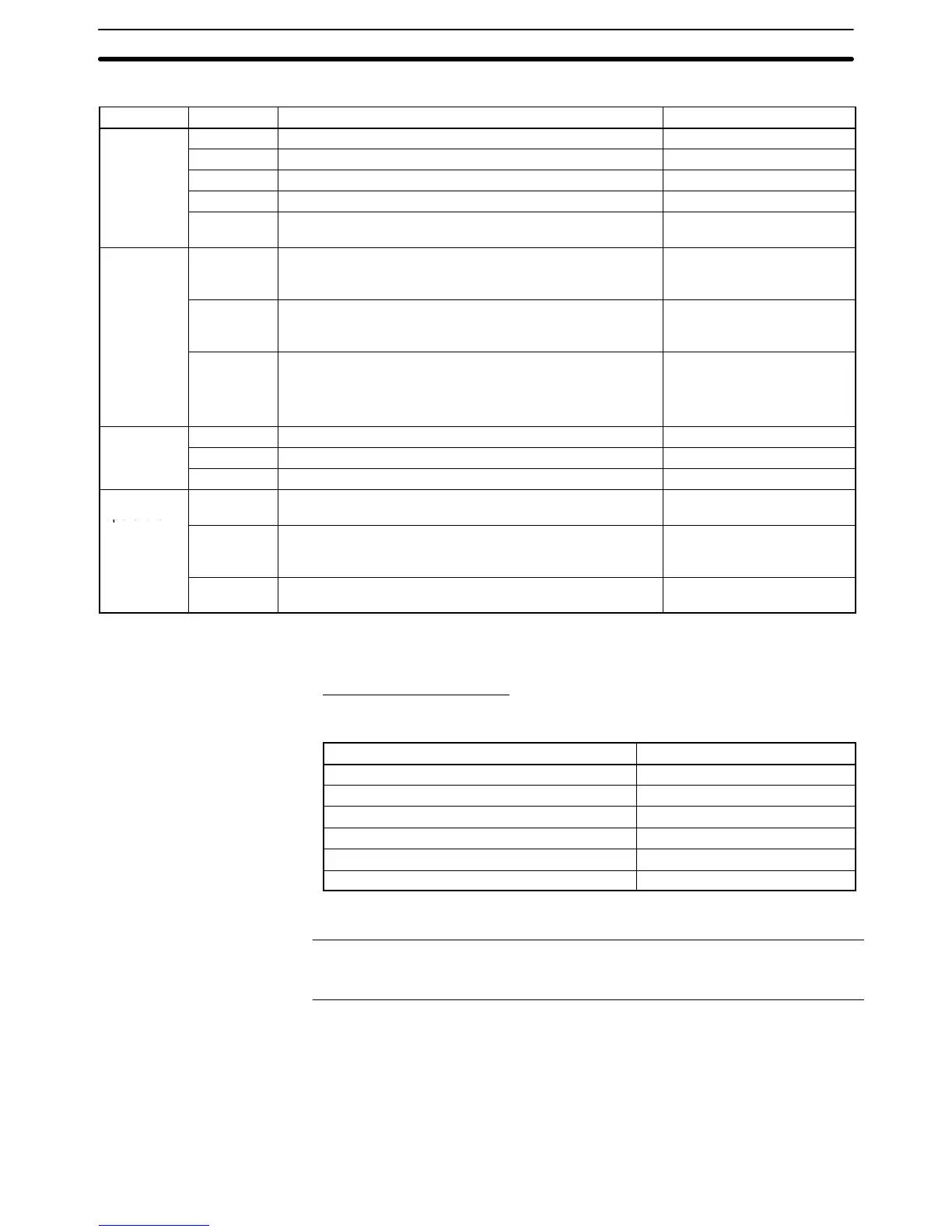
The following operators can be used by the mathematical function.
Type Symbol Function Result
Arithmetic
+ Addition Result of addition
operators
– Subtraction Result of subtraction
* Multiplication Result of multiplication
/ Division, yields the quotient Result of division (quotient)
% Division, yields the remainder Result of division
(remainder)
Boolean
operators
AND Yields TRUE (1) if the results of both the left formula and
right formula are TRUE (non-zero). Otherwise yields FALSE
(0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
OR Yields TRUE (1) if the result of the left formula, the right
formula, or both are TRUE (non-zero). Otherwise yields
FALSE (0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
XOR Yields TRUE (1) if the result of one formula is TRUE
(non-zero) and the other is FALSE (0).
Yields FALSE (0) if the results of both formulas are TRUE
(non-zero) or both are FALSE (0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
Bit-wise
& Logically ANDs the two bits. Result of logical AND
operators
| Logically ORs the two bits. Result of logical OR
^ Logically XORs the two bits. Result of logical XOR
Comparison
operators
< Yields TRUE (1) if the result of the left formula is less than
the result of the right formula. Otherwise yields FALSE (0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
> Yields TRUE (1) if the result of the left formula is greater
than the result of the right formula. Otherwise yields FALSE
(0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
= = Yields TRUE (1) if the result of the left formula is equal to
the result of the right formula, otherwise yields FALSE (0).
TRUE (1) or FALSE (0)
The operators shown in the table above can be used in any combination. The
operators have no priority order; the order of operations is determined by the pa-
rentheses in the formula pattern.
Example Formula Setting
The following kinds of calculations can be performed by combining formula pat-
terns and operators.
Desired calculation Formula and operators
Scaling calculation (2×X+Y) (2 * X) + Y
Bit inversion of X X ^ FFFF
H
Setting the most significant byte of X to 0 X & 00FF
H
Determining whether X is greater than Y X > Y
Determining whether 5×X+Y equals 100 100 = = ((5 * X) + Y)
Determining whether X is between 15 and 68 ((X > 15) AND (X < 68)) + 0
The calculations in the table above are examples. a wide variety of calculations
can be made by combining other formula patterns and operators.
Reference: All of the calculation results are stored in word units, including the results of bool-
ean and comparison operations. The results aren’t indicated by turning a particu-
lar bit ON or OFF.
The following storage locations or values can be specified for calculation results
and operands.
Calculation results:
Numeral memory table entries or PC addresses (PT memory)
Operands:
Numeral memory table entries, PC addresses (PT memory), or constants
Available Operators
Specifying Calculation
Results and Data